On-Page SEO
What is On-Page SEO?
As opposed to off-page SEO, on-page SEO refers to all search engine optimization initiatives that take place on your website, hence the name.
This includes everything from keyword and image optimization to link anchor texts and the quality of your content.
Also, technically, title and meta descriptions appear outside your pages on SERPs, but are considered part of on-page SEO as well.
Along with off-page and technical SEO, assuring your on-page optimization is top-notch is key to developing a successful SEO strategy.
We will take a more in-depth look at each individual on-page SEO tactic further down in the article, but for now let’s focus on why on-page SEO is so important.
Why is On-Page SEO important?
At the core of on-page SEO lies your website’s content and the keywords you optimize it for.
It serves two very important purposes: providing your target audience with the content they’re looking for and making sure they can find it organically – with keywords they are actively using.
Generating traffic is synonymous with generating leads, and higher-intent traffic has a better chance of purchasing from you.
While some business owners consider organic to be a vanity metric as it does not accurately reflect how good you are at converting said traffic into customers, higher amounts of organic traffic are typically associated with better performance.
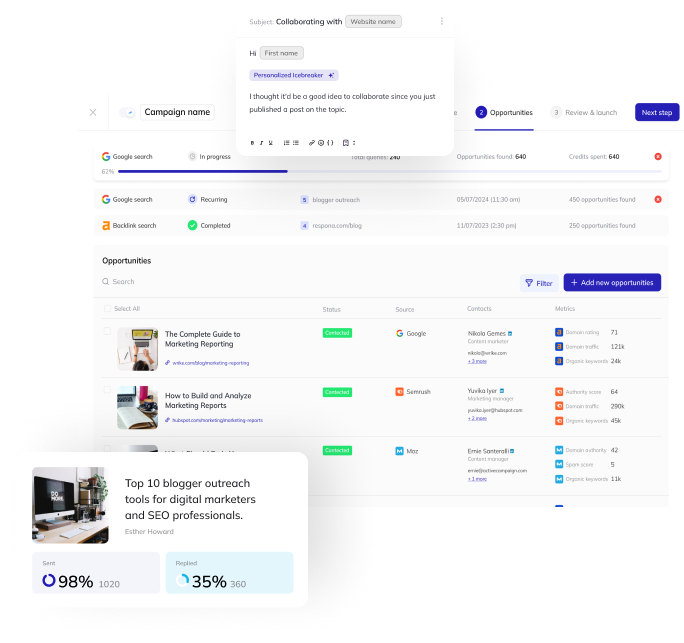
On-Page SEO Example
Optimizing content for keywords is one of the biggest aspects of on-page SEO:
Here are also Visme’s core web vitals, which are also a major part of on-page SEO, according to PageSpeed Insights:
How To Optimize Your Site for On-Page SEO
Now, let’s take a look at the exact strategies you can employ to improve your website’s on-page SEO.
Site Speed
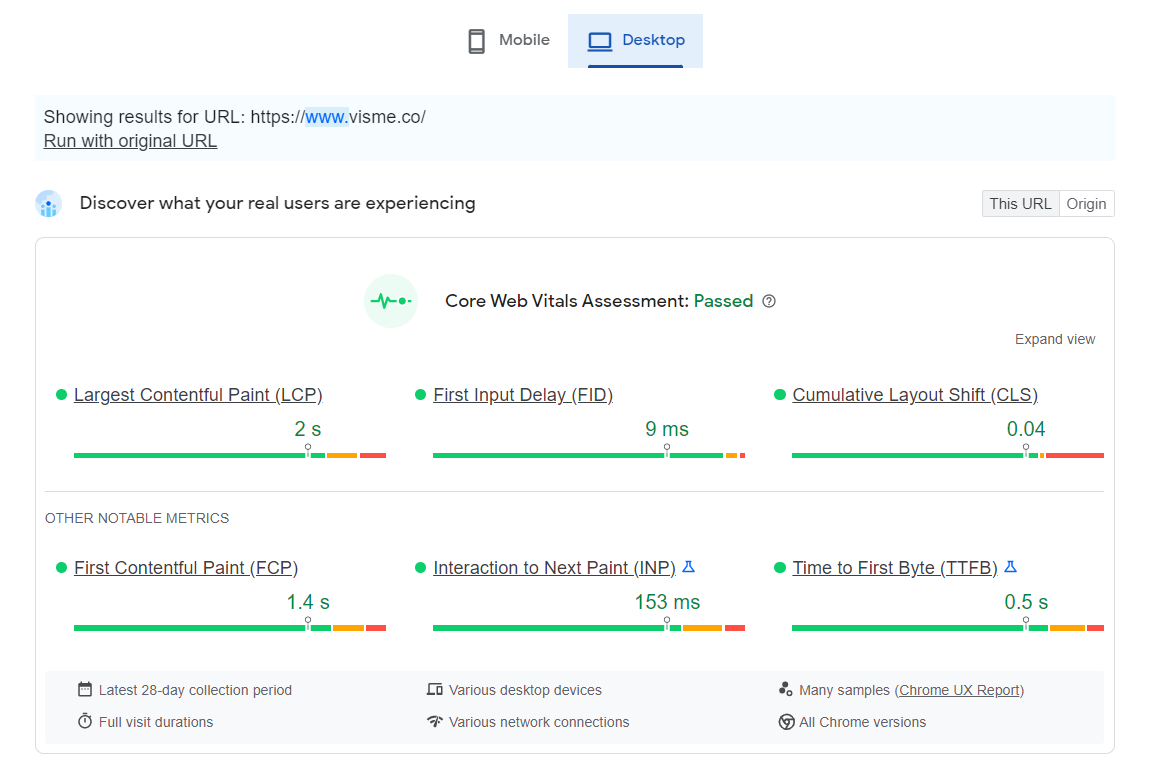
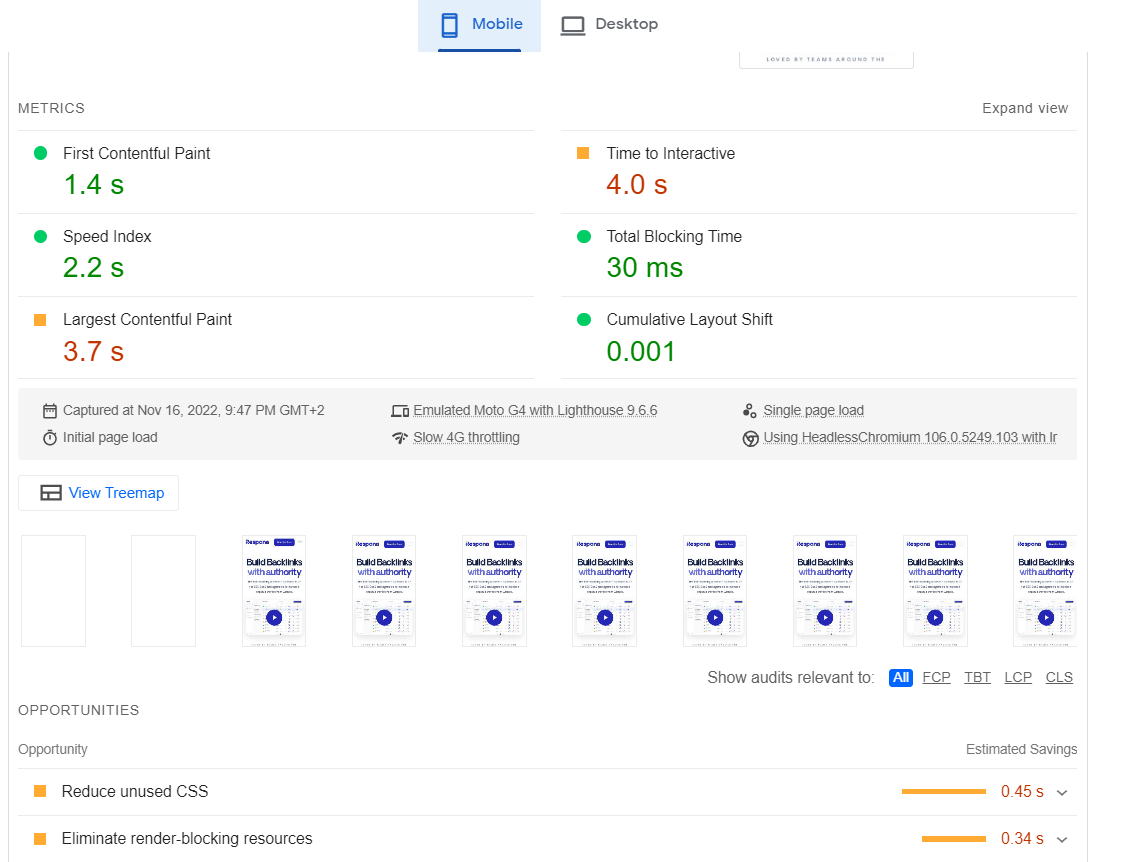
Site speed is the measure of how fast a web page loads. Core web vitals are a set of metrics that measure the performance of a web page.
