SERPs
What are SERPs?
SERP stands for search engine results pages.
These are the pages that greet you after you hit enter on a query in Google (or any other search engine).
In the world of SEO (search engine optimization), it is a constant race between companies to secure te number one spot on SERPs.
This is because ranking at number one for any keyword is the perfect way to generate a steady stream of highly targeted traffic which can not only increase your business’ online visibility but generate a considerable amount of revenue as well – either in ads or good, old-fashioned sales.
How do SERPs Work?
Google’s ultimate goal is to provide searchers with the ultimate user experience by offering them search results that are not only relevant to their query but also match their search intent.
However, relevance and search intent are only two of over two hundred ranking factors that can influence a website’s position on SERPs.
We will talk more about specific ranking factors further down in the article, but for now, let’s discuss the two types of results SERPs pull for any given query: organic and paid.
Organic Results VS Paid Results
As you may have guessed, paid results are the advertisements at the top and bottom of the SERPs.
Everything in between is organic.
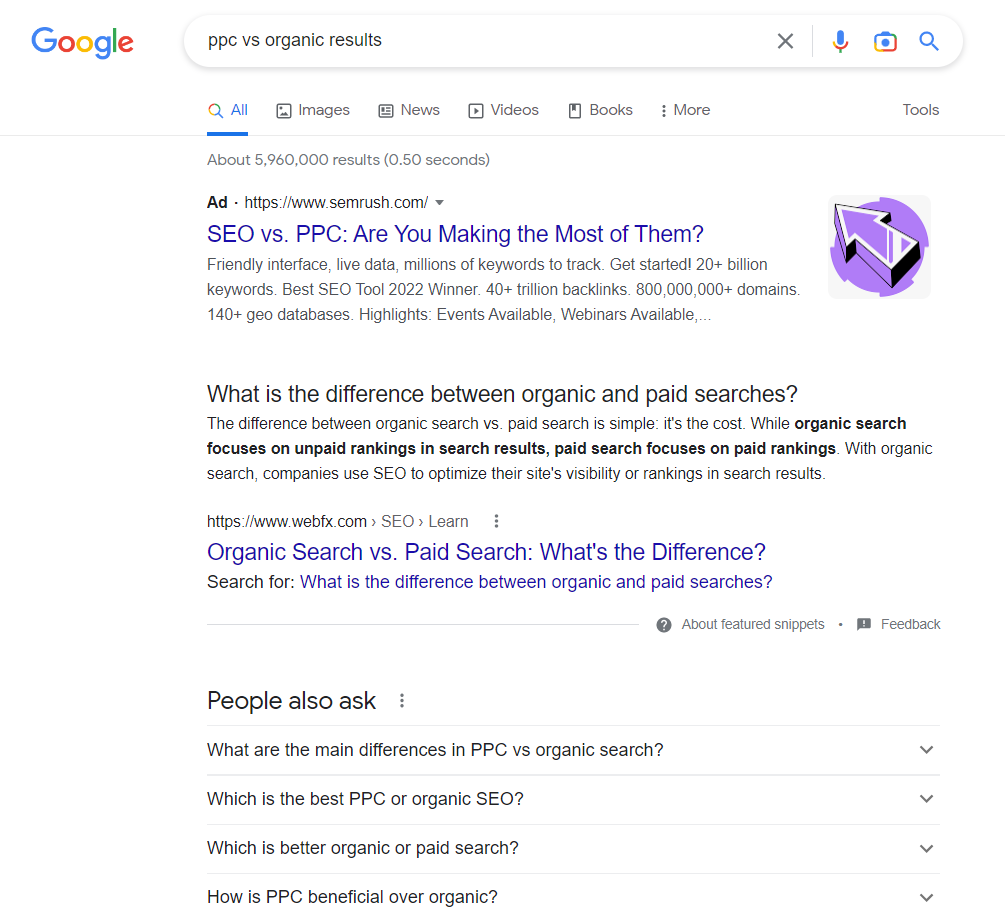
There are two wildly different mechanisms that determine page rankings both in organic and paid results.
While organic results compete with over 200 different ranking factors, the #1 spot in paid results typically goes to the highest bidder.
So, even if you’re a site that went live 20 minutes ago, you can show up at the very first spot as long as you have the budget for it.
Organic Ranking Factors
As we already mentioned, there are hundreds of organic ranking factors – far too many to cover in-depth in a single article.
