Organic SEO refers to all white-hat SEO strategies aimed at getting your business on the first page of Google.
Despite constant updates to the ranking algorithm, the SEO community is still going strong – and always figuring out what’s working and what’s not.
In this article, we’ll dive into:
- What exactly is organic SEO
- The difference between on-page, off-page, and technical SEO
- 15 strategies for mastering organic SEO
Let’s get started.
Link building cheat sheet
What is Organic SEO?
First things first, we need to clarify that “organic SEO” is not a separate idea from “regular” SEO.
Organic search engine optimization as a whole is aimed at generating traffic from organic channel – i.e. Google Search.
It does not include things like paid ad campaigns, and other paid search strategies – as well as black hat SEO.
Organic SEO is divided into three distinct categories:
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
- Technical SEO
The first one focuses on valuable content and overall user experience, so, everything that’s on your page.
Off-page SEO mostly revolves around link building, generating user reviews, and optimizing your Google Business Profile for localSEO.
Technical SEO, on the other hand, ensures that your website runs fast, is secure, and is easily crawlable by search engines.
All of these techniques are aimed at getting your website to rank higher on Google.
Let’s break them down, one by one.
On-Page Organic SEO Strategies
Content
High quality content is the core of all SEO – not just on-page.
You’ve heard this before, but relevant content truly is king, and queen, and honestly the whole court in the world of digital marketing.
Google prioritizes user experience, so your content must be easy to read, navigate, and understand.
And most, importantly, all SEO content needs to be optimized for user intent.
There are four kinds of search intent:
- Informational: The user is looking for information. They want to learn about a topic, answer a question, or understand something better.
- Transactional: The user is ready to make a purchase or take a specific action. They’re looking to buy something, sign up for a service, or download a resource.
- Navigational: The user is trying to find a specific website or page. They may not know the exact URL, but they know what they’re looking for.
- Commercial: The user is researching before making a purchase. They are not quite ready to transact, but they are comparing options and considering different products or services. They are further down the funnel than informational, but not quite transactional.
For informational intent, an example would be a blog post like “How to Bake Sourdough Bread” or explainer videos on “What is Quantum Computing?”.
Transactional intent is satisfied by product pages with clear “Add to Cart” buttons or SaaS free trial sign-up forms.
Navigational intent is addressed by pages like “Amazon login” or your website’s “Contact Us” page, while commercial investigation intent is served by comparison pages reviewing “Top 5 Project Management Software” or “Best Budget-Friendly Laptops.”
Keyword Optimization
Now, how do you know what to write?
You need to know which terms your audience is searching for – and this is what keyword research and optimization is all about.
You’ll need an SEO tool with keyword tracking functionality, like Ahrefs or Semrush.
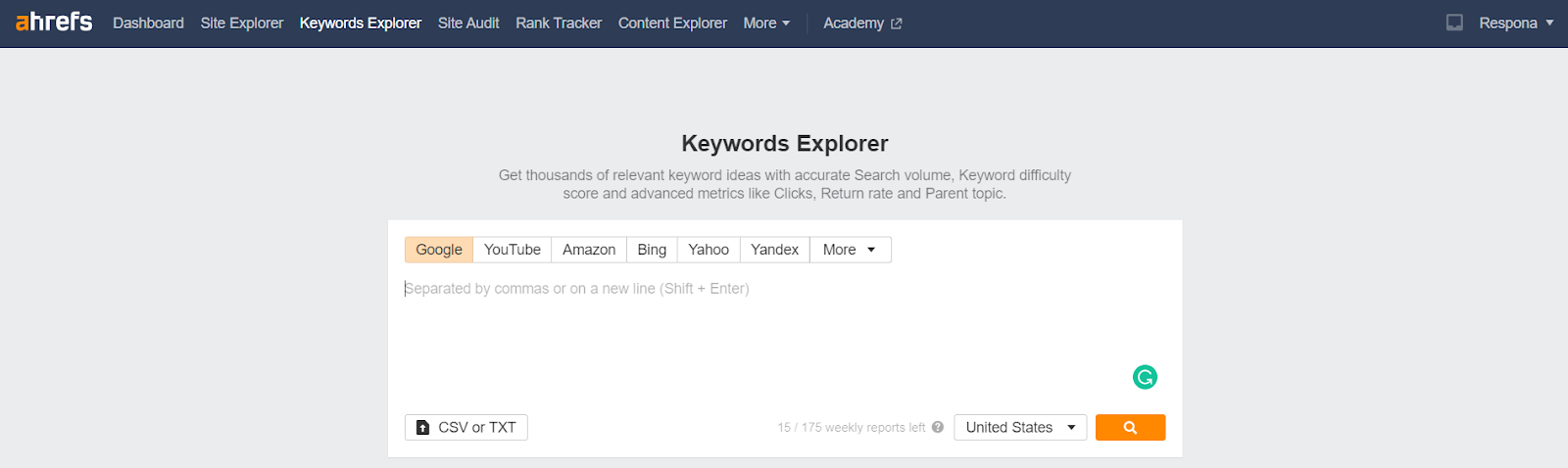
Start by entering your niche’s core term, your “parent keyword.”
For example, one of our parent keywords is “link building”.