They include things like page load time, first contentful paint, and time to interactive. These metrics are important because they affect the user experience of a web page.
A slow web page can be frustrating for users and may lead them to abandon the page entirely.
There are a few ways to optimize your website for speed. One is to reduce the size of your web pages.
This can be done by reducing the number of images on a page, or by using smaller images.
Another way to improve speed is to use a content delivery network (CDN). A CDN can help to deliver your content faster by caching it on servers around the world.
The best tool for measuring your site speed is PageSpeed Insights. It also points out exactly what speed issues your site has and offers suggestions as to how to improve it.
Quality Content
A website is similar to a house in that information serves as the foundation.
Creating a content strategy consists of four steps:
- Choosing the Best Keywords
- Assigning and sorting keywords based on relevance, traffic potential, and competitiveness
- Developing a blog content strategy
- Producing the content
Once your keywords have been found and rated, you can organize them into a content strategy to help you generate content more efficiently.
This content strategy may take numerous forms, ranging from a basic list of blog post ideas to a more extensive spreadsheet with content durations and outlines.
Instead of having to look for new keywords to target every time, having a content plan may help you keep organized and focused while developing fresh material.
Keyword Research and Optimization
You can’t produce good content if you don’t know which keywords to optimize it for.
We won’t go in-depth into keyword research here as we already have another glossary article dedicated entirely to keyword research and optimization.
Title Tags
Title tags are HTML elements that indicate the title of a web page. Title tags are commonly used to display the page’s title in search engine results pages (SERPs).
To optimize title tags for SEO, make them brief, relevant, and descriptive. It is also critical to add keywords that are related to the page’s content.
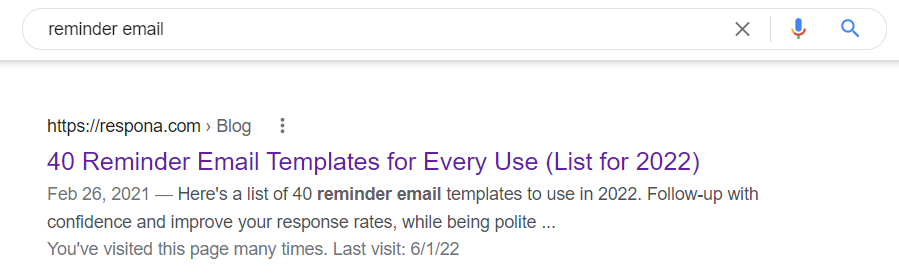
To avoid being shortened, your title tag should be no more than 60 characters long.
Furthermore, titles with their goal keywords at the beginning perform better in search engines than titles with their target keywords in the middle or finish.
That being stated, avoid keyword stuffing and utilize your term just once.
If you are unsure how your title tag will appear on search engine results pages, you may utilize a SERP preview tool to ensure it is not shortened.
