URLs
What Are URLs?
URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) are strings of characters used to identify a specific web page or resource.
They are used to locate and access web pages, images, videos, and other types of content.
URLs consist of several parts, such as the protocol (e.g. http), domain name (e.g. www.example.com), path (e.g. /page.html), and parameters (e.g. ?name=value).
The protocol part tells the browser which protocol to use for the request (e.g. http or https).
The domain name is the address of the web server that hosts the resource. The path is the location of the resource on the web server.
The parameters, if present, give additional information about the resource.
URLs are used by web browsers to locate and access web pages, images, videos, and other types of content.
They are also used by other web services, such as search engines, to locate and index web pages.
URLs are essential for the World Wide Web and are used to link web pages together.
Why Are URLs Important?
There are two main reasons why having a clear and organized URL structure is so important in SEO.
For Search Engines
URLs are one of the first things a search engine looks at when crawling a website, so having well-structured URLs can help improve visibility in search engine results.
A URL that is well-structured and optimized for SEO will typically include a keyword or phrase relevant to the page’s content.
This makes it easier for search engine bots to crawl the page and understand what the page is about.
For Users
URLs that are easy to remember make navigation quicker and simpler for users.
Using common categories like “blog”, “products”, etc. also make desired pages easier to find within those categories.
Having a URL that is descriptive, concise, and relevant to the content of the page can also help users quickly understand what the page is about and make them more likely to click through to the page from SERPs.
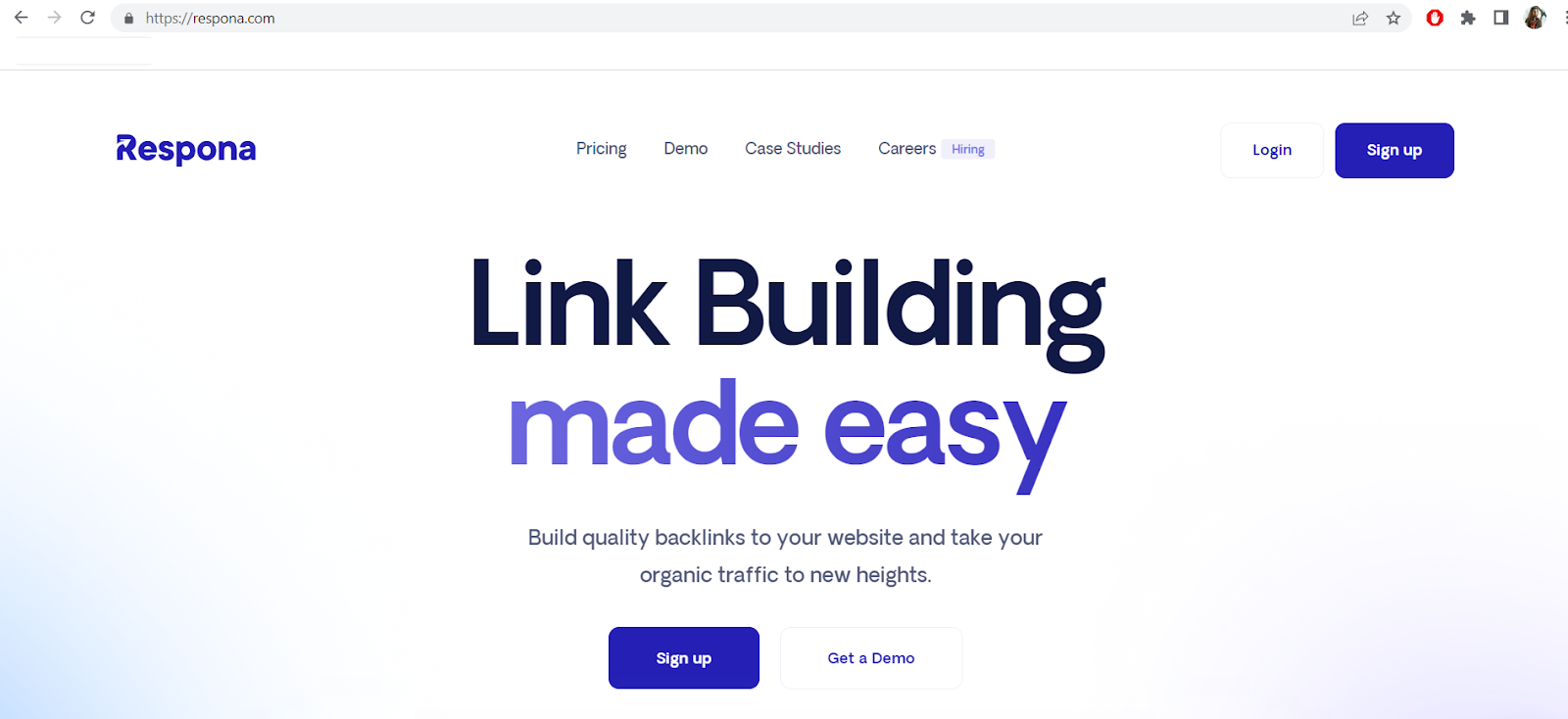
URL Example
Our homepage URL is, of course, https://respona.com:
How to Optimize Your URL Structure?