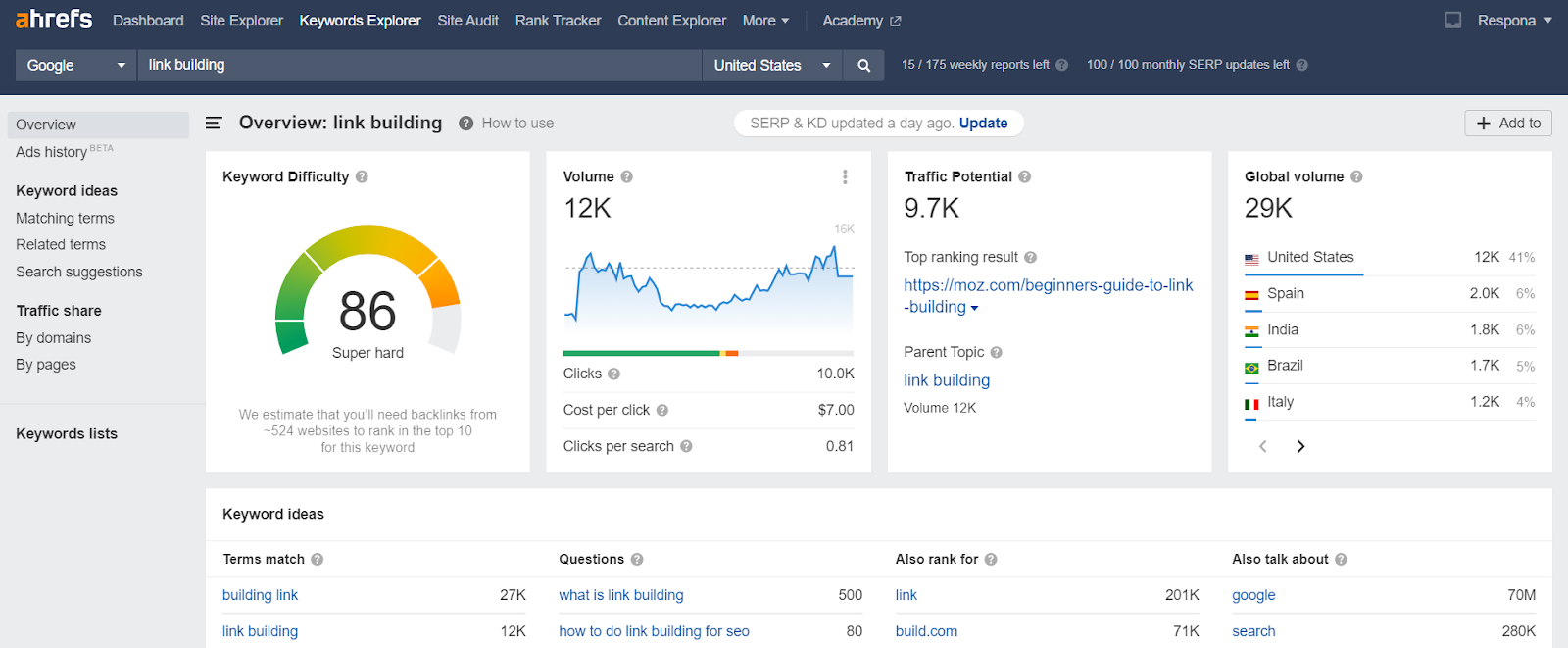
Once you get the overview of your keyword, check key metrics like search volume, keyword difficulty, and organic search traffic potential.
Use the search suggestions report to find related keywords and their respective data.
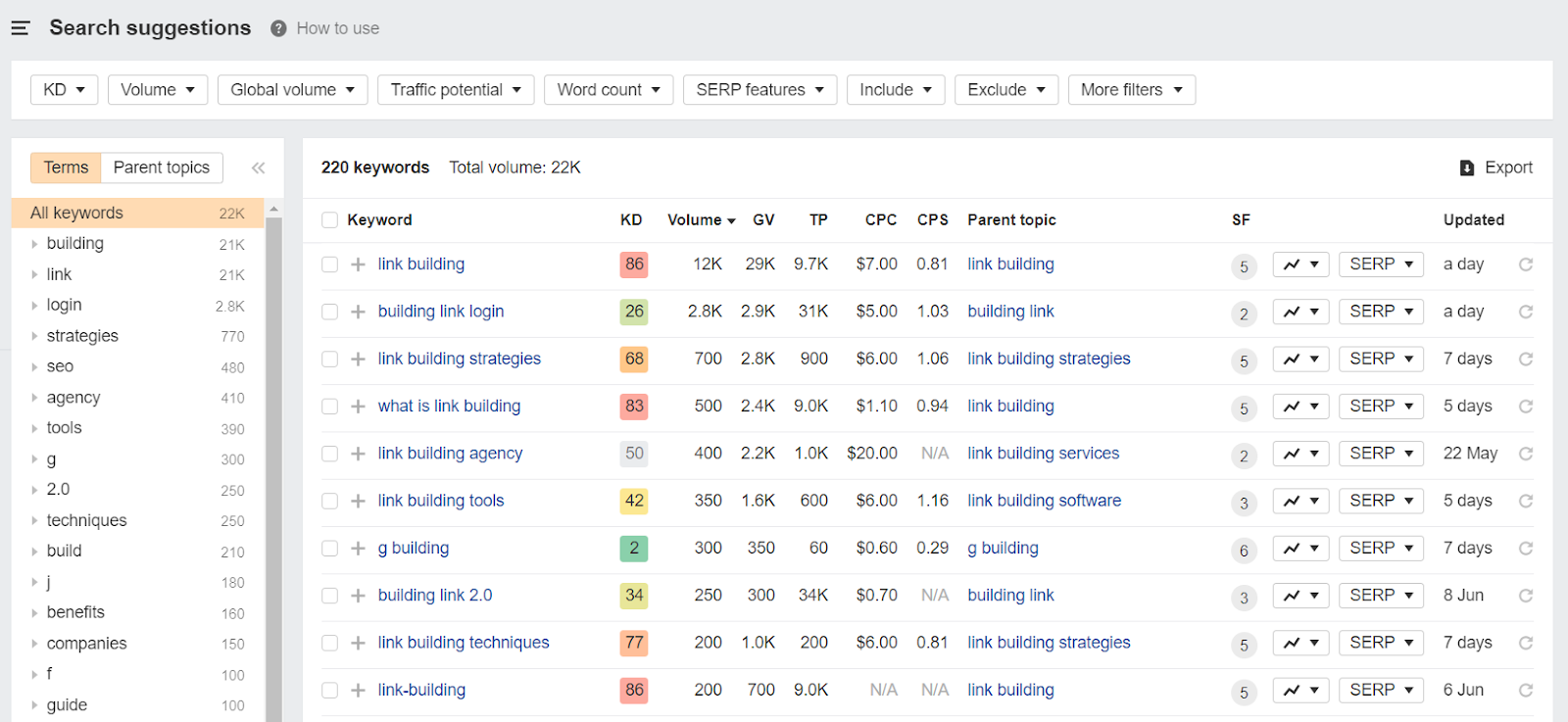
Keyword difficulty indicates how challenging it is to rank for a specific term.
While high search volume is great, targeting keywords with lower difficulty is a much easier way to quickly rank on page one.
However, it’s not as simple as just picking low-difficulty, high-volume keywords.