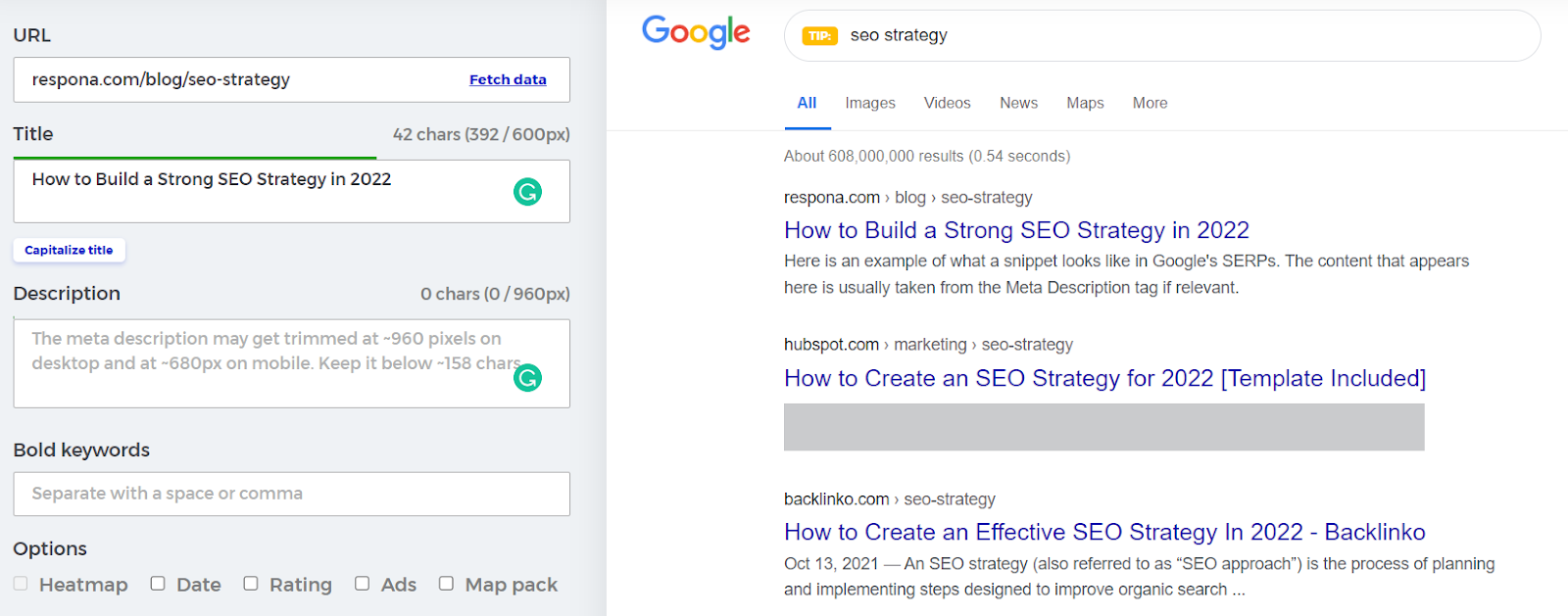
Meta Descriptions
A meta description is a brief summary of a website that appears on search engine results pages (SERP).
The meta description is intended to provide the searcher a quick overview of the page so that they may determine whether or not to go through to the page.
Meta descriptions are vital for SEO since they are one of the aspects that might impact the click-through rate of a searcher (CTR). A higher CTR might result in increased visitors to your website.
To improve the SEO of your meta descriptions, you should:
- Make them brief and to the point (less than 160 characters)
- Choose your keywords intelligently
- Use captivating text that entices searchers to visit your page
- Ensure that each meta description is distinct
As with title tags, you may use a SERP preview tool to ensure it is not shortened.
Header Tags
Header tags are HTML elements that are used to denote the section or subsection header on a webpage. The header element can be used to define a portion of text’s title, subtitle, or other heading.
The header directly above the previous paragraph, for example, is a header.
The number in the tag indicates the level of the header tag, which is one of six. For instance, the tag denotes the most significant header, whereas the tag denotes the least important header.
Header tags are vital for SEO because they assist search engines grasp the content hierarchy on a page.
For example, if a webpage includes an <h1> followed by a header tag <h2>, the <h1> tag suggests that the content that follows is more essential than the material that follows the <h2> tag.
To optimize header tags for SEO, use the proper tag for the text’s priority level.
In addition, header tags should include the keywords for which you are attempting to rank. For example, if a page is about SEO, the <h1> element must include some variant of “SEO.”
We exclusively utilize the <h1>, h2>, and h3> headers on our website.
The <h1> is the title, the <h2> headers separate parts in our text, and the h3> headers further subdivide those sections.
You may divide up your information even more if you like, but most of the time there is no need to go beyond <h3>.
