Some backlinks are way better than others.
Which is why it’s crucial to be able to tell between an awesome potential backlink opportunity and a link farm.
In this article, we’ll cover:
- What exactly is backlink quality analysis
- How to analyze the quality of any link (existing or potential)
- How to disavow bad backlinks
Let’s get started.
Link building cheat sheet
What is Backlink Quality Analysis?
Backlink quality analysis is the process of evaluating the impact a backlink has on your website.
It is part of a larger process of running a backlink audit which focuses on analyzing your entire backlink profile.
To perform backlink quality analysis, you’ll need access to a backlink checker tool, such as Ahrefs or Semrush.
Regularly checking your backlinks should be part of your overall SEO strategy for several reasons.
Which brings us to the next section.
Why Should You Audit Backlinks?
Measure your link building strategy efficiency
First off, without a backlink audit, you can never know whether your off-page SEO strategy is working or not.
A positive link velocity means you’re doing something right, while a negative one (more lost back links than new) means you’re missing out on referral traffic and valuable ranking signals.
Additionally, during link building, carefully checking every single link opportunity before proceeding with a collaboration ensures you don’t get scammed.
And I’m not talking about money.
Sometimes at a first glance, a site looks great but gets zero traffic upon checking it in Ahrefs.
For example, to the untrained eye, Time Business News looks just like any other news portal out there:
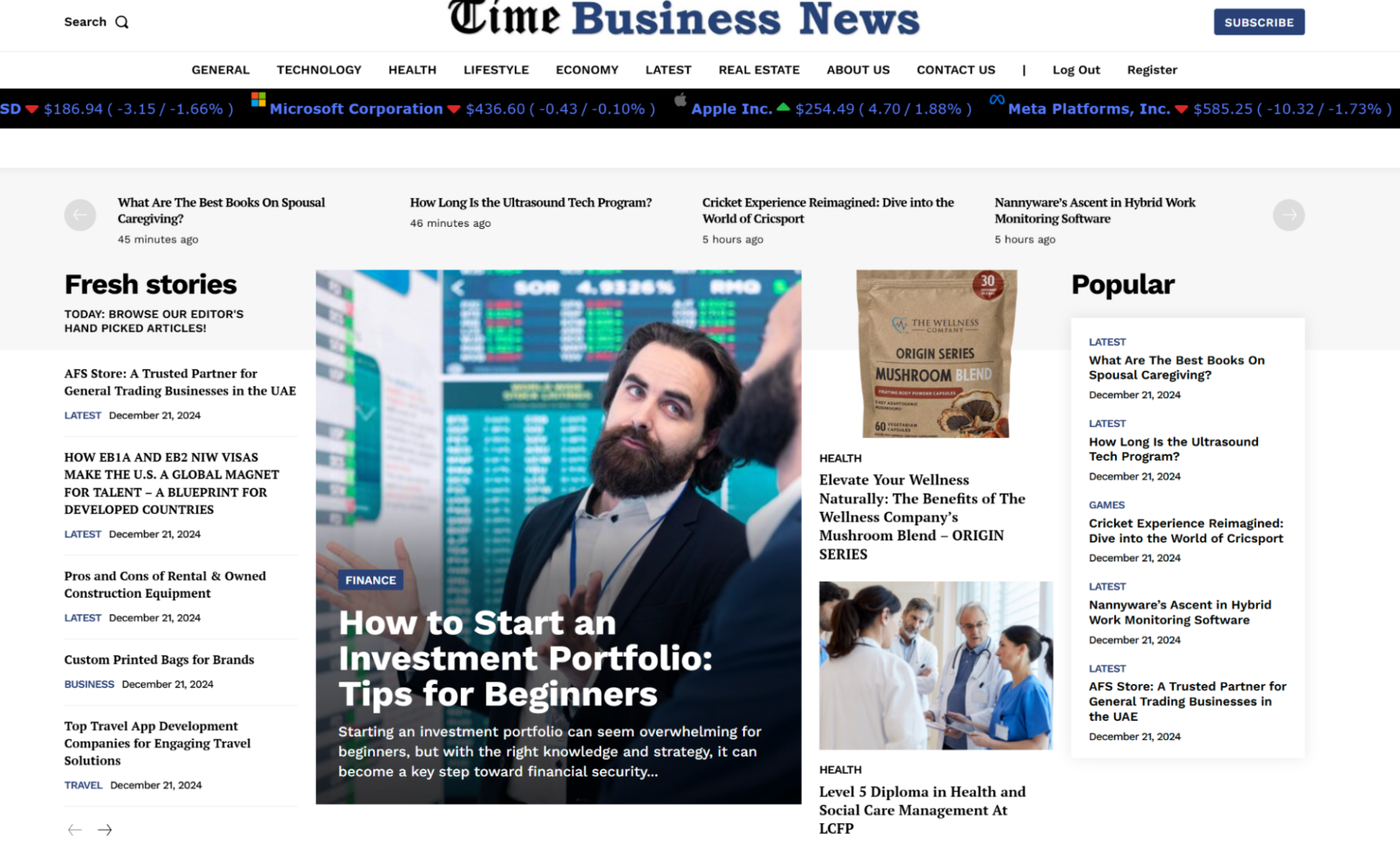
And up to late 2023 was receiving considerable amounts of traffic.
However, it’s actually a link farm, and has since been hit by a Google penalty, which is evidenced by a plummet in organic traffic.
You could only have received this valuable insight by spending some time on backlink analytics.
Identify toxic links
In this same way as evaluating potential linking opportunities, you can use backlink quality analysis to find toxic backlinks from your profile.
You can then either reach out to the bad websites and ask them to remove your link.
If they don’t respond, you can also disavow the links.
This means Google will ignore it and no negative ranking signals will impact your site.
Note: Disavowing backlinks is an advanced option and should be used with caution.
You should only disavow links if your website has received (or you’re certain you will receive) a penalty for link profile manipulation or are certain were a victim of a negative SEO attack.