Instead, we will list out the ones that we feel are the most important for any SEO strategy:
- High-quality blog content
- Keywords
- Site speed and mobile optimization
- Backlinks and their anchor texts
- Social signals
- Title and meta tags
- URLs
- Domain age
- Site security
- Content structure
- Site architecture
- Internal links
- External reviews and brand mentions
- And more
A thoroughly SEO-optimized website greatly increases your chances of ranking high in organic search results.
SERP Features
Even if you do manage to rank on the fabled #1 spot, that doesn’t mean that all of the users will immediately start clicking on your site.
Especially if there are some paid results or SERP features present on the page.
SERP features are things like People Also Ask and are commonly referred to as Position 0, as they often provide an answer to a searcher’s question without them even having to click on any links, and can overshadow any “regular” organic results.
Let’s have a closer look at all of the different types of search features there are.
People Also Ask
People Also Ask is one of the most common SERP features and takes the form of a FAQ containing answers to a set of questions that are relevant to your query.
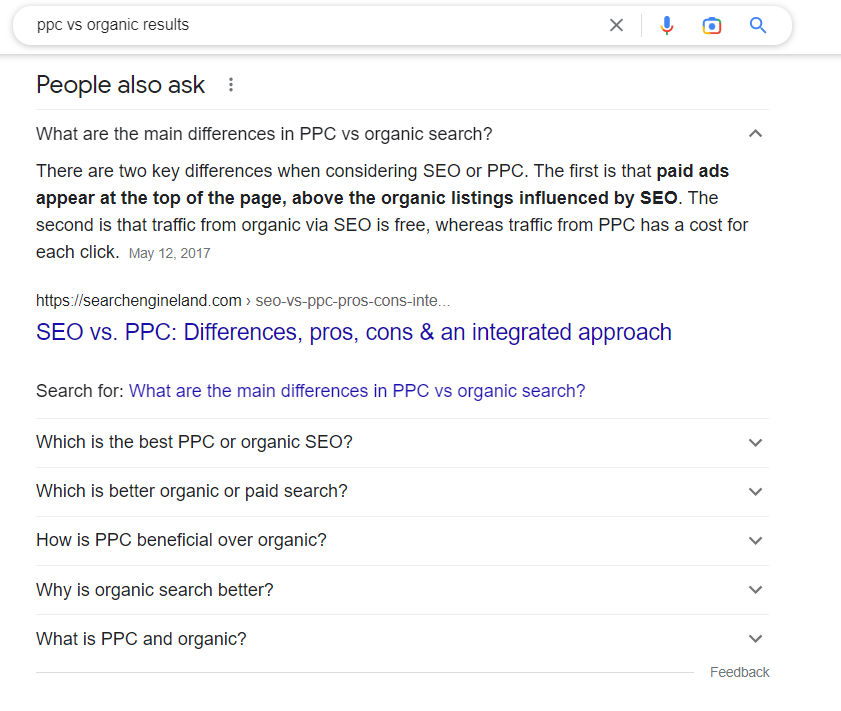
The answers to these questions are pulled from different webpages, as opposed to a singular one, which is the case with the next SERP feature, featured snippets.
Featured Snippet
Featured snippets are short pieces of content that are pulled out of a single page and directly answer the searcher’s question.
Because they lead to one page only, they are often the desired outcome of content optimization strategies.
If you manage to capture a featured snippet with your article, chances are that 99% of the users will read it or even click on your content over any other result.
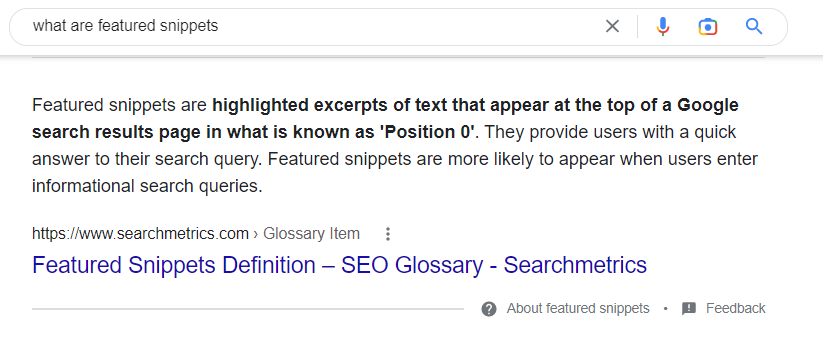
To optimize your content for featured snippets, you need to provide a brief and direct answer to a question – just like in the example above.
