Duplicate Content
What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content is when you have multiple pieces of content on your website that are the same or very similar.
This can happen if you have multiple pages with the same title or if you have the same content on multiple pages of your website.
Any content that is exactly the same (or extremely similar) on different websites is also considered duplicate.
What Makes Duplicate Content Important?
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and make it difficult for them to determine which piece of content is the most relevant.
This can lead to your website being ranked lower in search results or even being removed from search results entirely.
For example, if you publish a blog post and someone steals it, their page will never show up in search results, because Google knows that yours was the original one.
Duplicate content can also make it difficult for users to find the content they are looking for on your website.
When there is more than one piece of content with the same or similar information, site owners can see their rankings and traffic go down. The main reasons for this are:
It’s hard for search engines to decide which version of the duplicate content is the best one to show. This means that each piece of duplicate content gets less visibility.
Other websites also have to choose which version of the duplicate content to link to. This spreads link equity (the value that links add to a website) among the duplicates, rather than having all links go to one piece of content. Link equity is one of the things that affects a website’s ranking, so this can make it harder for duplicate content to rank well.
How Does Duplicate Content Happen?
There are three main ways in which duplicate content issues can occur:
1. URL variations occur when the same content is accessible via multiple URLs.
This can happen when a website uses different URL structures for the same page (e.g. www.example.com/page and example.com/page), or when a page can be accessed via multiple domains (e.g. www.example.com and www.example.net).
2. HTTP vs https or www vs non-www pages can also lead to duplicate content.
This happens when the same content is accessible via both HTTP and HTTPS versions of a website (e.g. www.example.com and https://www.example.com), or when a website can be accessed with or without the “www” prefix (e.g. www.example.com and example.com).
3. Finally, scraped or copied content can also cause duplicate content problems.
This happens when somebody copies content from another website and republishes it on their own site, or when a website scrapes content from other sources and republishes it on their own site.
What is Keyword Cannibalization?
Keyword cannibalization happens when two or more pages on a website are optimized for the same keyword or phrase.
This can happen inadvertently if a website has multiple pages that are relevant to the same topic.
As you can imagine, duplicate content is one of keyword cannibalization.
It can also happen on purpose if a website owner is trying to optimize their site for a particular keyword or phrase and create multiple pages that target that keyword.
Some webmasters believe that ranking several pages for the same keyword is beneficial as it lets them occupy two spots in SERPs at the same time.
However, even though it sounds good on paper, cannibalization causes a serious problem: it leads to one page ranking higher than the other, or the second one not showing up in search results at all.
To avoid keyword cannibalization, you should choose unique target keywords for all of your pages.
If you have multiple pieces of content tailored around a similar topic, you should conduct extra keyword research to find variations of that keyword that would help you avoid content cannibalization.
For example, if you’re planning on releasing multiple guides on link building, you can target two different keywords: “link building”, and “link building strategies”.
You can identify cannibalized keywords on your own website with the help of Ahrefs’ Organic Keywords function.