We recommend taking a more strategic approach.
Instead of guessing and picking keywords that sound good, prioritize keywords with high traffic potential, strong commercial intent (meaning users searching these terms are likely to convert), and low competition.
A helpful formula to identify prime keyword opportunities is:
(1 / Keyword Difficulty) * Traffic Potential * (CPC + 1) = Keyword Score
A higher keyword score suggests a more valuable and easily attainable keyword.
Experiment with variations of your parent keyword and other relevant terms, then export the data from your keyword tool.
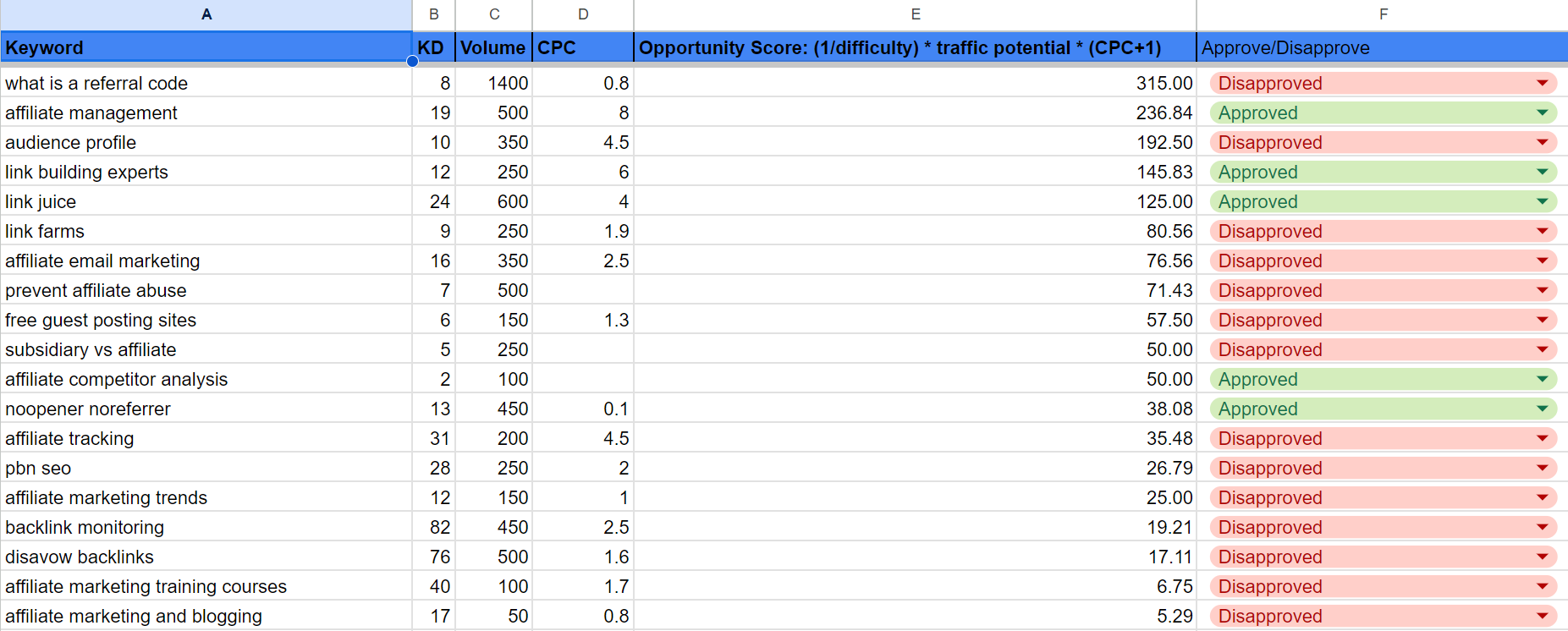
Finally, sort these keywords by their Keyword Score (highest to lowest), and prioritize the most promising targets for your content.
Just keep in mind that YOU still determine the relevance of any given organic keyword – this formula is only meant to make them easier to find.
Header Tags
Header tags provide structure and hierarchy, improving readability for both the user and search engines.
Use your primary keyword in the H1 and related keywords in subsequent headings.
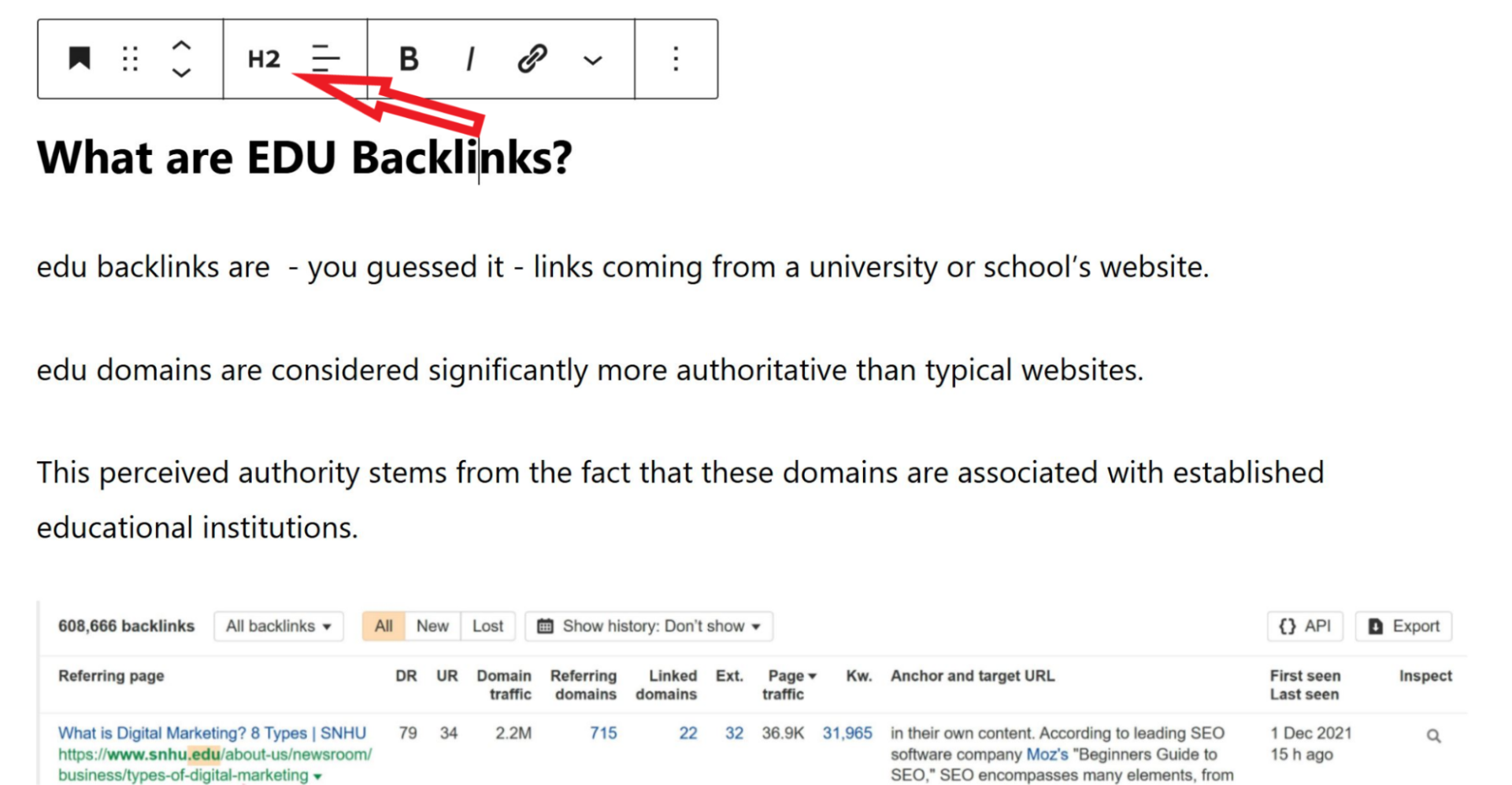
Normally, there should be only one H1 tag, with H2 tags marking sections and H3 tags further breaking them down into subsections.