Local Pack
As the name implies, the local pack is a set of local map results when searching for businesses like restaurants, hotels, etc.
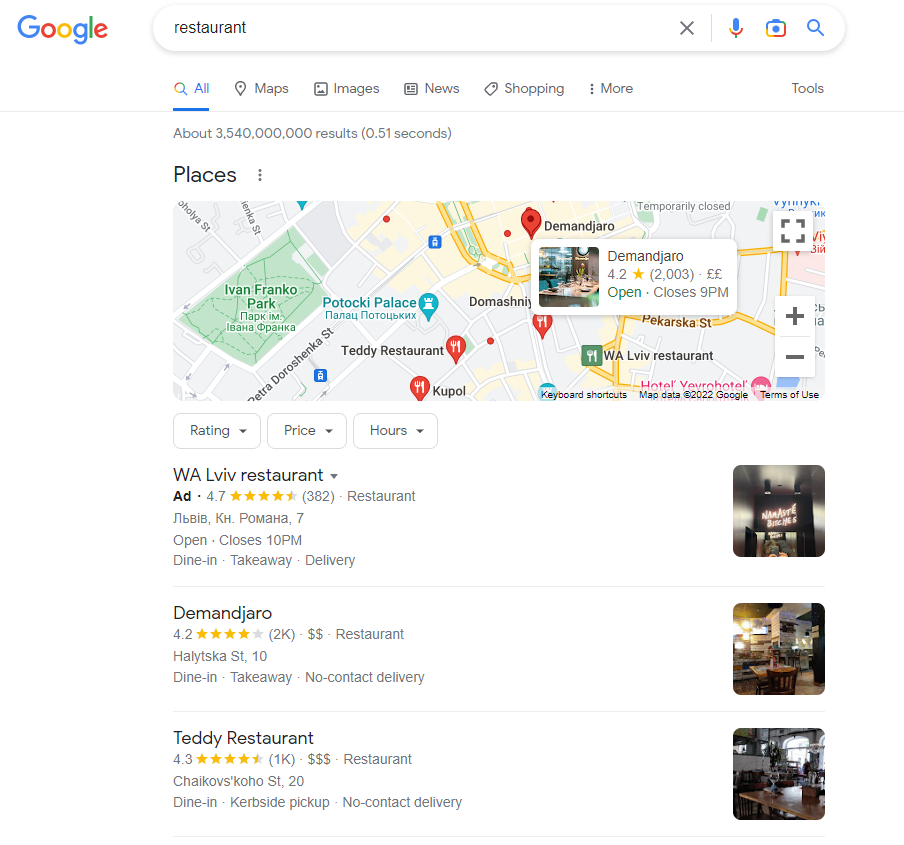
What’s interesting about local packs is the fact that they have their own ranking sub-algorithm that brings up only the best places to visit, according to their Google My Business profile, and, of course, people’s reviews.
Shopping Results
Shopping results are pretty straightforward: when a search displays commercial or transactional intent (by having the appropriate search modifiers, like “buy”), it pulls relevant product and shop pages with the desired item.