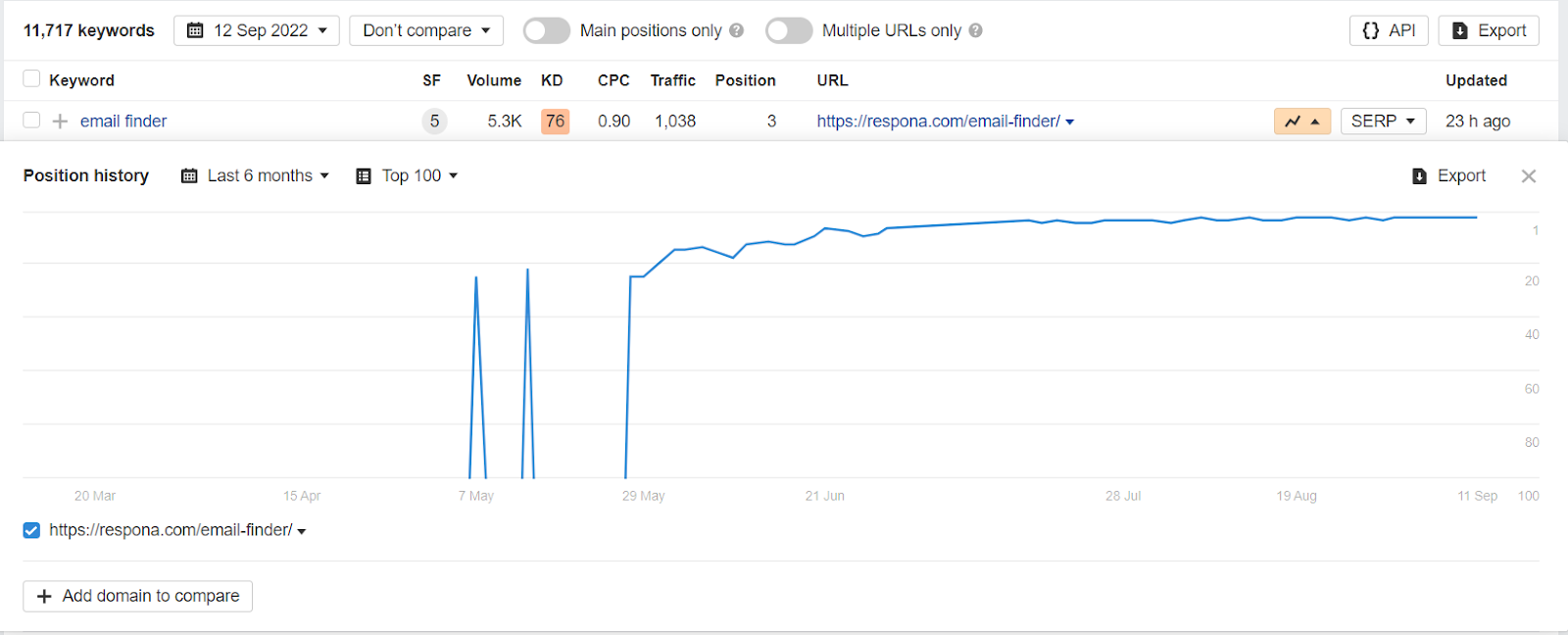
On the screenshot, there is only one line for the “email finder” keyword because we only have one page ranking for that keyword.
If there are two or more lines on the chart, that means you have multiple pages competing for your keyword, cannibalizing each other.
Duplicate Content Example
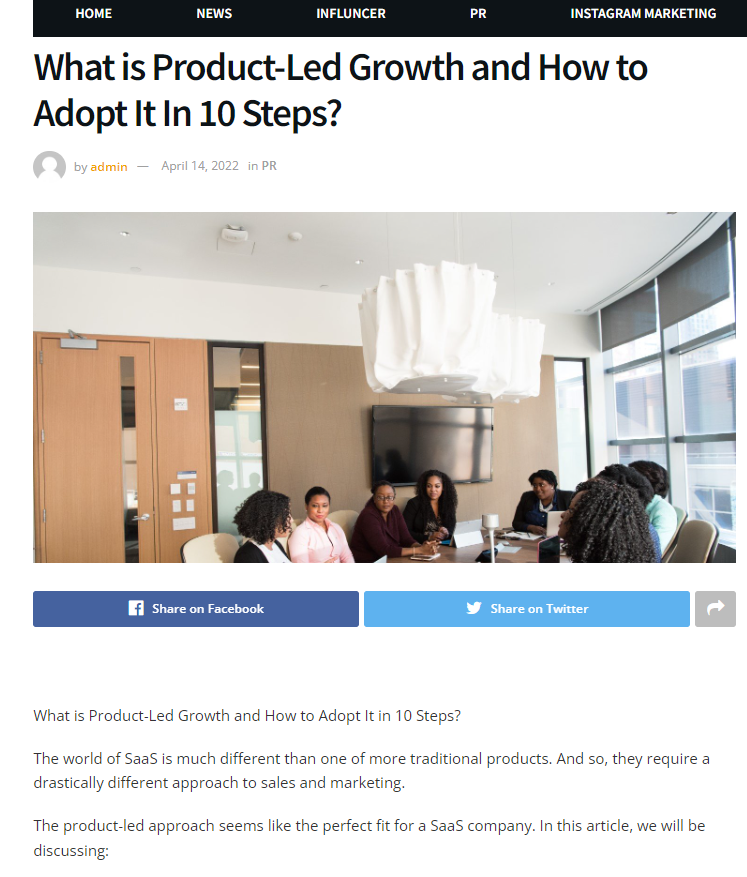
Here is an example of duplicate content: our own blog post that someone stole and published on their own site.