Your H1 tag will be pulled into the search results automatically, but you’ll need to add a meta description separately.
Internal Links
Internal links connect relevant pages, improve navigation and distribute link equity.
Auditing internal links involves analyzing link structure for proper navigation, user experience, and link equity distribution.
Every page on your website should be accessible in 3 clicks or less.
Also, a good rule of thumb is to ensure every single page on your website has at least five internal links pointing to it.
Fix broken internal links and review anchor text for descriptiveness, relevancy, and keyword inclusion without over-optimizing.
Image Optimization
All images must have descriptive file names and alt text containing relevant keywords.
Compress images for page speed without sacrificing quality.
You can use a plugin like Smush to automatically compress the images uploaded to your CMS – and make sure they are always hosted on your own domain and not a third-party resource.
Featured Snippets Optimization
Featured snippets appear above all organic search results, and catch the user’s attention first.
Think “People also ask” and these little snippets of your article pulled right to the search results.
To increase the chances of getting into these, structure content to directly answer common questions related to target keywords, starting with “who,” “what,” “where,” “when,” “why,” and “how.”
Focus on long-tail keywords and natural language phrases, using SEO tools like Answer the Public or Google’s “People also ask.”
CTA Optimization
The call-to-action is one of the most important on-page elements.
After all, you don’t just want the user to visit your site, you want them to become a customer.
Whether it’s a link to another article or landing page, or a newsletter registration, Google tracks click-through rates on your page.

Meaning, more users taking your desired action is seen as a positive ranking factor.
Most commonly these are placed above the fold or within content.
Make CTAs visually appealing with contrasting colors and clear fonts, without disrupting user experience.
A/B test different CTA wording and placement to figure out what’s working for your audience specifically.
Off-Page Organic SEO Strategies
Off-page SEO is all about getting as many links from other sources as possible.
Be it through getting backlinks from other blogs in your niche, getting user reviews, or putting up a listing on Google Maps.
Link Building
Link building is the meat and potatoes of off-page SEO.
It’s important because links pass PageRank – a value taken into account by Google’s algorithm.
In Layman’s terms, more high-quality backlinks = better rankings.
We’re not going to dive too much deeper into the theory behind it, but if you’d like to learn more, feel free to watch this video:
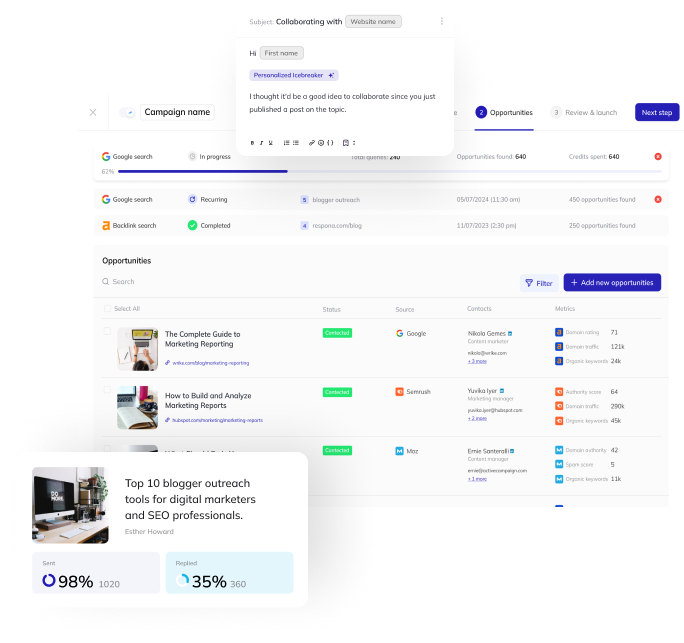
Now, let’s quickly run through how you can actually go ahead and get other websites to link to yours, with the help of Respona.
It automates every aspect of link building – from prospecting to finding contacts and personalization.
One of the easiest ways to start link building is through guest posting, so let’s do that.
To start, specify your target topics and share samples of your work.
Respona uses this to generate relevant search queries and personalize outreach, even suggesting AI-powered keywords.
The campaign editor offers pre-built, customizable email sequences.
Add personal touches, check for spam, include unsubscribe links, and adjust follow-up timing.
Respona’s AI variables, like “Icebreaker” and “P.S.,” automatically add unique, personalized content tailored to each guest post opportunity, going beyond simple name insertion.
You can create custom AI variables for even more targeted personalization, suggesting topics or referencing the prospect’s previous work.