There are several measures you can undertake to optimize your URL structure both for users and search engines.
Include Your Primary Keyword (And Keep It Short)
The shorter the URL is, the better it is.
In fact, there is no need to have the URL slug of each page longer than its focus keyword.
The slug is the part of the URL that is unique for each page and comes after your domain and category/subcategories.

Hyphens, Not Spaces
URLs cannot have spaces.
If you have a space in your address, it will automatically be replaced by the %20 symbol.
It looks weird and unprofessional.
If you have multiple words in your URLs, make sure to separate them with hyphens.
Categories/Subcategories
Categories and subcategories are an important part of organizing content on a website. They help users to easily find the information or content they are looking for.
When used in a website’s URL structure, categories and subcategories can help search engines to better understand the content of a website and rank it more accurately in search results.
To use categories and subcategories in website URLs, start by creating a hierarchy of categories and subcategories that accurately reflect the content on your website.
For example, a website about cars could have categories such as “Make”, “Model”, and “Price” with subcategories under each such as “Honda”, “Civic”, and “Under $10,000”.
Once you have the hierarchy of categories and subcategories created, you can add them to your website’s URL structure.
The structure should follow a logical pattern, with the most general categories and subcategories coming first and the most specific ones coming last.
For example, a URL for a page about a Honda Civic under $10,000 might look like:
www.example.com/make/honda/model/civic/price/under-10000
Using categories and subcategories in URLs helps search engines to better understand the content of a website, which can lead to improved rankings in search results.
It also makes it easier for users to navigate your website, as they can quickly find the information they are looking for by following the hierarchical structure of the URLs.
Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are HTML elements that help webmasters prevent duplicate or crawling issues on their sites.
They are useful for situations when you have a single page associated with multiple URLs or there are duplicate pages/content.
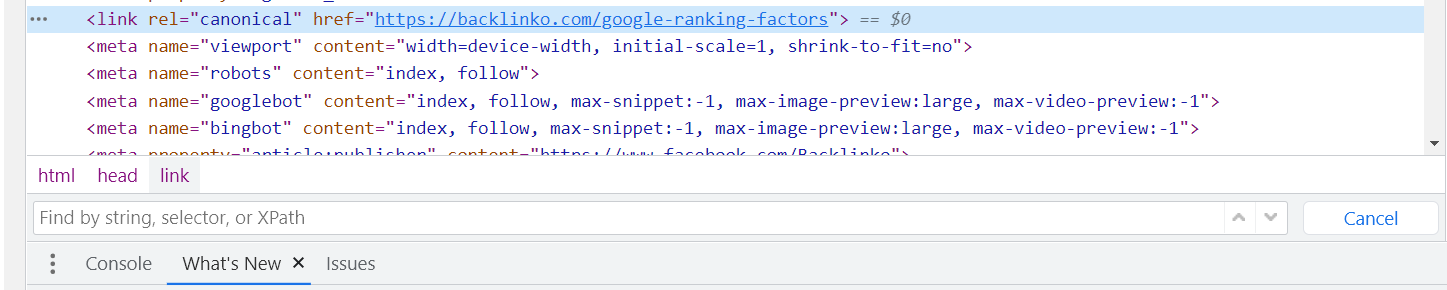
The canonical tag’s href property includes the URL of the page you wish to be regarded the “master” or “canonical” page.
This URL is often the content’s original source.
When a search engine detects a canonical tag on a website, it indexes the content of the canonical page while ignoring any duplicate material on other pages.
This helps to avoid duplicate content concerns by indexing just the most relevant and original material.
Bottom Line
Optimizing your URL structure is one of the most fundamental (and easy) SEO practices you can employ.
By doing so, you will both make it easier for search engines to understand and index your content, and improve your users’ search experience.