And this is the original upload:
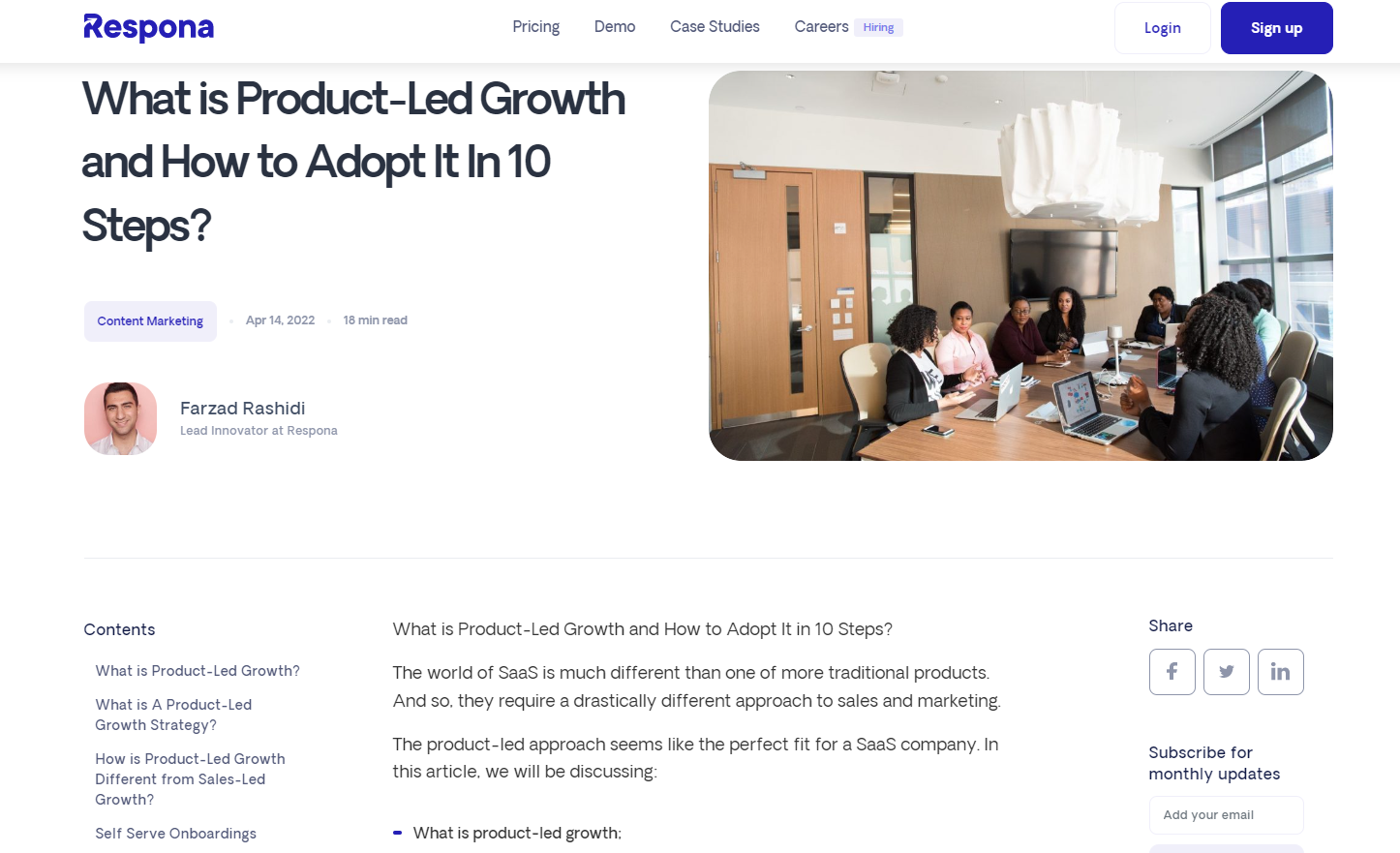
Their page will never show up in actual Google search results because the algorithm knows that our page is the original – it was published earlier.