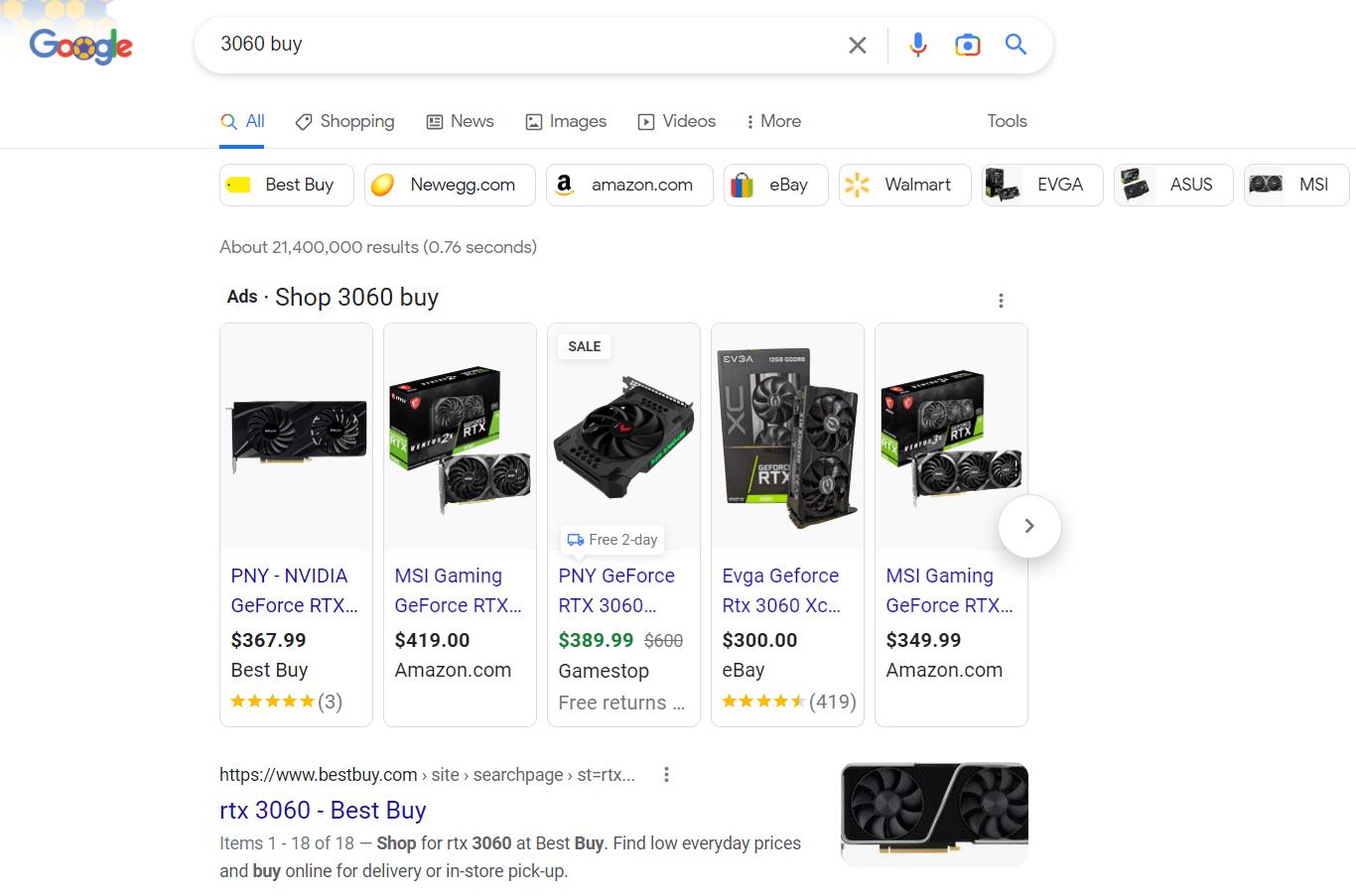
Also known as Product Listing Ads, they aren’t actually always paid as PLAs can pull pages for free.
However, if you want your product to show up as first on the list, you always have the option to place a bid for it.
Knowledge Panel
Knowledge panels are boxes that show up to the right of search results and are filled with information about a person, company, or known event.
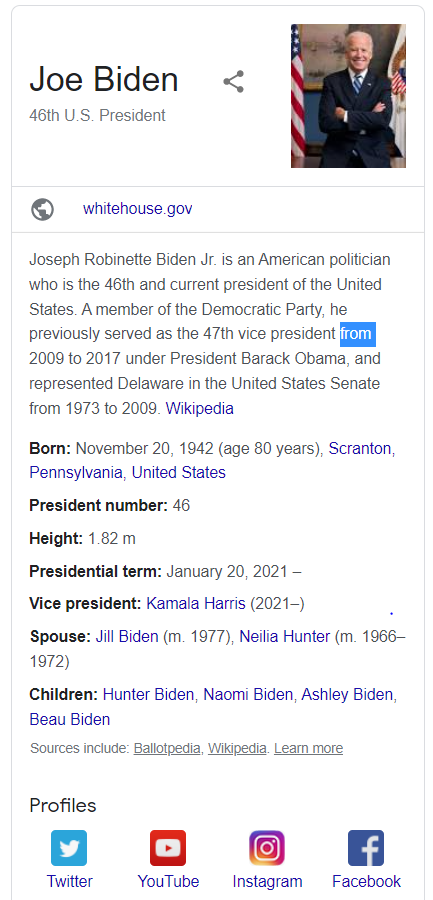
They may be similar to rich snippets in appearance, but the information in the knowledge panel is pulled from a number of sources, including social media pages and even Wikipedia.