Find link opportunities
Digging around in backlink reports can also help you spot gaps in your backlink profile.
More specifically, Ahrefs does competitor backlink analysis entirely for you and shows exactly which domains link to your competitors but not to you.
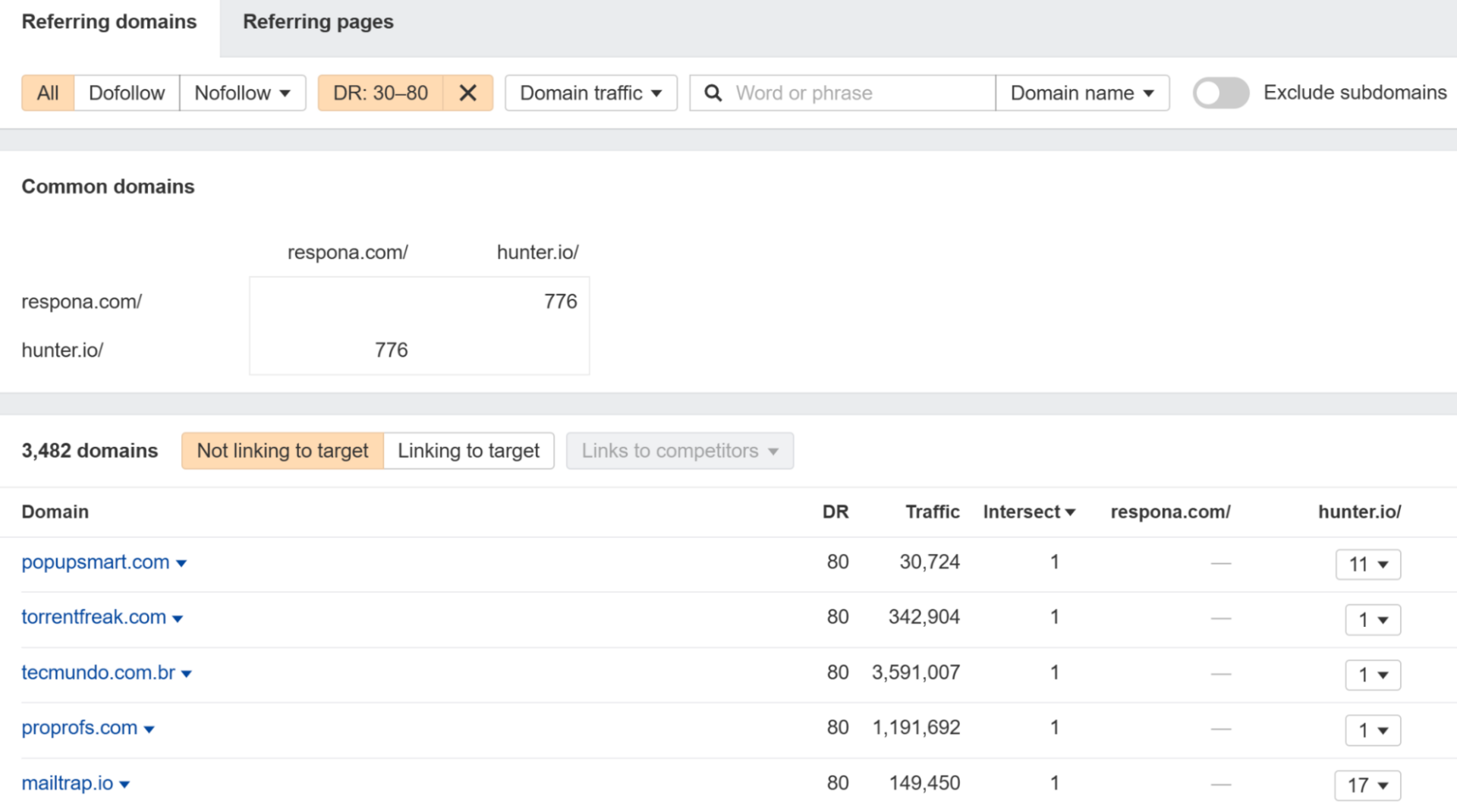
You can export these websites, run a skyscraper technique campaign to try and snatch them for yourself.
Additionally, you filter your top pages by Referring Domains to see exactly how many websites are linking to each page.
Use this (along with other backlink data) to strategize which posts you need to build quality links to next.
1. Referring Domain Quality
The first step in conducting backlink quality analysis is to check the actual website linking to you.
Beyond just clicking on it and visually scanning the page, there are three more things to keep in mind.
DR/DA
Websites with a higher DR/DA are much more sought-after by link builders.
A high domain rating indicates that the website has been around for a while, and has amassed a sizable backlink profile.
So, it can pass on a lot of link juice.
