Google Bot
What are Google bots?
A Google bot is a web crawler that discovers and indexes web pages. Its purpose is to crawl the web and find new and updated content so that Google can index it and make it searchable.
Google bots find and index web pages by following links from one page to another. They index the content of each page they find, including the text, images, and videos.
There are two different types of crawler bots: one that simulates a desktop user and one that simulates a mobile user.
Starting in 2020, all sites have switched to mobile-first indexing, so optimizing your website for mobile performance is now as important as ever.
How do Google Bots Crawl Websites?
On average, crawler bots access your site every few seconds. They can do so through either HTTP 1.1 or HTTP 2.0.
According to Google, their goal is to crawl as many pages of your site per each visit without overloading your server’s bandwidth.
In an attempt to minimize bandwidth usage, Google crawlers are run on computers that are physically located near (or, at least, comparably near) websites they might crawl.
You can also request Google to change the crawl rate of your site.
An important thing to note is that Google bots can only crawl the first 15 megabytes of your HTML file. Only these 15 megabytes will be considered for indexing.
Any additional media like videos and images are fetched separately.
Can You Stop a Google Bot From Crawling Your Pages?
There are a few different rel tags that can be used to stop Google bots from following a link.
These include:
rel=”nofollow” – This tag tells Google not to follow the link. This is often used when linking to untrusted or unknown sites.
rel=”noindex” – This tag tells Google not to index the linked page. This can be used to prevent duplicate content issues.
rel=”canonical” – This tag tells Google that the linked page is the canonical (official) version of the content. This is often used when there are multiple versions of the same content on a site.
If your link does not have any of the above tags, it will be followed and index by search engine crawlers.
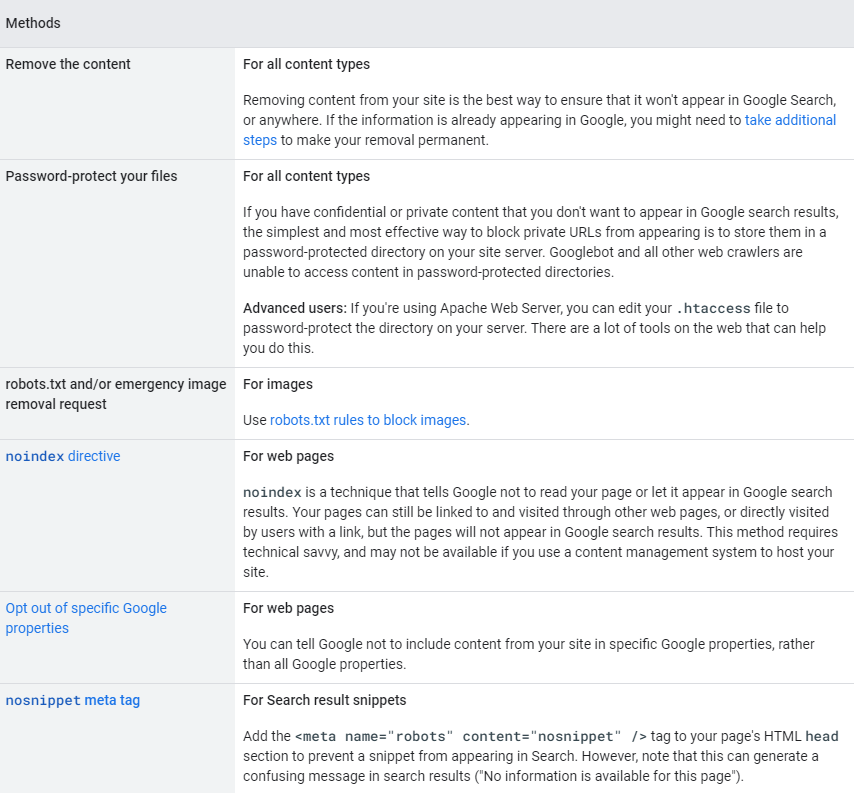
You can also use a robots.txt file to mark pages that should be off-limits to crawlers.
The robots.txt file is a text file that contains instructions for web crawlers and other web robots. The file is used to tell the robots which parts of the website should be crawled and indexed, and which parts should be ignored.
The robots.txt file must be placed in the root directory of the website. The file can contain instructions for multiple robots, and each instruction must be placed on a separate line.
An instruction line must always start with the user-agent name, followed by a colon (:). After the colon, you can specify one or more instructions. The most common instruction is “disallow”, which tells the robot not to crawl a specific URL.
Here is an example of a robots.txt file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
This file tells all robots to ignore everything on the website.
How to optimize your website for Google Bots?
And while you can’t directly influence how search engine bots work, you can definitely optimize your content for crawlability.
There are a few things you can do to optimize your website content for search engine crawlers with internal linking:
1. Use keyword-rich anchor text for your links.
This will help the crawlers understand what the page you’re linking to is about.
For example, at the end of each of our blog posts, we leave a link that leads to our demo page, usually with the “book a demo” anchor text.