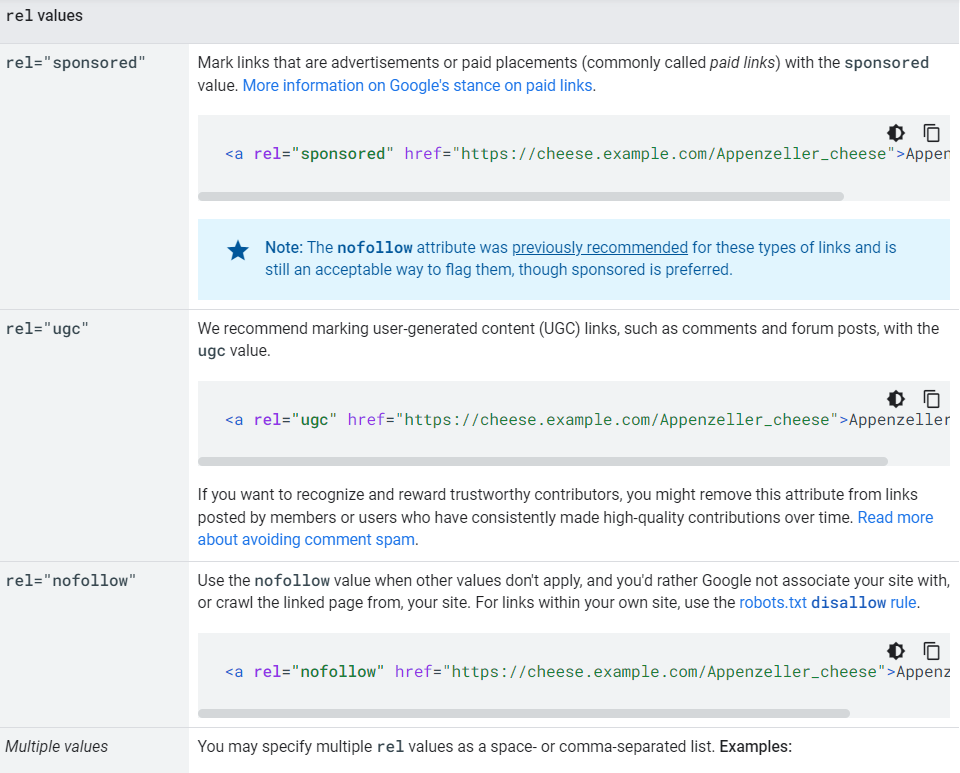
Link Tags
There are other tags that links can contain, but the three most significant are:
Dofollow is an HTML element that instructs search engines to follow the link to the page. This is the standard option for most links and is vital for SEO since it helps search engines to identify and index the connected sites.
The lack of a “dofollow” or “nofollow” tag causes the link to be “dofollow” by default.
Dofollow links pass on link equity as well.
The nofollow link tag is an HTML tag that informs search engines that the link to the page should not be followed. This is used for untrustworthy links or sponsored links.
Because nofollow links do not pass on link equity, they have no SEO impact.
They do, however, send visitors to the connected page and should not be disregarded.
Sponsored links are sponsored links that are normally specified as nofollow so that they don’t impact the search engine ranking of the website they’re linked to.
Google requires the “sponsored” tag on all paid links.
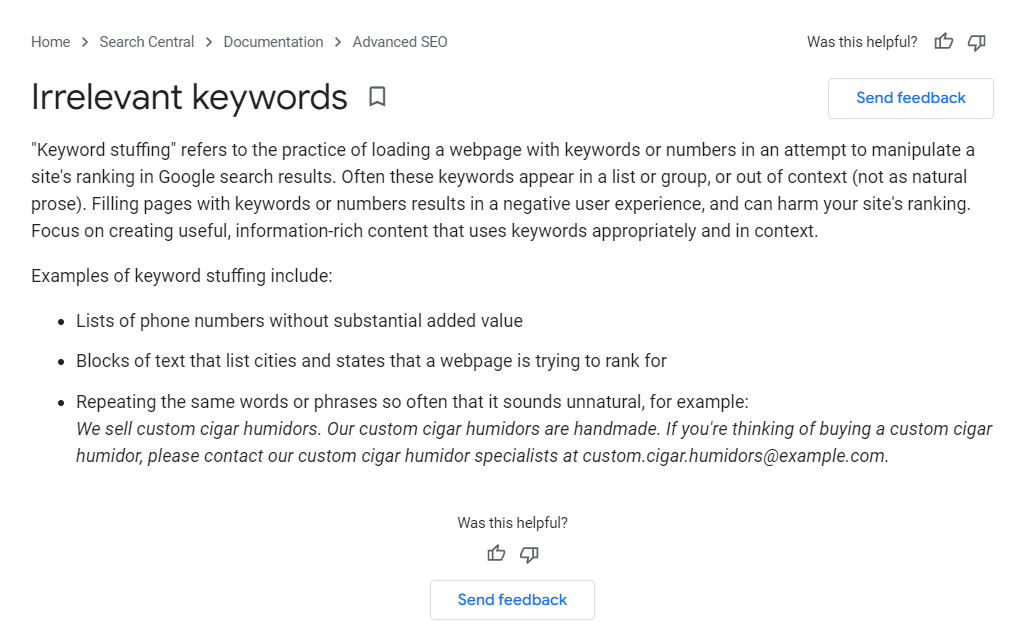
Keyword Density
Keyword density was formerly a significant ranking factor, and many SEOs filled their material with keywords in an attempt to influence their ranks.