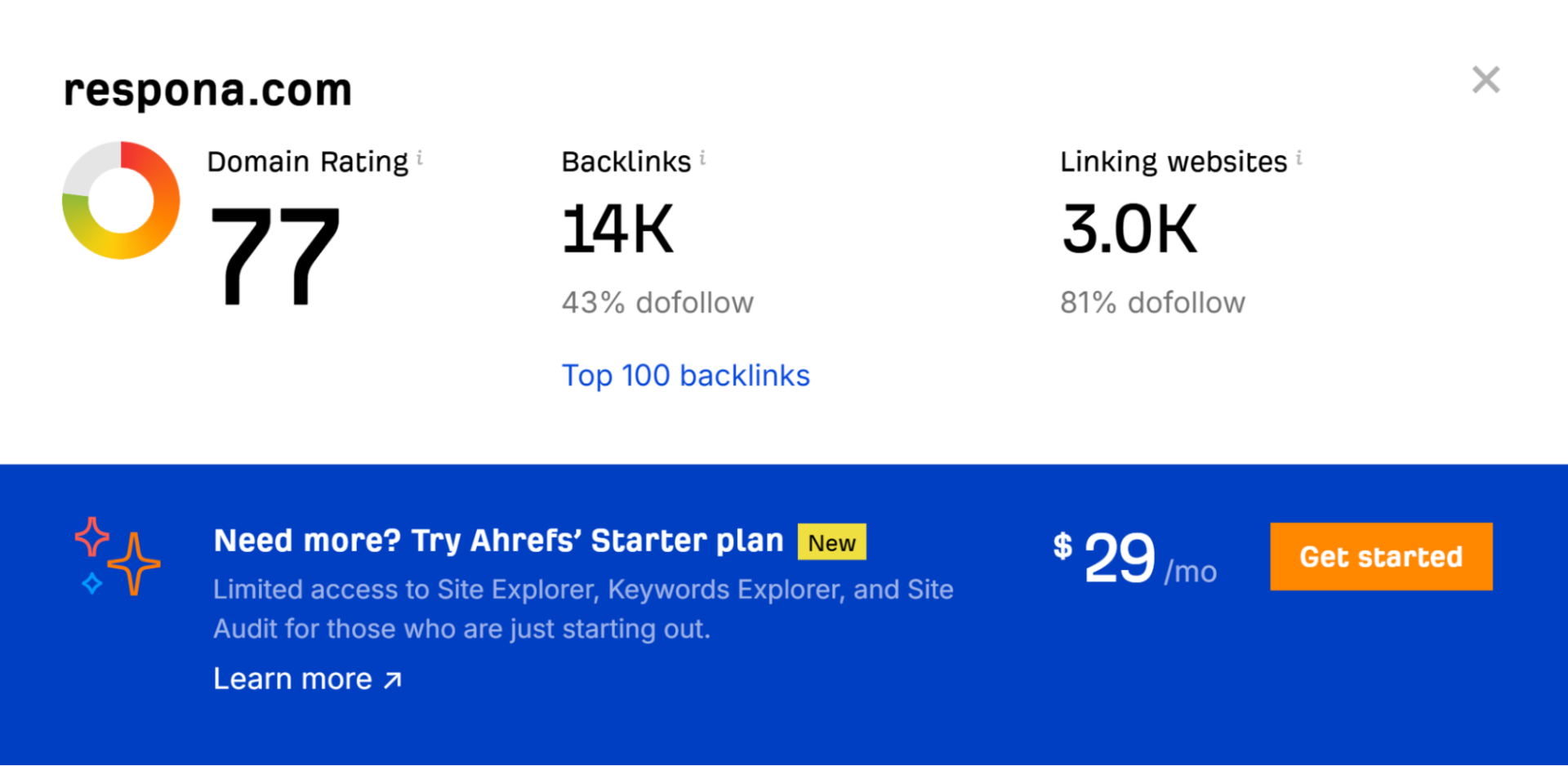
Keep in mind though, that it’s a third-party metric made up by SEO tool providers – it’s not an actual ranking factor.
Because of this, a lot of link farms have a high DR, so you should only look at this merics in combination with traffic and domain age.
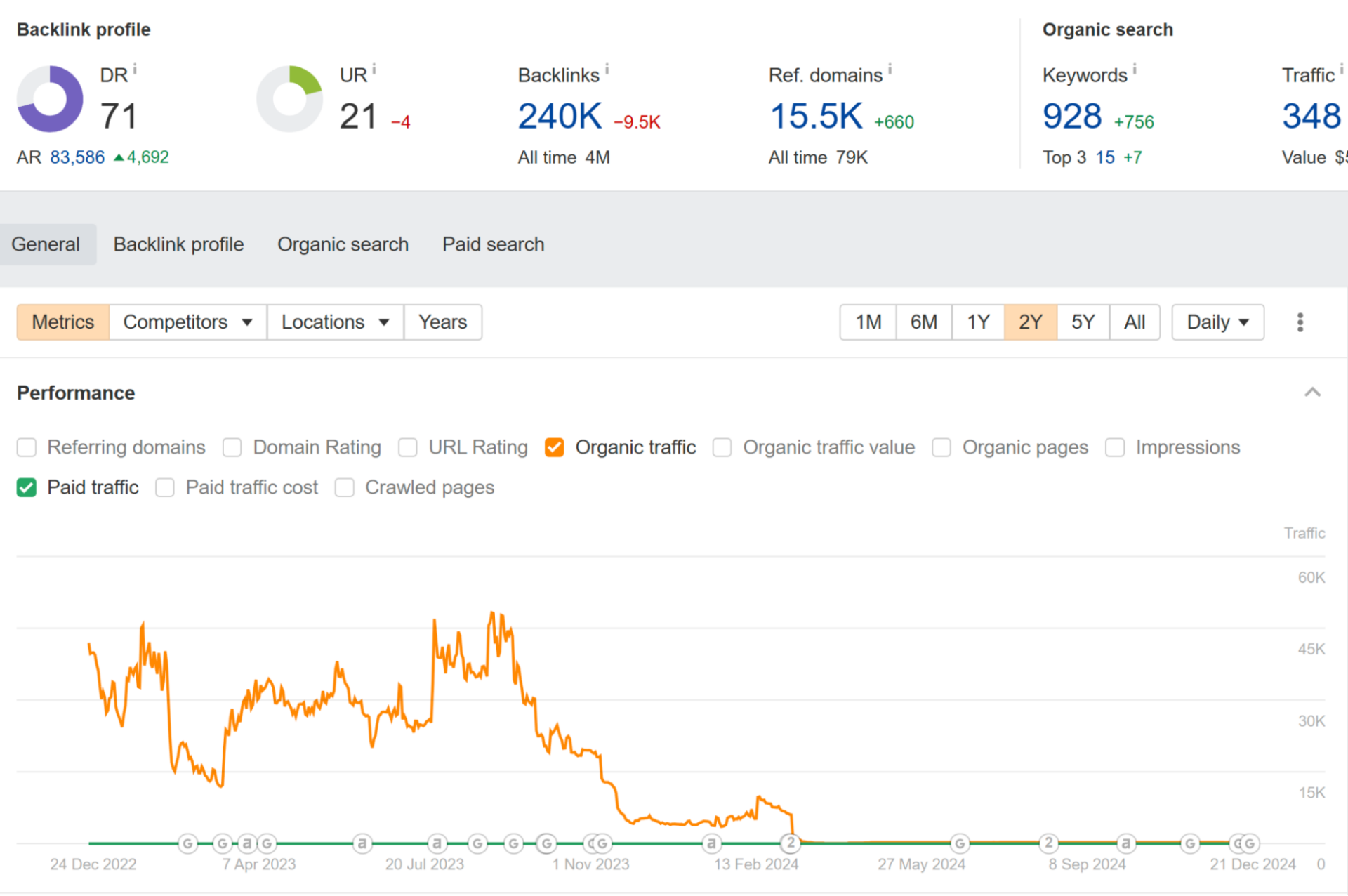
Traffic Chart
Links from domains with more organic traffic are more valuable.