This serves as a clear call-to-action for the reader, but also is a great example of a keyword-rich anchor text that makes it clear for the search engine crawlers that the link leads to our demo page.
2. Link to relevant pages.
Google’s algorithm is pretty good at recognizing relevant links and those that are spammy and don’t fit the context of the article.
Let’s look at another example.
This is a section about writing good subject lines in an article on how to craft a sales pitch that converts.
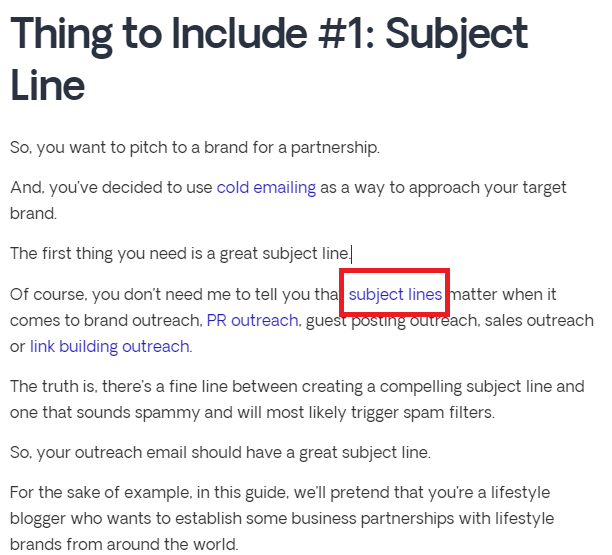
In the fourth sentence of this section, we link out to our other article that is dedicated solely to subject lines.
This is a natural link.
On the other hand, the first link on the following screenshot is a “bad” link:
Can you guess where it leads to? An article about reaching your business goals? No.
It leads to an article titled “8 Email Marketing Tips To Follow for A Successful Email Program”:

Not only is this unintuitive for the readers, but it also looks unnatural, or even spammy, in the eyes of search engine crawlers.
3. Use enough links.
Crawlers need to follow links to understand the structure of your website. Each page should have at least 5 internal links pointing to it. Having too few links may cause the crawling and indexing process to become slower.
4. Make sure your links are working.
Crawlers will try to follow every link on your website. If they find a link that doesn’t work, they’ll assume that your website is broken and will give it a lower ranking.
There are two ways in which you can check for broken links on your site.
The first one is, of course, to manually go through each page. Obviously, this is time-consuming.
Luckily, there are various tools available that can help you speed up the process.
In fact, SEMRush can do a full site audit for you in minutes and reveal any broken links that you might have.
There are also free tools and plugins like the Broken Link Checker that are less robust in their functionality, but will help you achieve your goals for free.
5. Use a sitemap.
A sitemap is a file that contains a list of all the pages on your website. This file is used by search engine crawlers to index your website and can help them index your website more effectively.
Here is an example of a basic .XML sitemap provided by Google Search Central:

To create a sitemap, you will need to use a text editor such as Notepad or TextEdit. The first line of your sitemap should be the XML declaration:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
The next line should be the opening sitemap tag:
<urlset xmlns=”http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9″>
Each page on your website should then be listed as a separate <url> tag. For example:
<url>
<loc>http://www.example.com/</loc>
<lastmod>2013-01-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>1.0</priority>
</url>
The <loc> tag contains the URL of the page, the <lastmod> tag contains the date on which the page was last modified, the <changefreq> tag specifies how often the page is updated, and the <priority> tag specifies the importance of the page.
Once you have added all of the pages to your sitemap, you should save the file as sitemap.xml and upload it to the root directory of your website.
6. Optimize for mobile.
In order to optimize your website for mobile-first indexing, you will need to ensure that your website is designed and developed for mobile devices.
1. Use a responsive web design: This means that your website will automatically adjust to fit the screen size of the device that it is being viewed on. This is the most common and effective way to optimize your website for mobile.
2. Use a mobile-friendly theme: If you are using a content management system (CMS) such as WordPress, there are many mobile-friendly themes that you can choose from. This will make your website look great on all devices.
3. Use a separate mobile website: This is a website that is designed specifically for mobile devices. It will usually have a simplified design and layout and will be much easier to use on a small screen.
4. Use app-based solutions: There are many app-based solutions that you can use to optimize your website for mobile. These include using a dedicated mobile app, using a mobile browser extension, or using a mobile website builder.
5. Use AMP pages: AMP stands for Accelerated Mobile Pages and is a Google-backed project that aims to improve the performance of web pages on mobile devices. AMP pages are designed to load faster and use less data, making them ideal for mobile users.
Bottom Line
Google bots crawl your website every few seconds, and it’s in your best interest to make sure they can index all of your content in a timely manner – this will help you rank higher search results.
By following the tips above, you should be able to improve your site’s crawlability, or block certain parts of your website from indexing.