Crawlability
What is Crawlability?
Crawlability is the ability of a search engine to reach and index the content of a website.
Crawling is performed by Google crawler bots. They are essentially computer programs that visit websites and collect information about those websites. The information they collect is then used to help Google index websites and show relevant search results.
Google crawlbots start with a list of web page URLs, generated from past crawls and sitemaps provided by webmasters.
As Googlebot visits each page, it detects links on the page and adds them to its list of pages to crawl. New sites, changes to existing sites, and dead links are noted and used to update the Google index.
It is important to ensure your website’s crawlability in order to ensure that search engines are able to index your site properly.
If your site is not crawlable, then it is likely that some of your pages will not be indexed by search engines, which can negatively impact your site’s visibility and organic traffic.
Another thing you should keep in mind is that since 2020, all websites have been switched to mobile-first indexing, further reinforcing the importance of optimizing your website for mobile devices.
How to Improve Your Website’s Crawlability?
For quicker and more effective indexing, you need to make sure that your website is highly crawlable.
In general, there are five strategies to follow to improve your website’s crawlability.
Submit Your Pages for Indexing
One of the best ways to get your pages crawled by search engines is to submit your pages directly to them for indexing.
This can be done by adding your pages to their respective search engine’s webmaster tools. By doing this, you are essentially telling the search engine that your pages exist and that you would like for them to be indexed.
The search engine will then crawl your pages and index them accordingly.
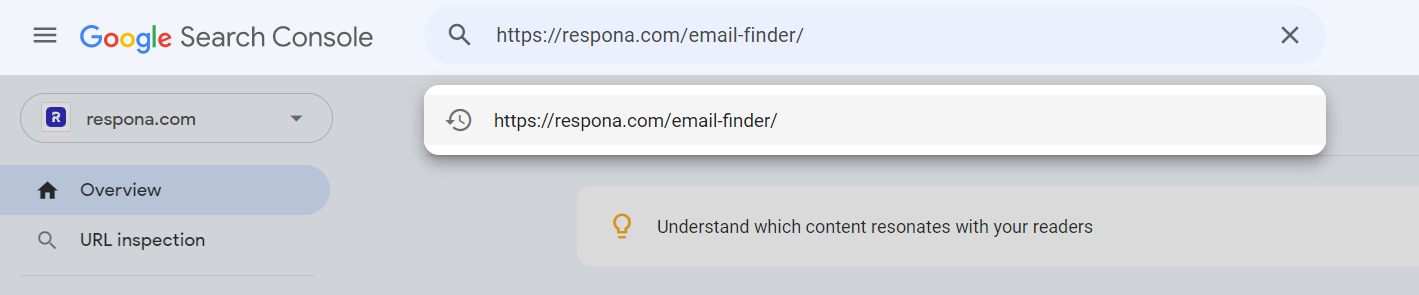
For example, to submit your page for indexing on Google Search Console, all you have to do is paste your URL into the search bar:
And if your page is not on Google, click on the “Request Indexing” button:
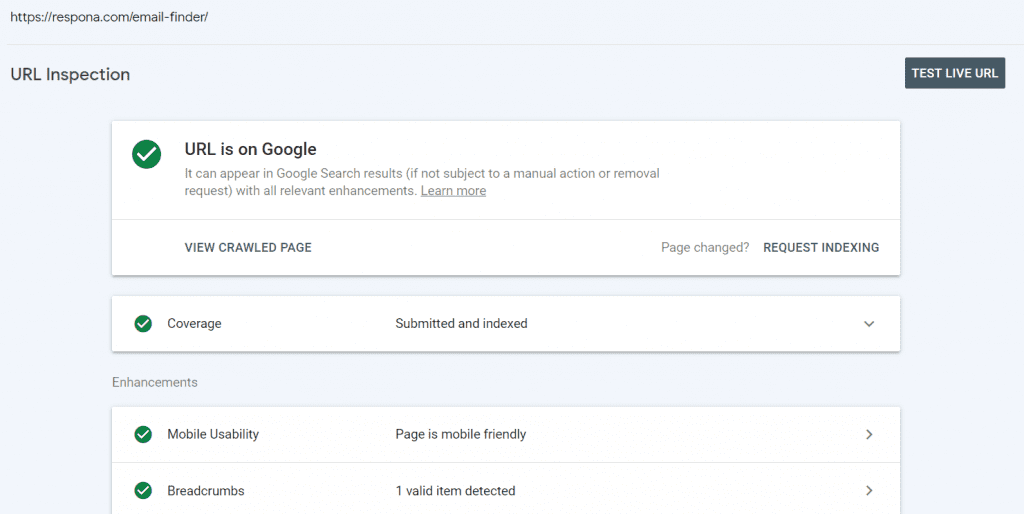
You can also request re-indexing by following the same steps if you have considerably edited your page to the point where it would require re-evaluation and you don’t want to wait for crawler bots to do it on their own.