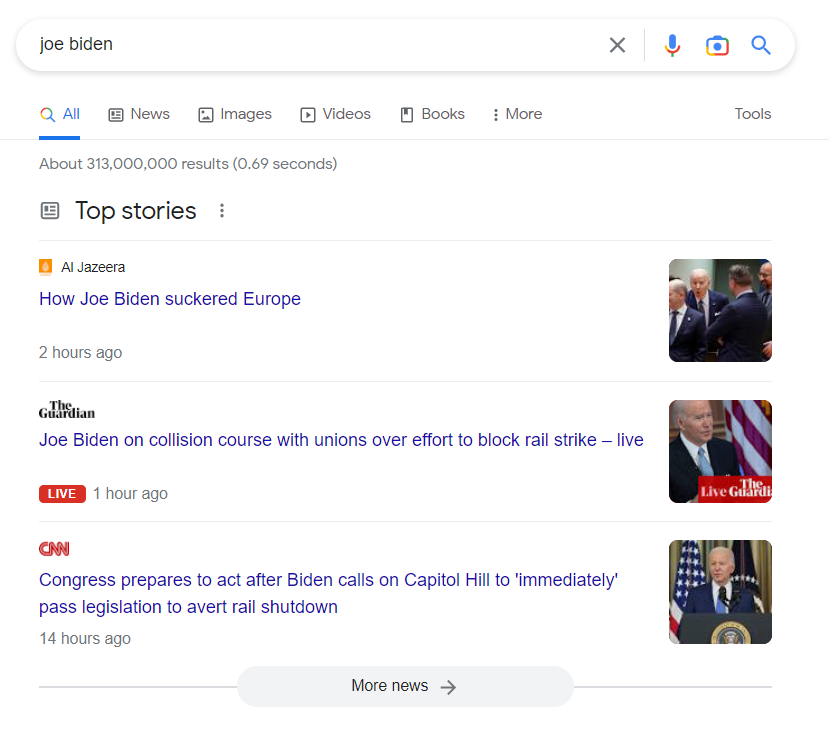
Top Stories
Top stories are the latest news article related to the query – often live or published within one or two hours before the search.
Knowledge Card
If a searcher is enquiring about some very specific information that is a concrete value, the knowledge card SERP feature will pop up giving them a precise answer.
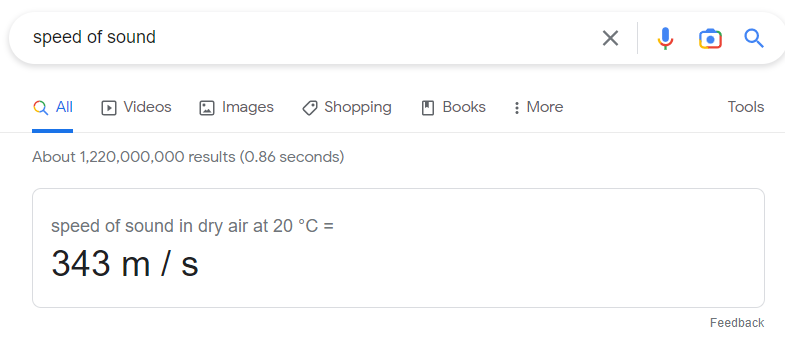
Since knowledge cards only work with data that is public knowledge, they don’t link to any pages.
Image and Video Results
Video and image results are pulled directly from video and image search respectively, and most often appear during informational searches when a user is willing to find out more about a specific thing or how to perform a particular task.