In 2022, it is sufficient to have your major keyword in both the URL slug and the page title.
Including several variants (particularly longer-tail variations) in your content, on the other hand, can help your page rank for numerous keywords at the same time.
Only target keywords that are related to your content, and spacing them out organically rather than packing them in large chunks.
There are several tools available to assist you in optimizing your content for keywords.
SurferSEO and MarketMuse are two good examples.
In our office, we utilize MarketMuse. When you enter the main keyword you want to target with your article and copy and paste the text, it will show which keywords need to be included and how many times throughout the post.
Image Optimization
Image optimization is the technique of reducing the file size of an image while preserving its original quality.
This can be accomplished in a variety of methods, including lowering the resolution, compressing the file, or utilizing an alternative file type.
You may increase your website’s efficiency and speed, as well as its SEO, by optimizing your photos.
Alternative text is another aspect of picture optimization.
The text that shows in lieu of an image on a web page if the picture fails to load on the user’s screen is known as alternative text, sometimes known as “alt text” or “alt tags.”
The alt text serves numerous functions, including assisting visually challenged people in understanding what is on a web page and assisting search engines in indexing the content of a website.
When it comes to optimizing alt text for SEO, the most important thing to remember is to make the language informative and keyword-rich.
This will assist guarantee that search engines properly index your photographs and that users can find them when they search for relevant keywords.
Every image on your website should include alternate text.
If you use WordPress (like we do), adding alternative text to your photographs is a breeze.
Simply open the article with the desired image, click on it, and input the alternative text in the image settings box that appears in the right sidebar.
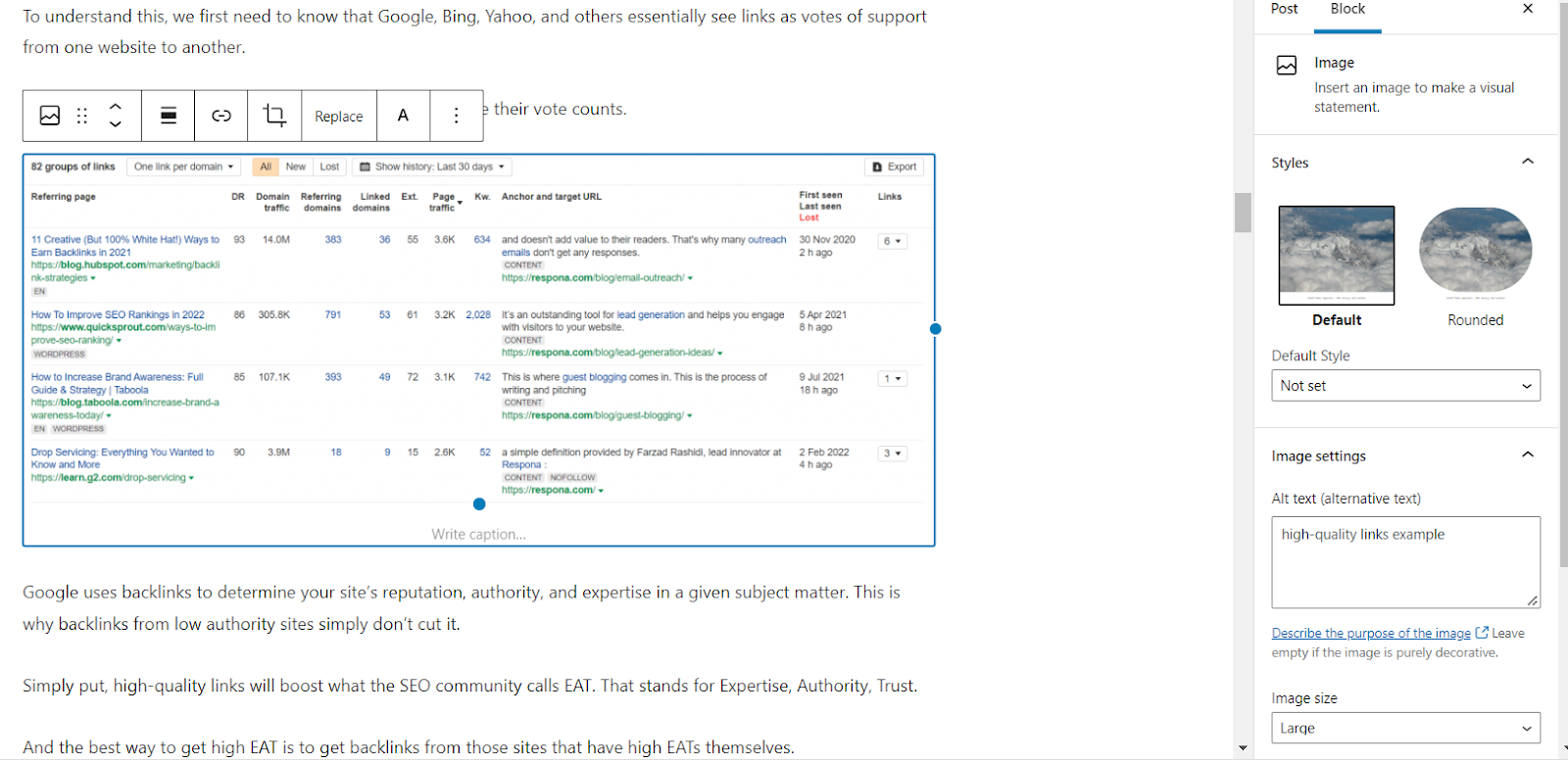
It’s also a good idea to utilize a plugin that automatically compresses all of your on-site photos without loosing too much quality, because manually scaling every image down can be time-consuming.
Link Anchor Text
Anchor texts are text that can be clicked on a webpage.
They can be internal links that transport the user to another page on the same website, or external links that take the user to another website.
The anchor text is the visible portion of the link that is generally highlighted.
Anchor texts are significant for SEO since they are one of the variables used by search engines to establish a website’s relevance.
A website is more likely to rank higher in search results if it has a number of links with anchor texts that are related to the page’s content.
In contrast, if a website contains a large number of links with anchor texts that are unrelated to the website’s content, the website is less likely to rank high in search results.
A good, relevant, and SEO-optimized anchor text is keyword-rich and descriptive of the page to which it links.
