PageRank
What is PageRank?
PageRank is a link analysis algorithm that assigns a numerical weighting to each element of a hyperlinked set of documents, such as the World Wide Web, with the purpose of “measuring” its relative importance within the set.
The algorithm may be applied to any collection of entities with reciprocal quotations and references. The numerical weight that it assigns to any given element E is referred to as the PageRank of E and denoted by {displaystyle PR(E).}
PageRank was developed at Stanford University by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1996 as part of a research project about a new kind of search engine.
Sergey Brin had the idea that information on the web could be ordered in a hierarchy by “link popularity”: a page ranks higher as there are more links to it.
Rajeev Motwani and Terry Winograd co-authored with Page and Brin the first paper about the project, describing PageRank and the initial prototype of the Google search engine, published in 1998.
Shortly after, Page and Brin founded Google Inc., the company behind the Google search engine.
While just one of many factors that determine the ranking of Google search results, PageRank continues to provide the basis for all of Google’s web search tools.
The name “PageRank” plays off of the name of developer Larry Page, as well as the concept of a web page.
The word is a trademark of Google, and the PageRank process has been patented (U.S. Patent 6,285,999).
However, the patent is assigned to Stanford University and not to Google. Google has exclusive license rights on the patent from Stanford University.
The university received 1.8 million shares of Google in exchange for use of the patent; it sold the shares in 2005 for $336 million.
PageRank is one of the many important metrics Google uses to determine the ranking of websites in its search engine results pages (SERP).
It is a measure of the importance of a particular page, as voted by the links pointing to it.
How is PageRank Calculated?
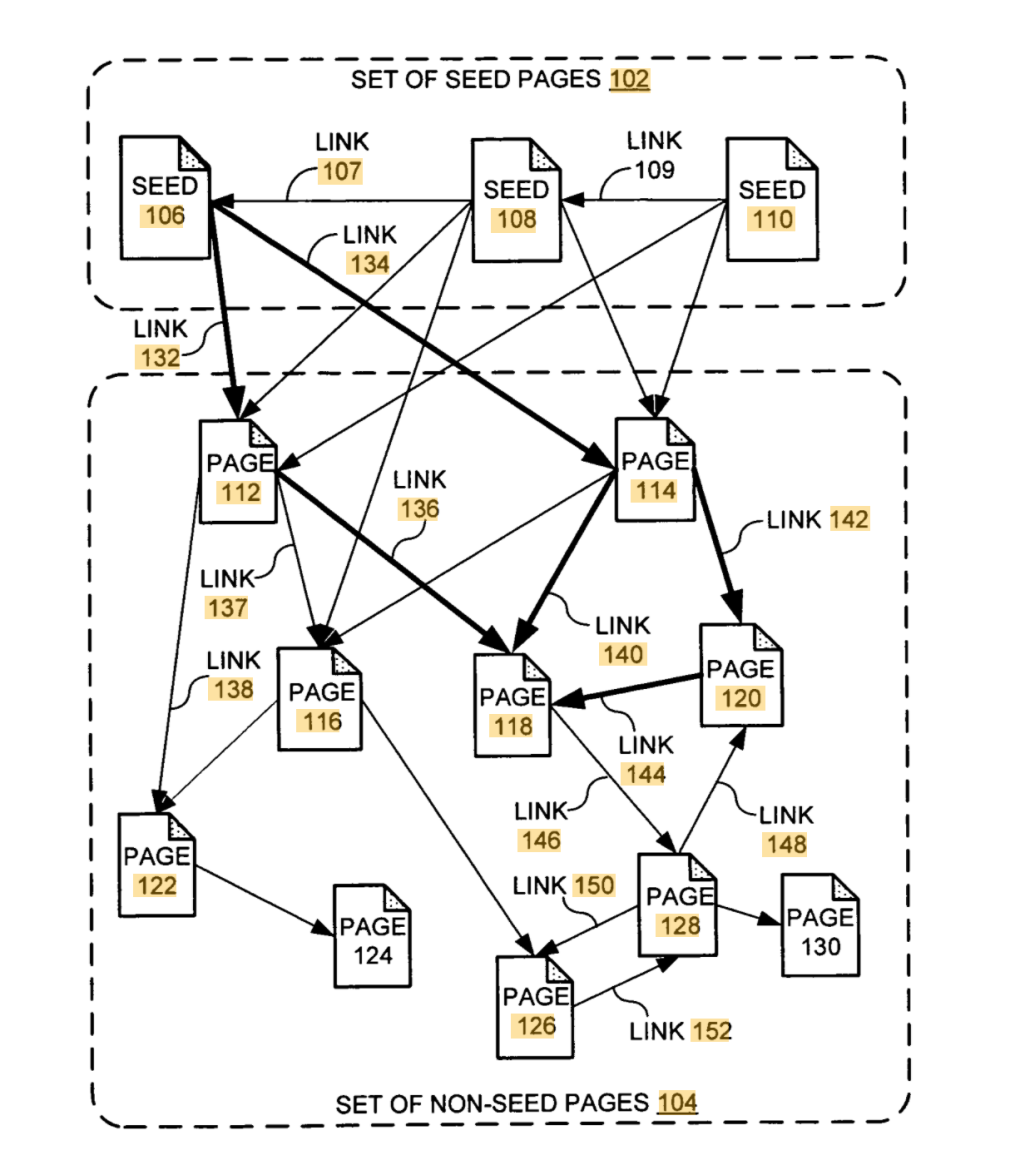
In its most basic form, PageRank is calculated by summing the PageRanks of all the pages linking to a given page and then dividing that sum by the total number of links on those pages.
The resulting value is then multiplied by a damping factor, which can be set between 0 and 1.
The purpose of the damping factor is to prevent what is known as the “PageRank cascade”, where one highly ranked page links to a series of poorly ranked pages, which in turn link to more highly ranked pages, ad infinitum.