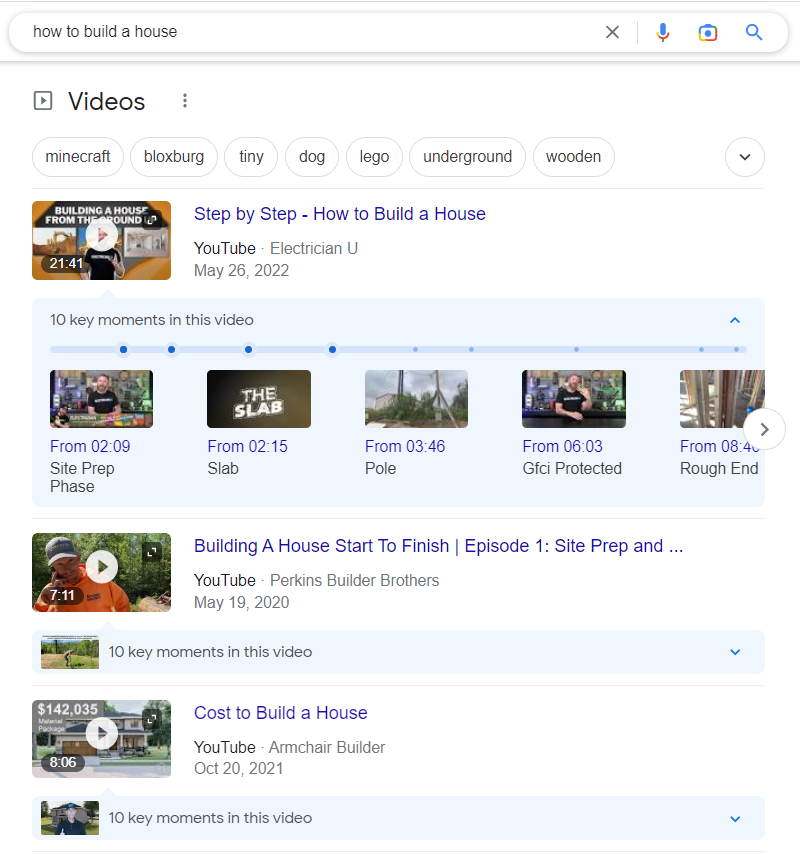
If the video has timecodes, the snippet will actually showcase the most important bits right there, in the search to make it even easier for the users to find exactly what they’re looking for.
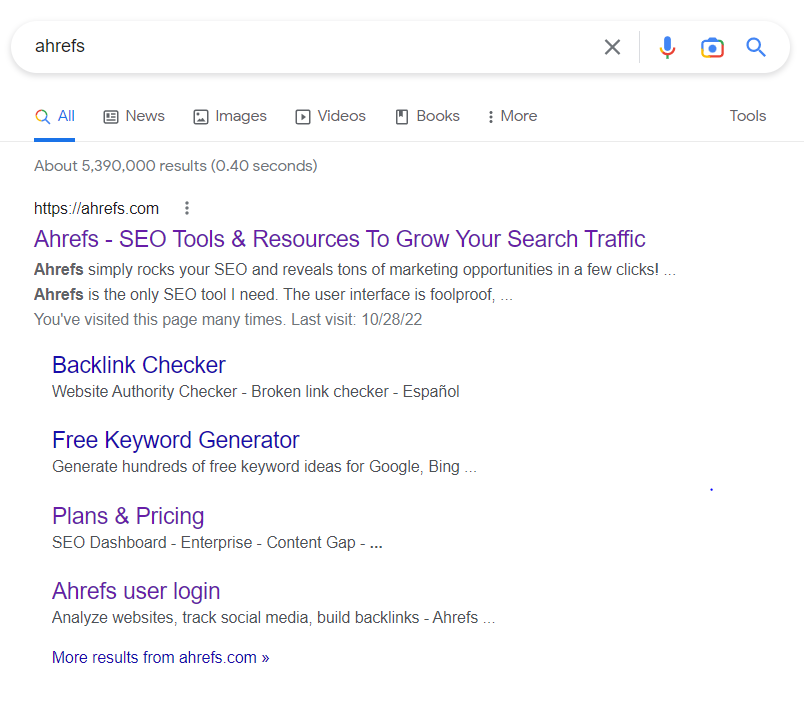
Sitelinks
Sitelinks appear for navigational searches (for example, when someone looks up a specific company), and pull the website’s navigational links directly to the SERP, helping users get to the exact portion of the site they’re looking for even quicker.