Submit a Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that contains a list of all the pages on your website.
It is used to improve your website’s crawlability, by directly telling the search engine about all of your pages.
Creating a sitemap is a three-step process.
1. First, you need to create a list of all the pages on your website. This can be done manually, or you can use a sitemap generator tool (like XML-Sitemaps.com).
2. Once you have a list of all the pages on your website, you need to create an XML file that contains this information. This XML file will be your sitemap.
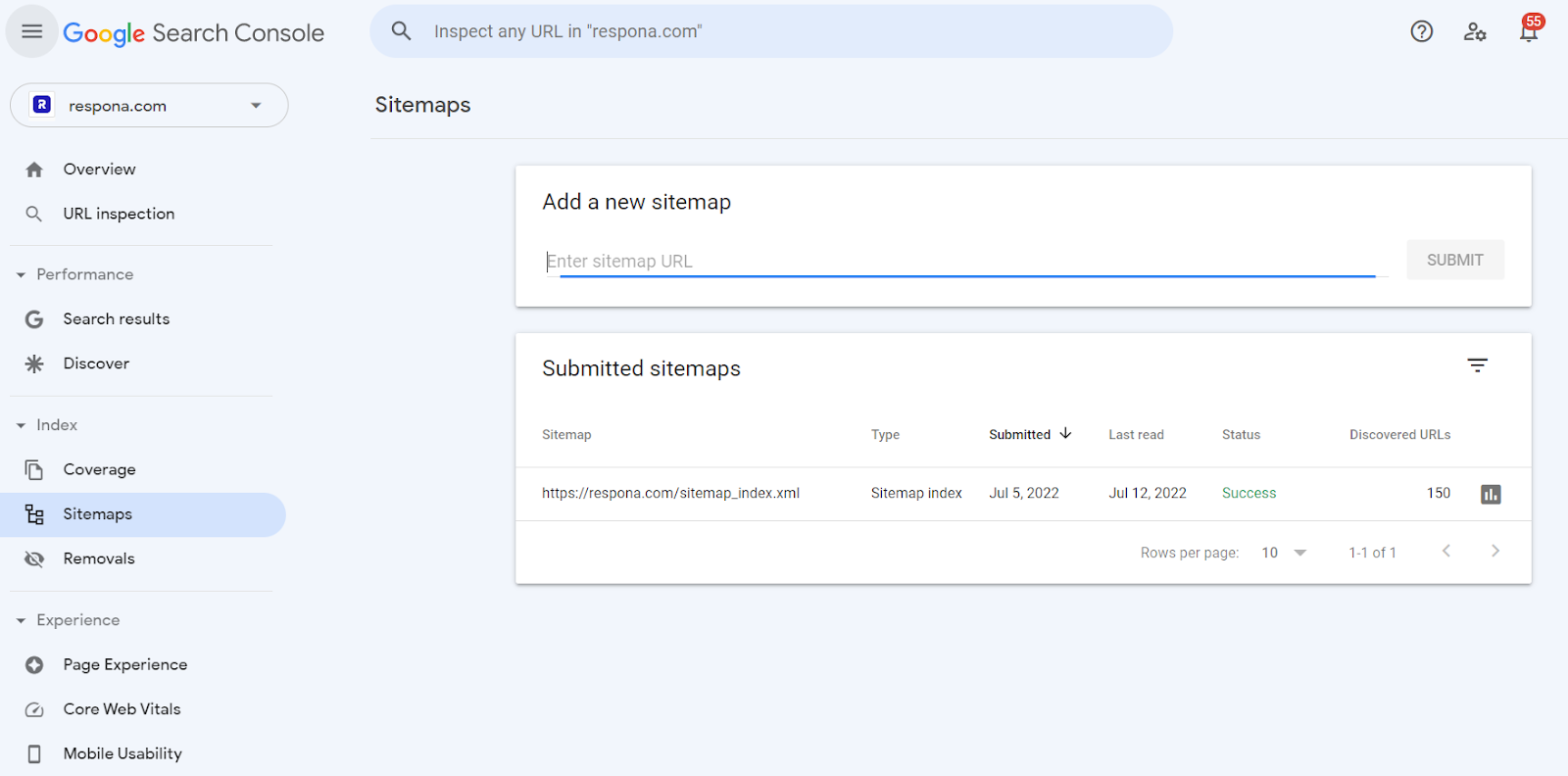
3. Once your sitemap is ready, you need to submit it. For example, to submit it to Google, you can navigate to Google Search Console’s Indexing tab > Sitemaps, and upload it there.