It’s simple math: more people see your link, more click on it, more end up converting.
However, in addition to how much traffic a website is receiving currently, it’s important to be aware of its history.
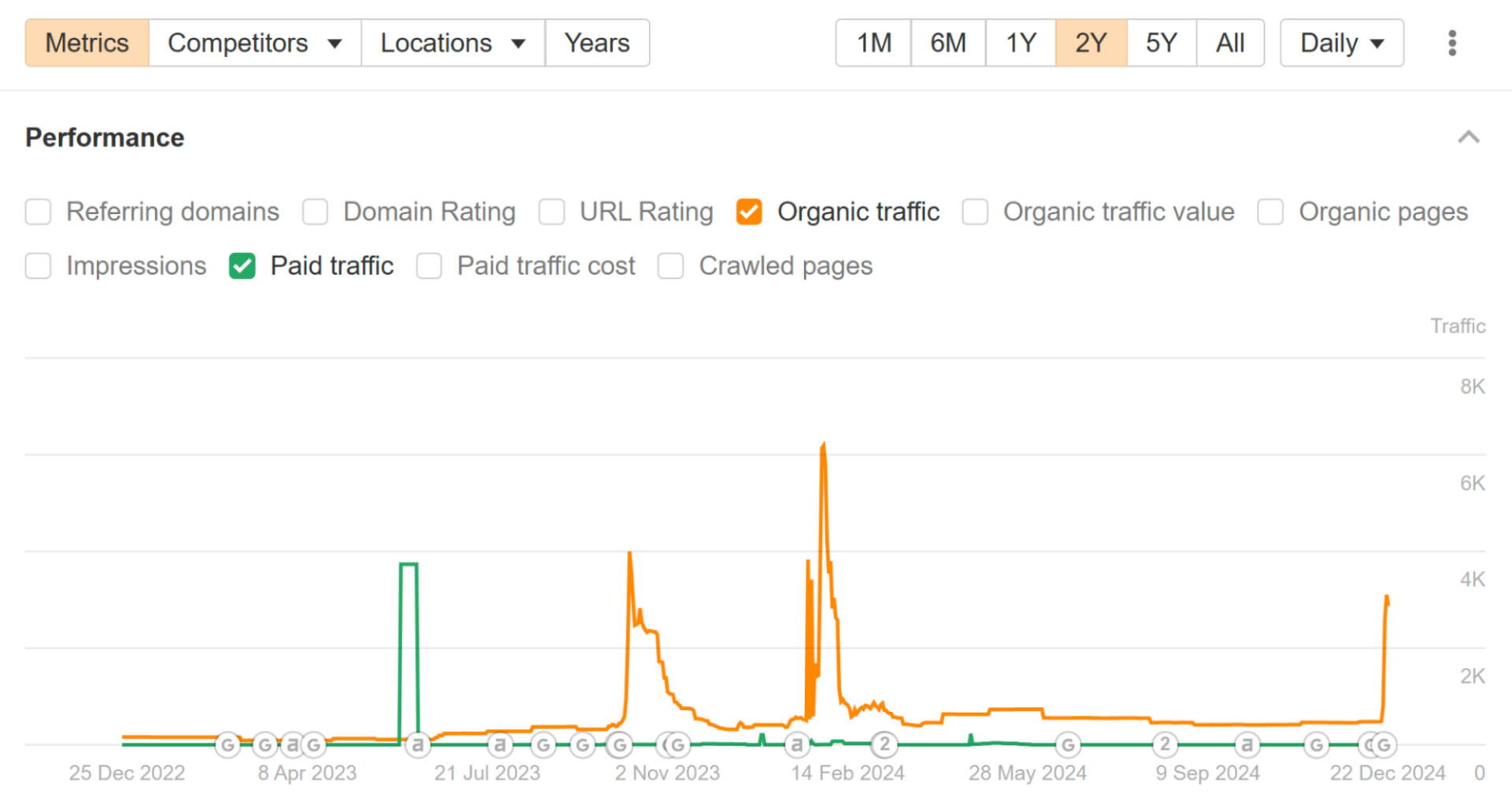
For example, this is the chart of another link farm, Zupyak.
Normally, it receives next to no traffic.
However, it has occasional spikes – so you might be fooled into thinking it’s a legitimate website.
If you’re lucky enough to be in the middle of such a spike, and didn’t bother to check the chart that is.
Age
Older websites have more reputation and contextual backlinks, so typically, an inbound link from an older domain is more valuable.
However, just like domain rating or organic traffic, it means nothing on its own and you need to look at the combination of other factors to determine whether your target would make for a good backlink.
2. Referring Page Quality
So, your target website has a high domain authority and has been getting consistent traffic for years.
The next step of link analysis is to look at your referring page as a whole, not just the section with your link.
