SEO may seem like a bunch of technical mumbo-jumbo to the uninitiated.
But in reality, it’s not nearly as complicated as it might seem to the untrained eye.
In this article, we’ll teach you how to do SEO on your own – even if you have zero prior experience.
We’ll walk you through:
- How to find keywords people are searching for & optimize content for them
- How to improve your online presence through link building, local SEO, and getting user reviews
- 3 easy steps to top-notch technical SEO
Nothing that requires a degree or the help of an SEO agency.
Let’s get started.
Link building cheat sheet
Keyword Research
Keyword research and optimization are SEO basics.
It’s the most important step in optimizing your website since it involves finding terms that your target audience searches for, and providing them with content that answers their questions (or offers a product that solves a particular pain point).
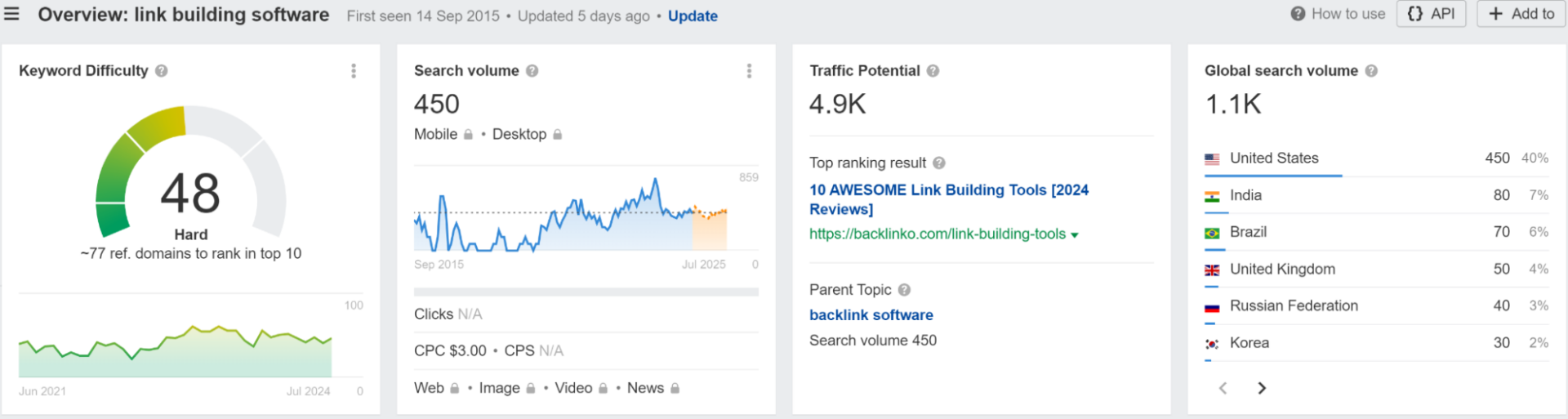
The beauty of this SEO strategy is that this information is readily available – all you need is a keyword tracking tool like Ahrefs or Semrush.
Keywords are the foundation of SEO, and with countless options, it’s crucial to choose the right ones for your SaaS business.
Effective keyword research helps you attract the right audience and stand out in a crowded market.
Types of Keywords
Keywords generally fall into two categories:
- Long-tail keywords: These are longer, more specific phrases with lower search volume but higher conversion rates (e.g., “digital marketing automation for e-commerce”).
- Short-tail keywords: These are broader terms with higher search volume but more competition (e.g., “email marketing”).
Long-tail keywords are usually much easier to rank for, so you should generally aim for quick wins.