How to Resolve Duplicate Content Issues?
There are several ways to prevent duplicate content on your website.
Ensure Each Page Has A Unique URL
Unique URLs are the absolute most basic measure that prevents duplicate content issues within your own domain.
This will help search engines to more easily index and rank your content, and it will also make it more likely that users will be able to find the specific piece of content they are looking for.
In addition, setting unique URLs for each piece of content will also help to ensure that any inbound links pointing to your content are going to the correct page. This is important because if multiple pages on your site are competing for the same inbound link, it can dilute the link’s value and make it less likely to help any of the pages rank higher in search results.
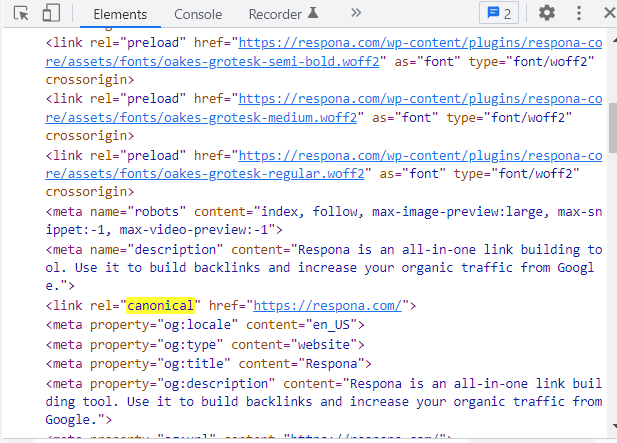
Canonical tags
A canonical tag is an HTML element that helps webmasters prevent duplicate content issues on their websites.
Canonical tags are used to tell search engines which version of a web page is the original, or “canonical,” version.
This is important because search engines often index multiple versions of the same web page, which can lead to duplicate content issues.
By using canonical tags, webmasters can tell search engines which version of a web page they want to be indexed.
To use a canonical tag, simply add the following element to the <head> section of your web page:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.example.com/>
Replace “http://www.example.com/” with the URL of the canonical version of the web page.
Canonical tags are a great way to prevent duplicate content issues on your website. By telling search engines which version of a web page is the canonical version, you can make sure that only one version of the page is indexed.
This will help to improve your website’s search engine optimization and help you avoid any penalties for duplicate content.
301 Redirects
One way to fix duplicate content issues is to use 301 redirects. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect from one URL to another. When you use a 301 redirect, it tells search engines that the content has been moved permanently to the new URL. This ensures that all of the PageRank and traffic from the old URL will be transferred to the new URL.
To use a 301 redirect, you will need to edit your .htaccess file. This file is located in the root directory of your website. You will need to add a line of code that looks like this:
Redirect 301 /old-page.html http://www.example.com/new-page.html
This will redirect any traffic that goes to old-page.html to the new page. You will need to do this for each page that has duplicate content. Once you have added the redirects, the search engines will update their indexes and your duplicate content issue will be resolved.
Just like unique URLs, custom title tags and meta description help search engines differentiate between the different pages on your website, preventing duplicate content issues.