The damping factor is set to 0.85, which gives a reasonable probability that the random web surfer will click on an arbitrary link from any page they visit.
The PageRank algorithm has serious flaws, which cause it to give incorrect results in certain situations.
Also, keep in mind that the exact PageRank calculation is only known by the select few at Google, so the mechanism described above is just the most basic form of the algorithm.
Despite the flaws, PageRank remains one of the most popular ways to rank pages on the web. It is still in use by many search engines, including Google.
Over the years, the algorithm has seen many changes, but its core function remains very similar.
Why is PageRank Important?
A high PageRank directly correlates with higher online performance.
Increased Visibility
A high PageRank indicates that your website is more likely to be seen by potential visitors.
This is because websites with a high PageRank are more likely to appear at the top of search engine results pages (SERPs), which means they are more likely to be clicked on by users.
More Traffic
More visibility often leads to more traffic.
If your website is more likely to be seen by potential visitors, it stands to reason that more people will actually visit your site. This, in turn, can lead to more sales and conversions.
Better Branding
A high PageRank can also help to improve your brand image.
A strong PageRank indicates that your website is a credible and authoritative source of information, which can help to build trust and confidence in your brand.
Improved ROI
Finally, a high PageRank can also lead to improved ROI.
This is because a higher PageRank often leads to increased traffic, which can then lead to more sales and conversions.
This means that your investment in SEO (which can help to improve your PageRank) is likely to pay off in terms of increased revenue.
PageRank Example
PageRank is not publicly available, so there is no way to check your own PageRank.
How to Increase Your PageRank?
Since PageRank is a value mainly influenced by your website’s backlink profile, the only way to reliably increase it is by building high-quality backlinks.
Feel free to refer to the following guides to learn more about specific link building strategies.
Bottom Line
Despite being secretive when it comes to the exact calculations of PageRank, Google has admitted that a modernized version of it is still being used as part of the ranking algorithm.
So, even though you can never know your exact PageRank values, it remains one of the most impactful factors for your SEO strategy.