Respona finds potential guest blogging opportunities by targeting “write for us” pages and running multiple simultaneous Google searches.
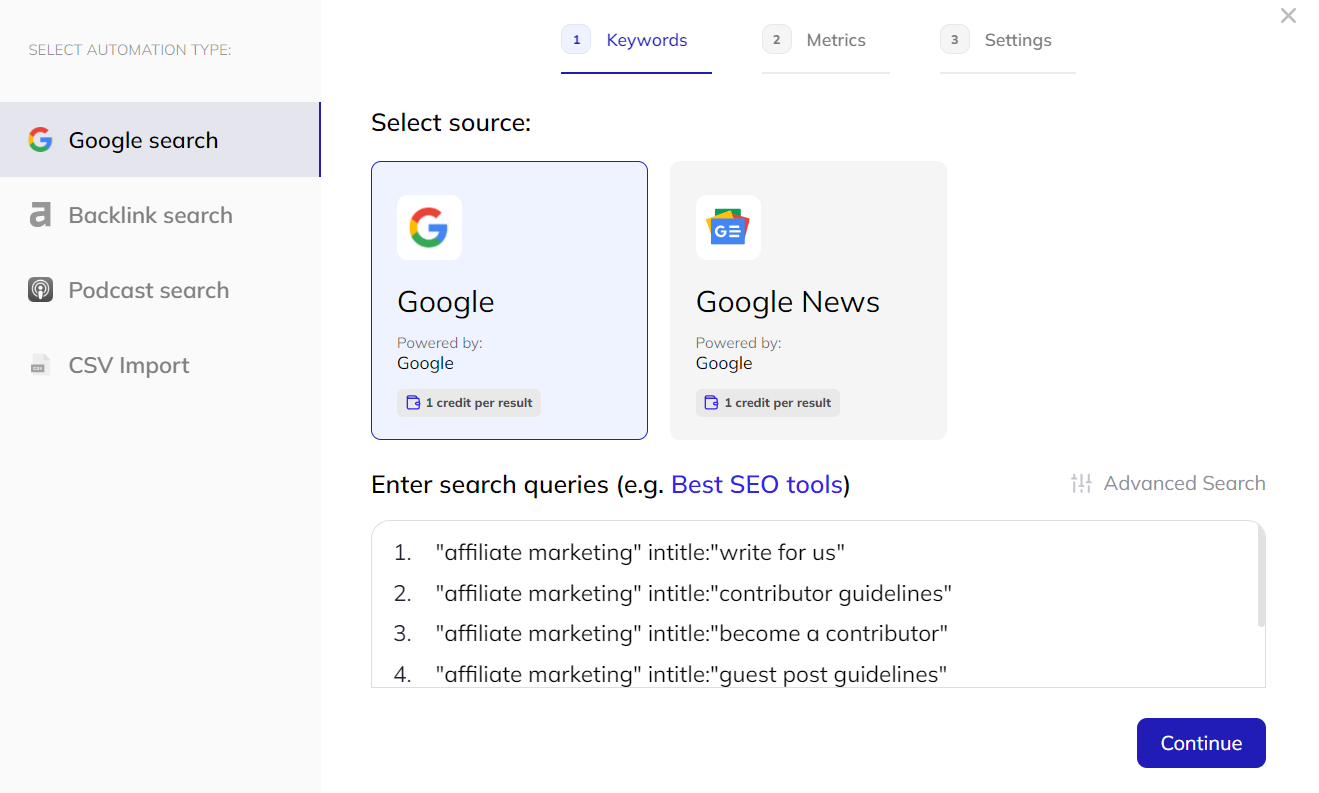
Refine results using SEO filters to only target high quality link opportunities.
Respona’s contact finder, configured for guest posting campaigns, automatically locates the website owner and other relevant contacts.
Next, fine-tune the AI personalization by providing examples of your editing style or even instruct it to generate unique guest post ideas for each opportunity.
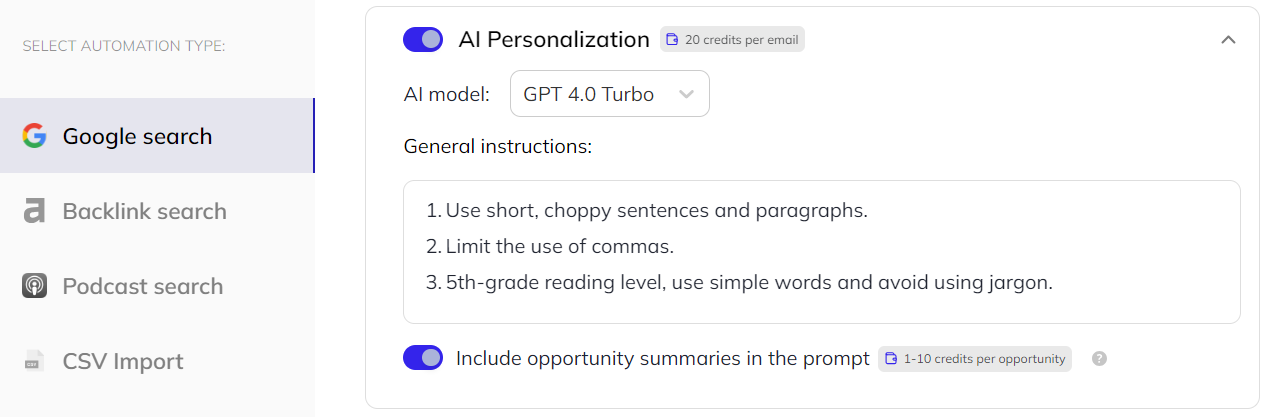
You can make the search recurring, meaning Respona will automatically re-run it every once in a while, so all you have to do is log in and launch fresh opportunities.
Everything is done in real-time, and you’ll see link opportunities on your screen as soon as they’re found.