It should be brief and to the point, with no use of broad words like “click here” or “additional information.”
For example, the links in the screenshots below lead to our articles on, you guessed it, link kinds and white-hat SEO tactics.

Canonical Tags
A canonical tag is an HTML element that assists webmasters in preventing duplicate content concerns on their site.
It does this by indicating to search engines which version of a page is the “canonical” or “master” version.
This is vital for SEO since it helps search engines index and rank your material more properly.
To use a canonical tag, just include the following HTML element into your page’s head section:
link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” />
Replace “http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” with the URL of your canonical page.
The “canonical” link tag can also be used to direct search engines to the canonical version of a page on a separate domain.
For example, if you have a page on your site that is also available on another site, you may notify search engines that the version on your site is the canonical version by using the canonical tag:
href=”http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” /> link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” />
“http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” should be replaced with the URL of your canonical page.
The “canonical” link tag is one of several methods for informing search engines about the canonical version of a page.
robots.txt file
A robots.txt file is a text file that instructs search engine crawlers on which pages of your website to index and which to ignore.
This is vital for SEO since it allows you to select which pages are indexed by search engines and hence which pages are eligible to rank in search results.
To utilize a robots.txt file on your own website, create a text file and upload it to the root directory of your website.
The file should include a list of crawler instructions, instructing them which pages to index and which to ignore.
It takes two steps to create a robot.txt file.
- Choose which pages on your site should be crawled and which should not. This is accomplished by generating a “disallow” list of pages that should not be crawled.
- Upload the robot.txt file to the root directory of your website.
The following is an example of a robot.txt file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /cgi-bin/
Disallow: /tmp/
Disallow: /admin/
This file instructs all web robots to avoid accessing the cgi-bin, tmp, and admin folders.
Bottom Line
So, to sum it up, the three most important on-page SEO factors are:
- Site Speed
- Quality, optimized content
- Keywords
Site speed is one of the most important on-page SEO factors because it directly affects the user experience.
A slow website will frustrate users and cause them to leave before they even have a chance to engage with the content.
Quality content is another important on-page SEO factor because it helps to establish the website as an authority on the subject matter.
Finally, keywords are important on-page SEO factors because they help search engines to understand what the website is about.