Relevance and On-Page Content
Google’s mantra is user experience, so relevance between linked pages is one of the first things the algorithm looks at.
If a local bicycle store randomly links to a PR agency from Hungary, Google will notice.
Beyond relevance, the quality of the actual content matters as well.
Meaning, the site looks and runs nice, and the article is actually helpful to the reader.
Location of the Link
Next, you’re going to find your link on the page.
Since the average website heatmap is “hotter” to the top, so links placed closer to it are more sought after.
Other Links on Page
The more outgoing links a page has, the less “link juice” each one is able to pass on.
While 2-3 external links per post is fine, 10+ is too much, and the SEO benefits of a link from such a page would be minimal.

UR/PA
URL Rating and Page Authority are another set of metrics developed by Ahrefs and Moz respectively.
Similar to DR/DA, they rate a page based on its backlink profile.
This makes them a great link building opportunity as they have a lot of “link juice” flowing through them.
3. Type of Link
There are two types of links – regular (or “in content”), and image.
Text links are more valuable than image links for a very simple reason.
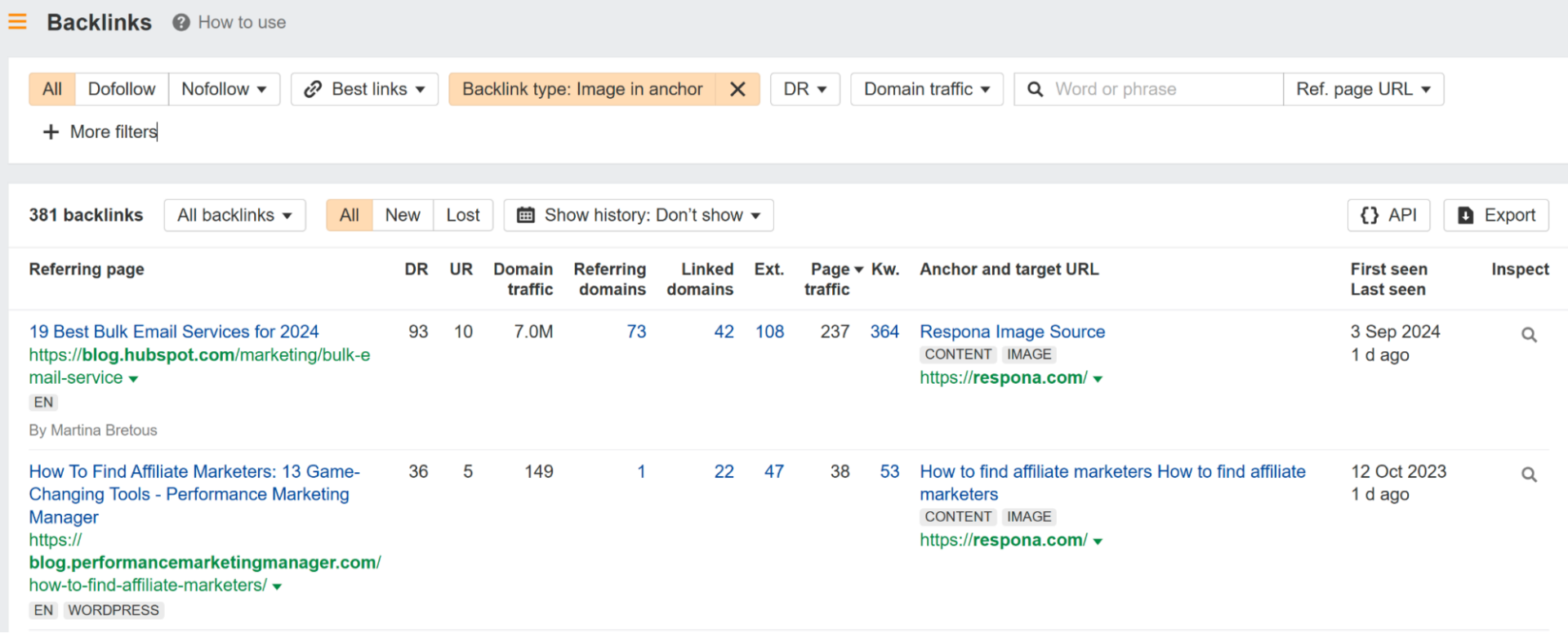
Google is great at reading, but it’s not quite good enough to understand images to the same extent.
Meaning, it can’t always tell whether the image and the link on that image make sense. Yet.
Still, things like infographics make for amazing linkable assets and you should definitely still implement them throughout your content.
4. Dofollow vs Nofollow
While we’re on the topic of link types, there are two more you need to know about: dofollow and nofollow.
These are html tags that you can check by right clicking > inspect > finding your link in the page code.
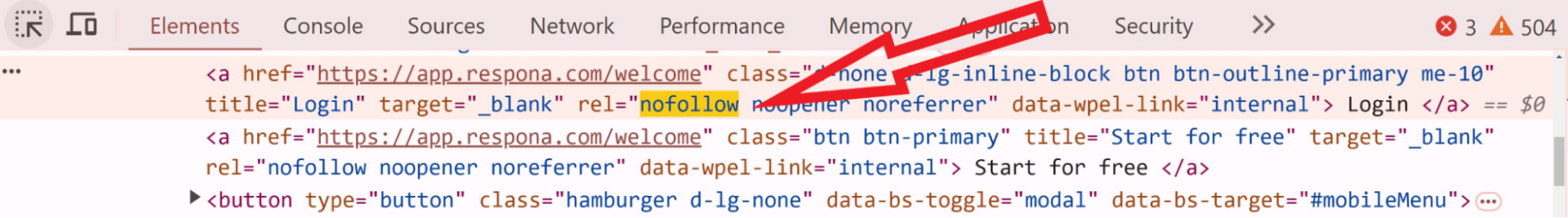
The difference between dofollow and nofollow links is simple:
Nofollow links don’t pass on search engine ranking signals.