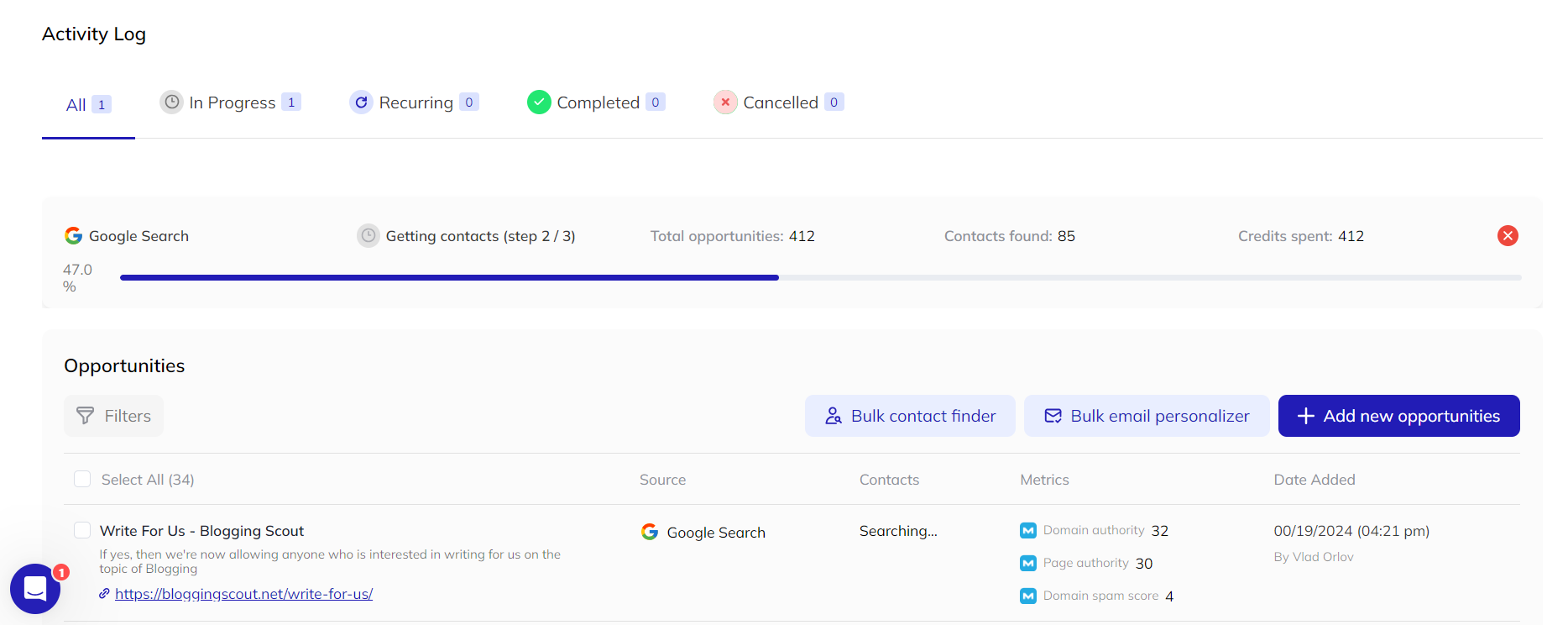
Before launching, review AI-generated personalizations and make manual edits where necessary to increase reply rates.
In addition to email addresses, Respona retrieves LinkedIn profiles for additional connection opportunities.
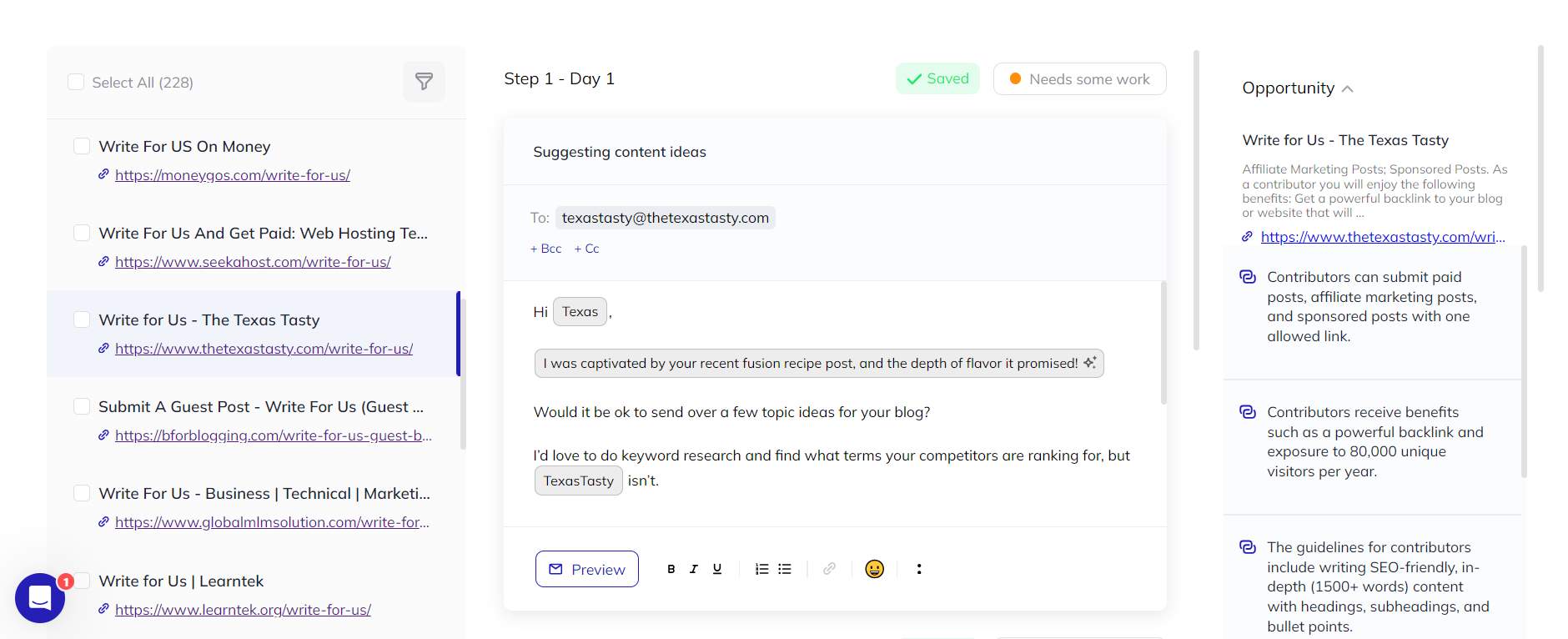
Monitor responses within Respona’s shared inbox, consolidating multiple inboxes for easier management.