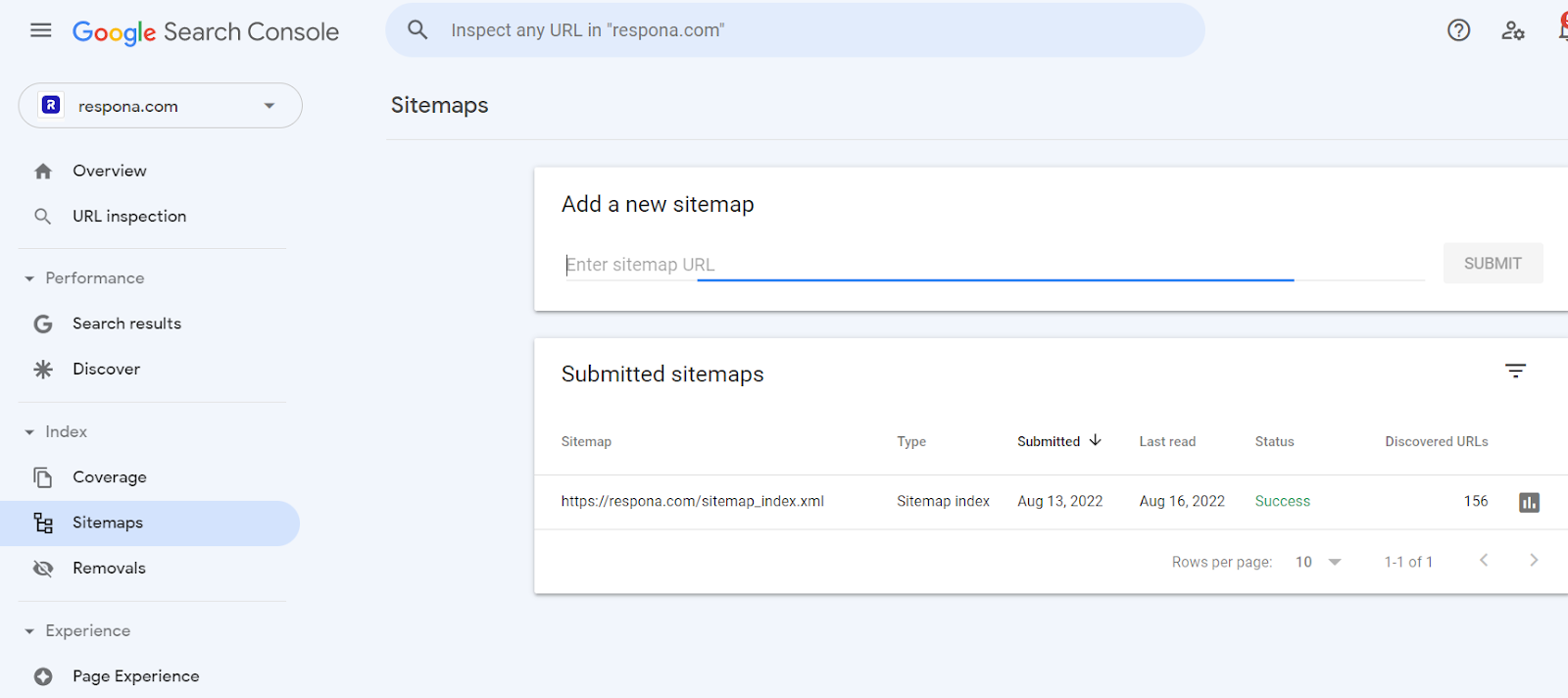
Sitemaps
A sitemap is an XML file that contains all of the URLs for a website. This file is used by search engines to crawl a website and index its pages.
Sitemaps can help prevent duplicate content issues by providing search engines with a complete list of all the pages on a website. This ensures that search engines index the correct versions of pages, and do not index multiple versions of the same page.
To create a sitemap, you can use a sitemap generator tool, or write an .XML file yourself.
Once your sitemap is generated, you can submit it to Google Search Consolel in the Indexing > Sitemaps section.
Bottom Line
Duplicate content can harm your rankings or even completely prevent your pages from showing up in search.
However, if you keep producing unique, helpful content, you won’t ever really run into any issues with duplicate content anyways.
If someone steals your content, it will never rank in search, because Google knows that your piece is the original.
If you ever have to publish content that is similar or practically identical on your own website, you can use canonical tags or 301 redirects to eliminate any duplicate content issues that may arise.