If a link has neither of these attributes, it’s treated as dofollow by default.
When building backlinks, it’s best to always negotiate for dofollow links.
However, a healthy link profile has a mix of both types of links.
Even though nofollow links don’t pass ranking signals, they can still bring you highly targeted traffic, so don’t neglect them.
There are also “sponsored” and “ugc“ tags – they act similar to “nofollow”, and are used to mark paid or user-generated content.
5. Is it Reciprocal?
One more factor that helps determine link quality is the way in which it has been acquired.
If it’s an organic link that you got passively or through an ABC link exchange, great.
If you got it as part of a direct link exchange, however, the value of it drops drastically.
Google treats them as part of a link scheme and is really good at spotting them.
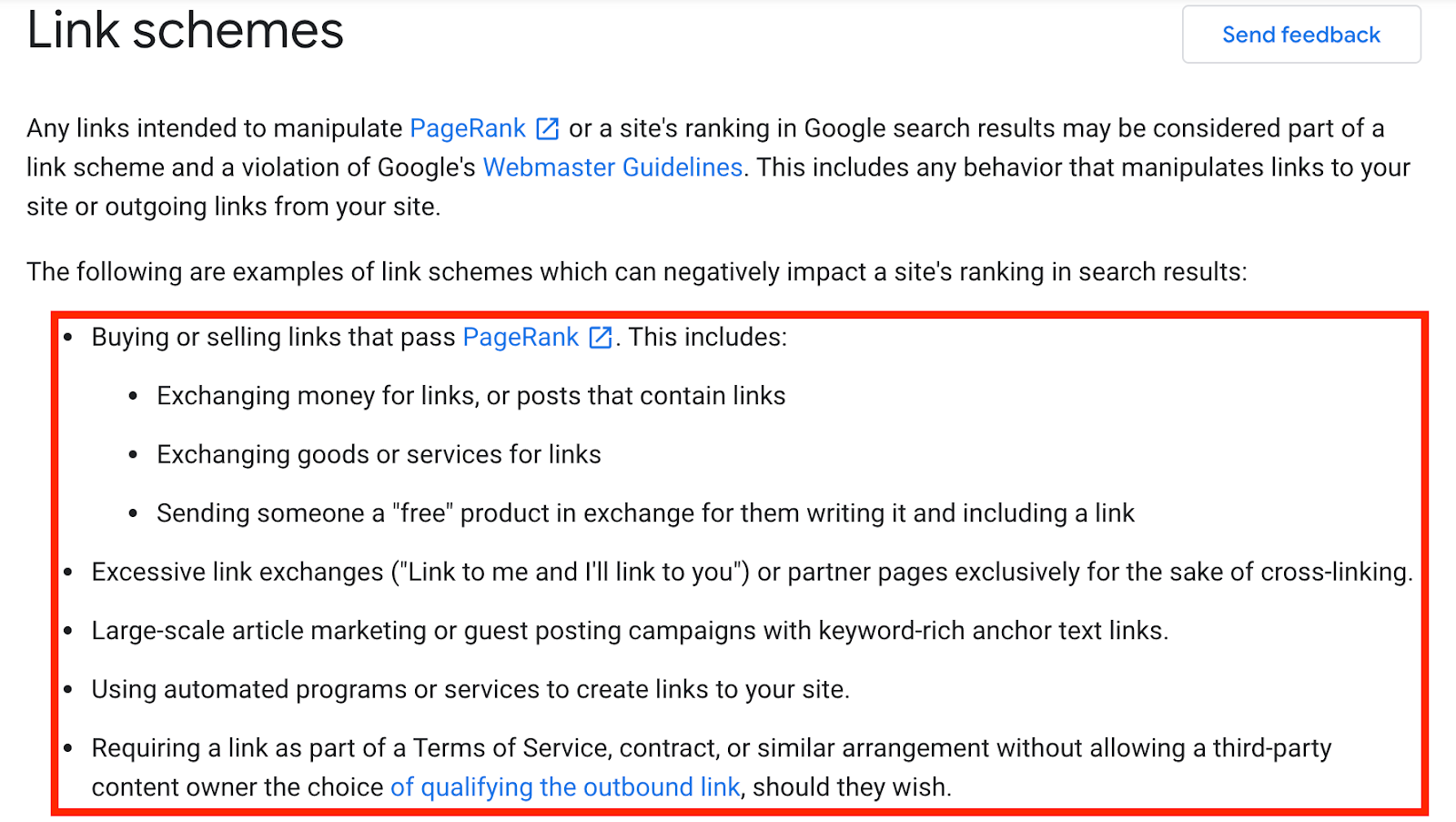
What happens next is these links get devalued by the algorithm, meaning they don’t send any ranking signals at all.
But reciprocal links aren’t always a bad thing.
Which leads us to the next section.
6. Use Common Sense
Remember, you can only see the link’s true value if you analyze it holistically. There is no be-all-end-all condition under which a link is good.
For example, if it’s a reciprocal link (that should be bad) but it’s coming from a page that gets thousands of traffic that matches your buyer persona perfectly, is it worth it?