Google Business Profile
For businesses with a physical location or serving a specific geographic area, a Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business) is essential.
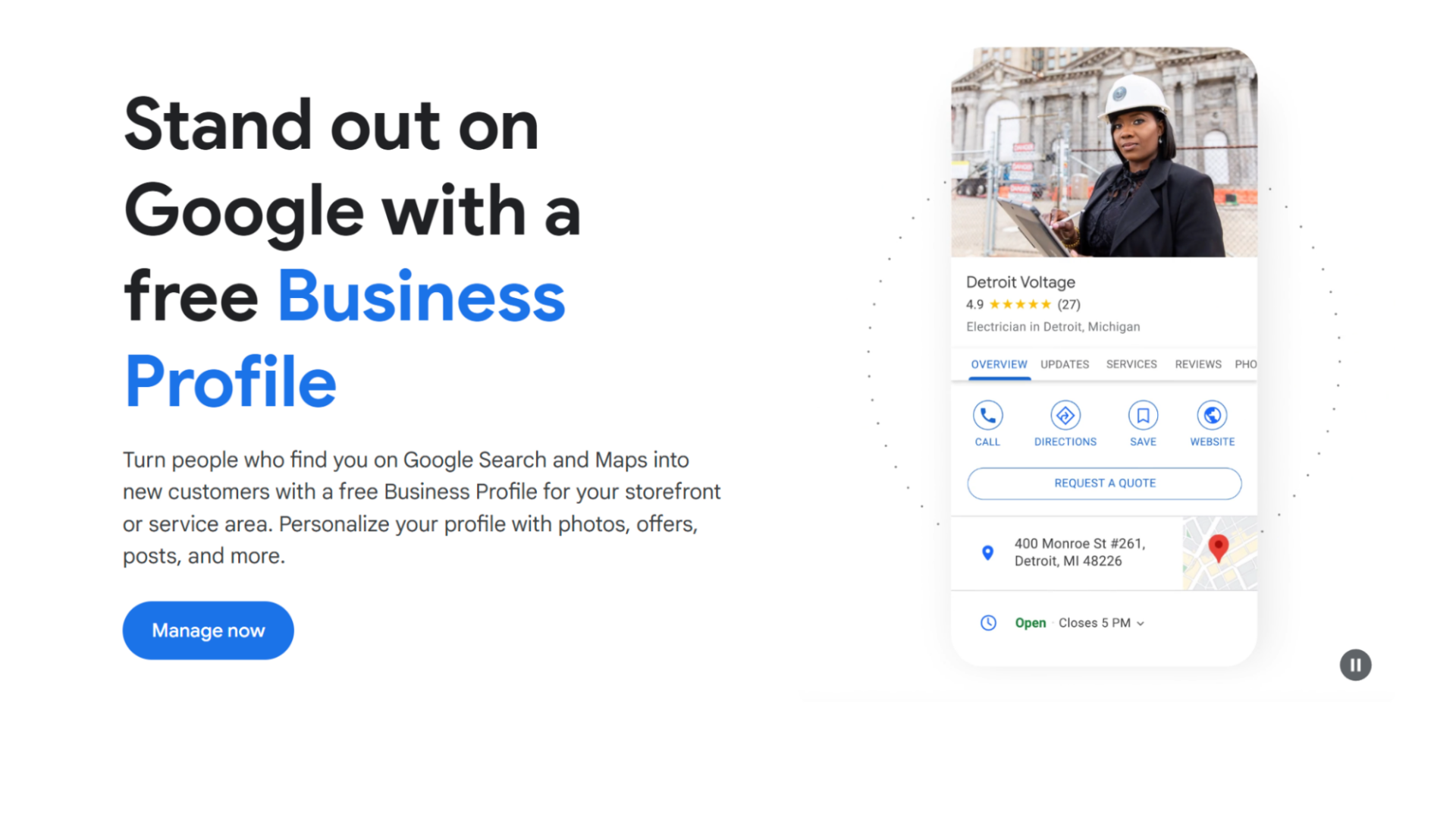
This free profile allows you to manage how your business appears in Google Search and Maps.
Ensure your profile is complete and accurate, including your business name, address, phone number, website, hours of operation, and relevant categories.
Add photos of your business and encourage customers to leave reviews.
User Reviews
Positive reviews build trust, and encourage potential customers to choose your business.
Actively encourage satisfied customers to leave reviews on Google, Yelp, and other relevant platforms.
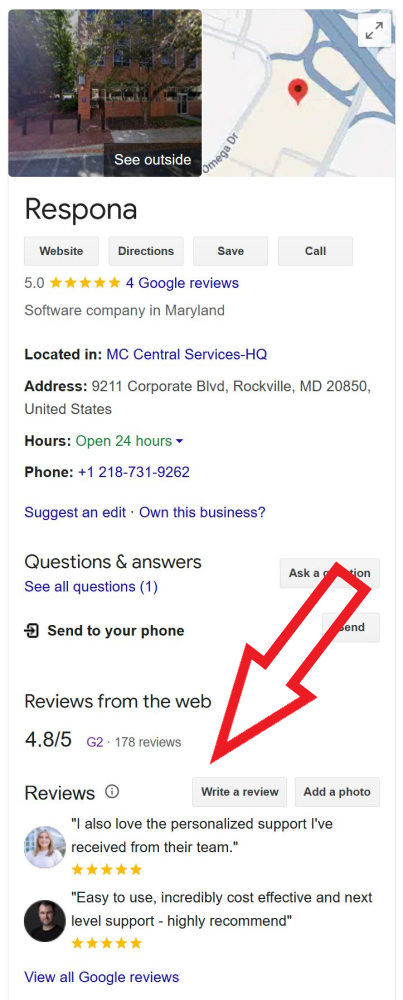
Don’t be shy – politely ask after a positive interaction, whether in person, over the phone, or via email, while the experience is fresh.
Make it easy by providing a direct link to your review section, perhaps via a shortened URL or QR code.
While offering incentives can be a gray area, it’s very common.
Avoid anything that could be seen as buying positive reviews, as Google’s guidelines discourage incentivizing reviews in a way that could create bias.
If you offer an incentive, ensure it’s available to all reviewers, regardless of sentiment.
Technical Organic SEO Techniques
Page Speed & Mobile Optimization
Page speed and mobile optimization are crucial for both user experience and SEO.