Use a Robots.txt File
A robots.txt file is a text file that contains instructions for web robots (also known as web crawlers or spiders). These instructions tell the robots what they are allowed to crawl and index on your website.
Robots.txt files can improve your site’s crawlability by telling robots which pages they should and should not crawl. This can help to prevent duplicate content, and can also help to improve your site’s performance in search engines.
To create a robots.txt file, you will need to use a text editor such as Notepad or TextEdit. Once you have created the file, you will need to upload it to your website’s root directory.
The contents of your robots.txt file will need to be in a specific format, and will need to include a list of user agents and disallow directives.
Here is an example of a robots.txt file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /cgi-bin/
Disallow: /tmp/
Disallow: /admin/
The first line, User-agent: *, tells all web robots to crawl all pages on the website. The three lines after that tell the web robots to ignore the /cgi-bin/, /tmp/, and /admin/ directories.
You can also use the robots.txt file to tell web robots when they can crawl your website. For example, you might only want web robots to crawl your website during off-peak hours. To do this, you would add a line like this to your robots.txt file:
Crawl-delay: 3600
This line tells web robots to crawl the website once every hour.
Optimize Your Site Architecture
Site architecture is the organization of a website’s content. It includes the structure of the website’s pages and the way in which they are linked together.
A well-organized website will have a clear hierarchy and a logical structure. The most important pages should be easy to find, and the website should be easy to navigate.
Site architecture affects SEO in two ways.
First, it can help search engines understand the structure of the website and index the site’s pages more effectively. Second, it can help visitors find the information they are looking for, which can improve the website’s click-through rate and conversion rate.
There are a few simple rules to follow when optimizing your website’s architecture:
- Make sure the most important pages are easy to find.
- Use descriptive titles and keywords in your URLs.
- Use breadcrumb navigation to help visitors find their way around the website.
- Use internal linking to help search engines index your website more effectively.
- Use redirects judiciously to avoid 404 errors.
- breadcrumbs navigation example
Internal Links
Internal links are hyperlinks that point to other pages on the same website.
They are important for SEO because they help search engines understand the structure of a website and the relationships between its pages.
They can also help to increase the PageRank of a website by passing link equity from one page to another.
To optimize your internal link structure, you should ensure that your links use descriptive anchor text and point to pages that are relevant to the context in which they appear.
You should also avoid using too many links on a single page, as this can dilute the link equity that is passed.
A good rule of thumb is to have at least five internal links pointing to every single one of your pages with relevant, clear anchor texts.
Optimize for Mobile
To optimize your website for mobile-first indexing, you need to design and develop your website specifically for mobile devices.
This can be done in a number of ways, such as using a responsive web design, using a mobile-friendly theme, or using a separate mobile website.
You can also use app-based solutions or AMP pages to further improve the performance of your website on mobile devices.
Bottom Line
If Google is able to effectively crawl your website, it will be able to index your new content on time, leading to it showing up in search results faster.