Like this mention of Respona on Backlinko:
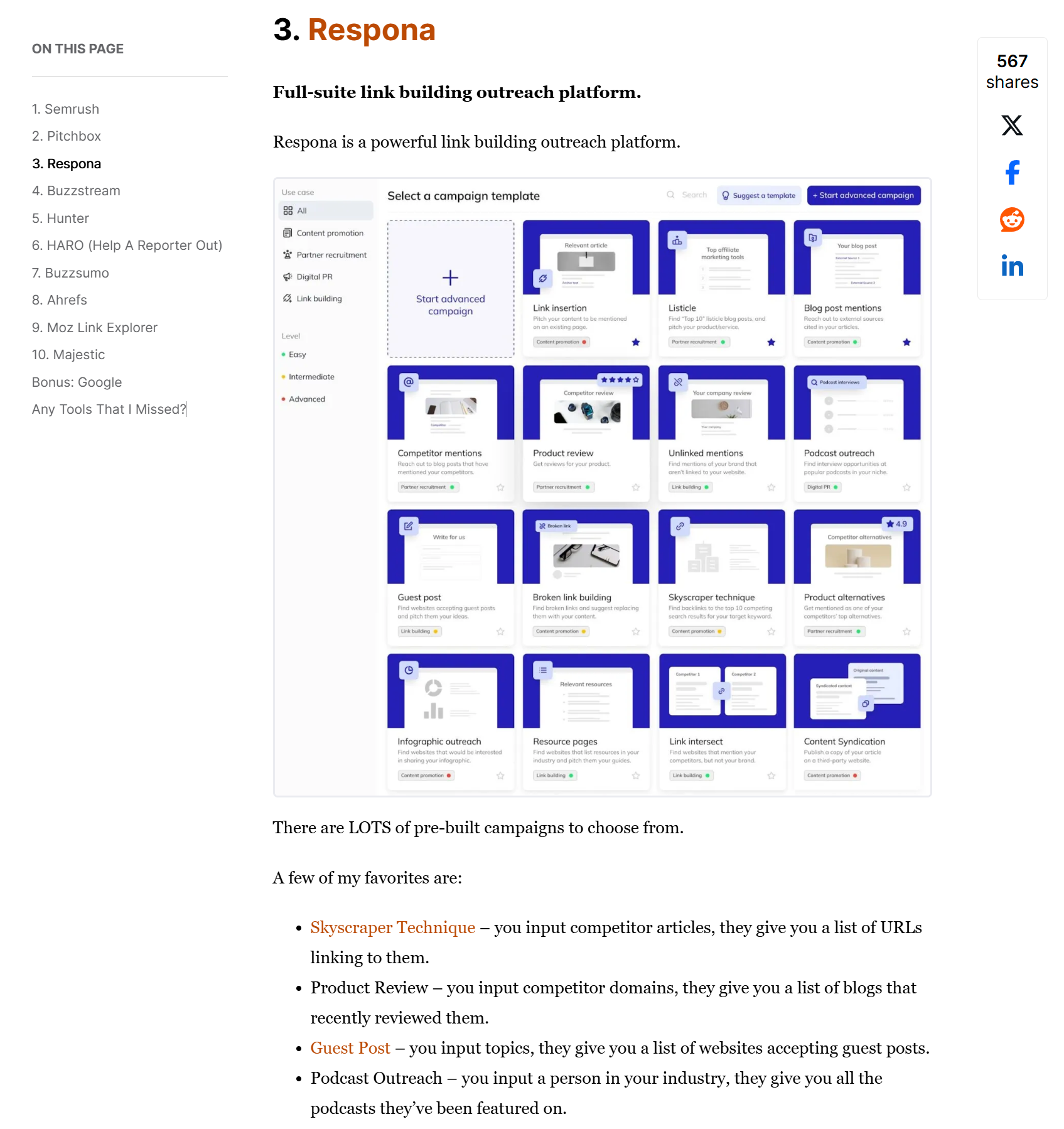
I’d say it’s still worth getting – even if there are 50 other links on the page.
It won’t impact your rankings (although one from a site like Backlinko absolutely will), but will bring you business, which is more important.
What to Do with Toxic Backlinks
So, during your backlink quality analysis you found a bunch of links you don’t like.
Like links from a bunch of random domains with the same content, or even an adult site.
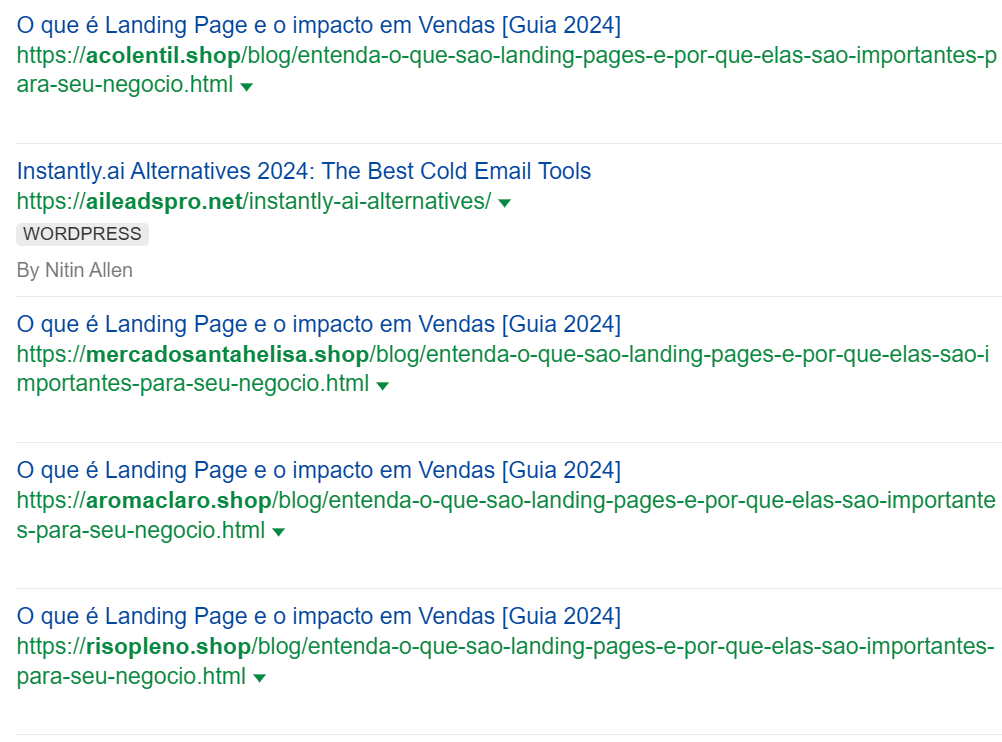
What should you do with them?