Core Web Vitals, including Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), are key performance metrics.
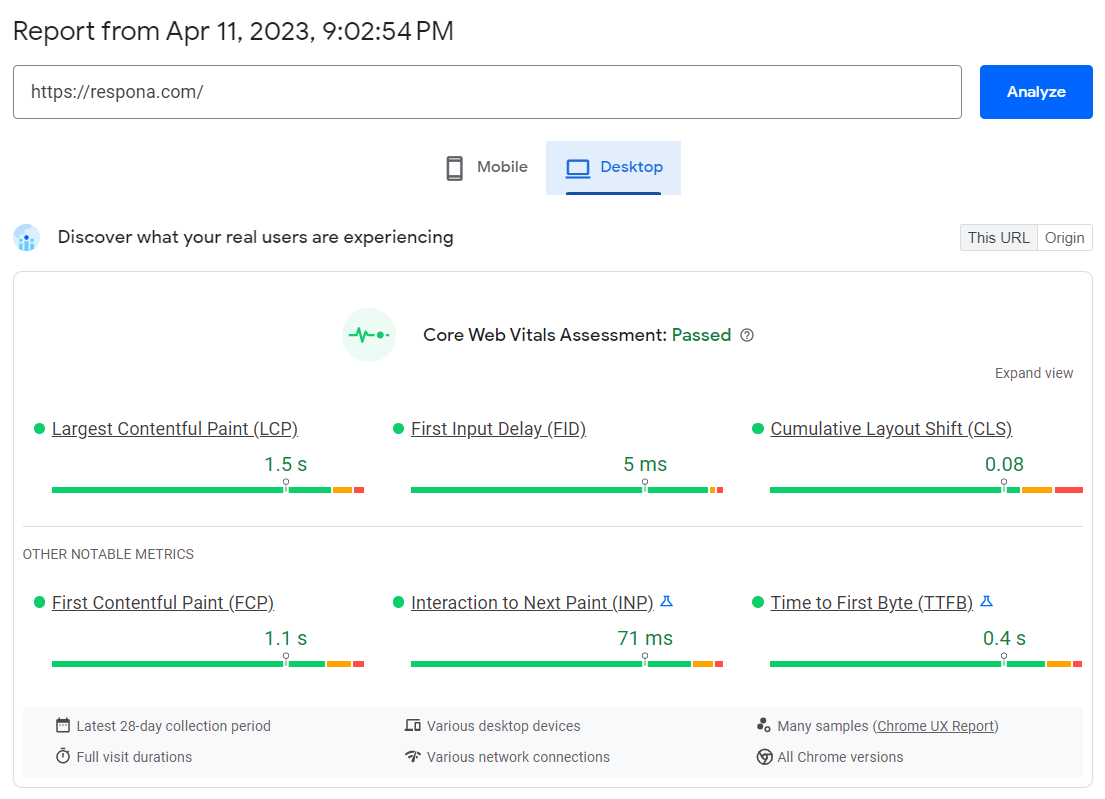
Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Search Console, Lighthouse, or WebPageTest to audit these vitals and identify areas for improvement, such as image optimization, reducing JavaScript execution time, and improving server response times.
Ensure mobile responsiveness by testing your site on various devices and screen sizes using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and manual checks.
Pay attention to load times on mobile, as slow pages can hurt user experience and rankings.
Optimize CSS by minifying code, removing unused styles, and merging files to improve load times.
Optimize server response time (TTFB) by using updated server software, a CDN, optimizing scripts and queries, and potentially upgrading from shared hosting to one of the cheapest VPS options.
SSL Certificate
An SSL certificate (HTTPS) encrypts communication between users’ browsers and your web server, protecting data and boosting SEO.
Search engines prioritize secure sites.
Check for the padlock icon and “https://” in your URL. If absent, obtain and install an SSL certificate.
Use online SSL checkers like SSL Labs’ SSL Server Test to ensure proper implementation.
Redirect all HTTP website traffic to HTTPS and verify correct indexing in Google Search Console.
Sitemap
An XML sitemap acts as a blueprint for search engines, outlining your site’s architecture and crucial pages.
It streamlines content discovery and indexing.
Use online generators or plugins to create a sitemap and submit it to search engines like Google and Bing via their webmaster tools (e.g., Google Search Console).
Regularly check for broken links or outdated details in your sitemap.
Schema Markup
Schema markup is code added to your website that helps search engines understand the content on your pages.
This can improve your site’s visibility in search results, potentially leading to rich snippets.
Use schema markup relevant to your content type, such as articles, products, or local businesses.
Redirects and Broken Links
301 redirects are permanent, passing link equity to new URLs, while 302 redirects are temporary.
Use 301 redirects for permanently moved content.
Audit redirects using tools like Screaming Frog, Moz, or Ahrefs, checking for redirect chains or loops.

Broken links and 404 errors negatively impact user experience and SEO.
Use tools like Semrush or Ahrefs to find and fix broken links, either by updating the link or using a 301 redirect to a relevant page.
Last but not least, canonical tags help manage duplicate content by specifying the original URL.
Link building cheat sheet
Now Over to You
In conclusion, to stay in the top ranking positions on Google, you have to regularly run SEO audits and ensure each one of the points above is taken care off.
SEO never really ends – especially off-page.
Need help with getting backlinks to your site?
Don’t hesitate to start your 14-day free trial with Respona to see how we can help.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does it take to see results from organic SEO?
Any SEO strategy is long-term.
While some improvements may be visible relatively quickly, significant results typically take several months of consistent effort.
Is organic SEO still relevant in 2025?
Absolutely.
Despite algorithm updates, organic search engine optimization remains a powerful way to drive targeted traffic to your website.
It’s a cost-effective strategy for building long-term online visibility.
Can I do organic SEO myself, or do I need to hire an expert?
Many aspects of SEO can be learned and implemented independently.
However, complex technical SEO or large-scale campaigns may benefit from the expertise of a professional SEO agency.
How often should I check my website’s SEO performance?
All the time.
Track key metrics like keyword rankings, organic traffic, and backlink profile at least monthly, or even more frequently for competitive niches.
What’s the most important factor in organic SEO?
While all aspects of SEO are important, high-quality, user-focused content remains the most important.
Content that satisfies user intent and provides value is essential for both rankings and engagement.