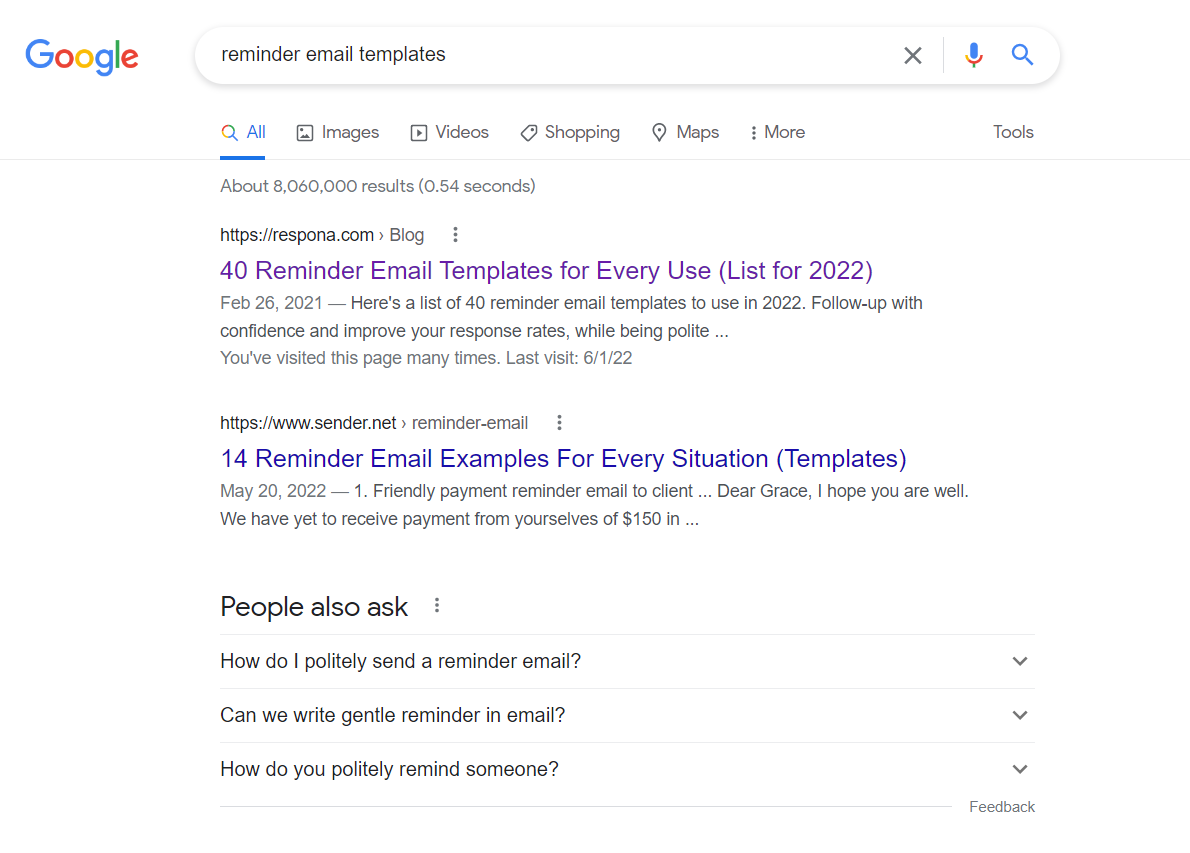
SERP Example
This is a SERP result for the “reminder email templates” query:
How to Show Up Higher in SERPs?
There are two ways to increase your SERP rankings: the long and the quick.
The long one is an all-encompassing process taking advantage of content marketing and search engine optimization.
Some of the most important steps in it include:
- Researching your audience to find topics to write about
- Finding keywords people are actually looking for and optimizing content for them
- Ensuring that your on-page, off-page, and technical SEO are perfect
- Running regular content and backlink audits to find pages that are underperforming
- Distributing your content through owned, earned as well as paid channels, and promoting it after publication
This, of course, can take months and even years – but the end result is very much worth it, generating you what essentially is free traffic once you pass a certain point.
The quickest way to rank at #1 is to pay for advertisements.
This might seem like a no-brained for companies that have the budget for it but setting up PPC campaigns is a skill in its own right and when done incorrectly can waste you valuable time and money.
A healthy strategy takes advantage of both paid and organic channels for maximum reach.
It is also wise to avoid trying to rank for keywords that bring up a lot of SERP features, as they can “steal” your attention even if you’re ranking on the first organic spot and significantly decrease your click-through rate as a result.
Bottom Line
Google is the first thing that people pull up when they need to find something, buy something, or learn about something.
And for a business (especially a Software-as-a-Service one), there is no greater source of traffic and revenue than the #1 organic search spot.
And this doesn’t just apply to revenue – being the #1 for any query also does wonders for your brand recognition, puts you as an industry expert, and makes it that much easier to win over the trust of new potential customers.