Nothing.
Really.
It’s 2025, and Google’s AI is competent enough to tell that they’re just spam.
Don’t worry, they won’t affect your rankings at all.
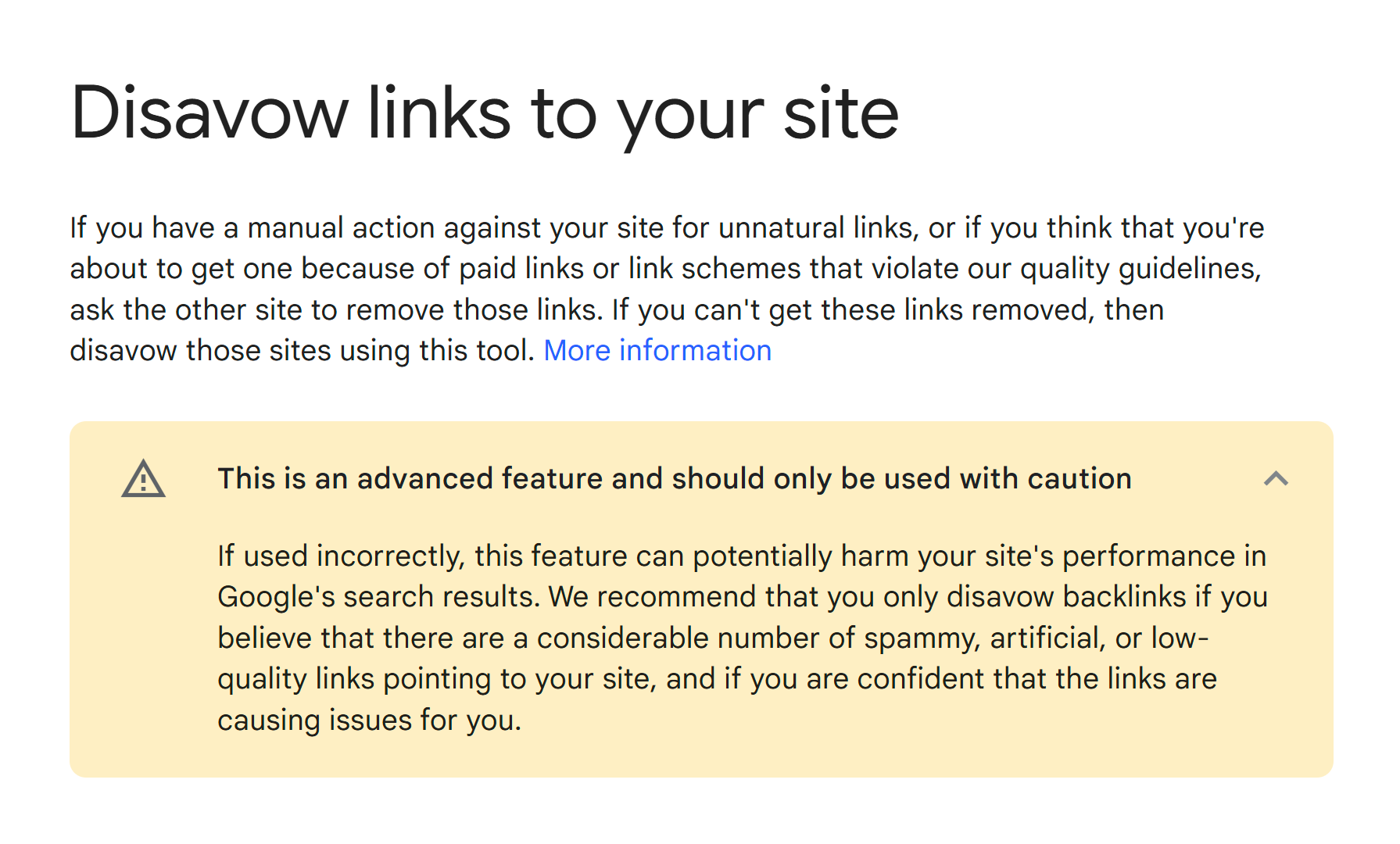
“But what about the disavow tool?” – You ask.
Yes, it exists, but you should only ever disavow backlinks if your website has (or is going to) receive a penalty.
If you haven’t bought links or haven’t worked with link farms, there’s no need to use it.
Even Google warns that incorrect use of the tool may harm your site’s performance in search enine results:
Now Over to You
In conclusion, a good link is:
- From a relevant, high quality website that generates consistent traffic
- On a page with few other outbound links (and many inbound)
- A dofollow text link
- Non-reciprocal
Need help getting more of these?
Don’t hesitate to start your 14-day free trial with Respona to see how we can help.
Link building cheat sheet
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the most important factor in determining backlink quality?
Relevance.
A high- uality backlink comes from a website and page that are topically relevant to your own.
This signals to search engines that the link is natural and valuable for users seeking information on that specific topic.
How do I know if a backlink is “toxic”?
Toxic backlinks often come from spammy, low-quality websites, link farms, or sites with irrelevant content.
They may also involve unnatural anchor text or be part of a link scheme.
These links can negatively impact your search rankings.
What’s the difference between Domain Rating (DR) and URL Rating (UR)?
Both are third-party metrics that estimate the strength of a website or webpage’s backlink profile.
DR (Ahrefs) measures the overall strength of a domain, while UR focuses on the strength of a specific page.
Both are helpful indicators but should be considered alongside other quality factors.
Should I always aim for “dofollow” links?
While dofollow links pass link equity and contribute to ranking, a natural link profile includes a mix of both dofollow and nofollow links.
Nofollow links can still drive valuable traffic and contribute to brand awareness, so they shouldn’t be entirely disregarded.
When should I use the disavow tool?
The disavow tool should be used sparingly and only when you have a significant toxic backlink problem that is likely harming your site’s rankings and you’ve been unable to have them removed directly.
Incorrect use can negatively impact your search engine optimization.