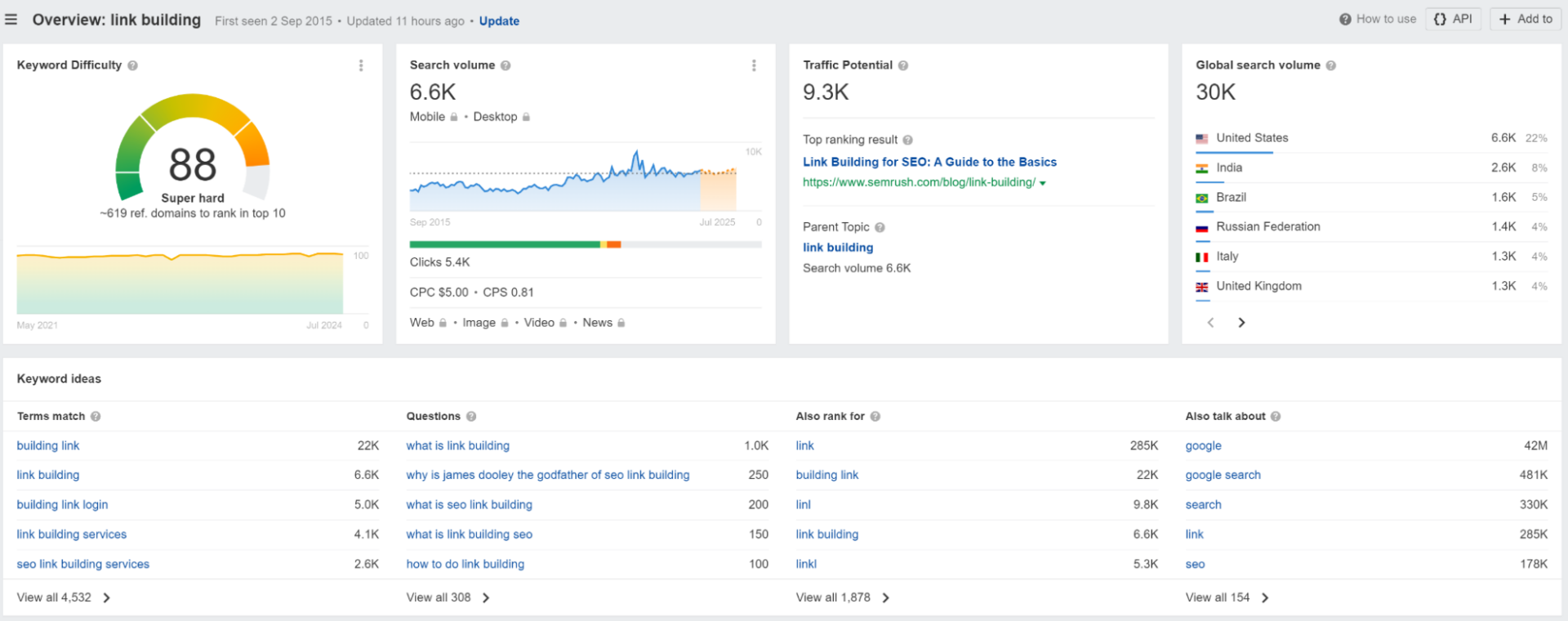
Short-tail ones are much more competitive, so to rank for these terms, you will most likely need to build a LOT of backlinks.
Or, at least more than your competitors.
User Intent
Understanding user intent is key to choosing the right keywords.
Here are the four main types:
- Navigational: Users seeking a specific website (e.g., “Facebook login”).
- Informational: Users looking for information (e.g., “how to improve email open rates”).
- Transactional: Users ready to make a purchase (e.g., “Respona free trial”).
- Commercial: Users researching and comparing products (e.g., “best link building software”).
Each type of user intent requires a different kind of content.
Keyword Metrics
Prioritize keywords based on:
- Difficulty: How hard it is to rank for a keyword.
- Traffic potential: Estimated number of visits a top-ranking page might receive.
- CPC (Cost-Per-Click): How much advertisers pay per click, indicating commercial intent.
Ideally, you want to go for keywords with low difficulty and high traffic potential, but the “easy” keywords typically have less than 500 traffic.
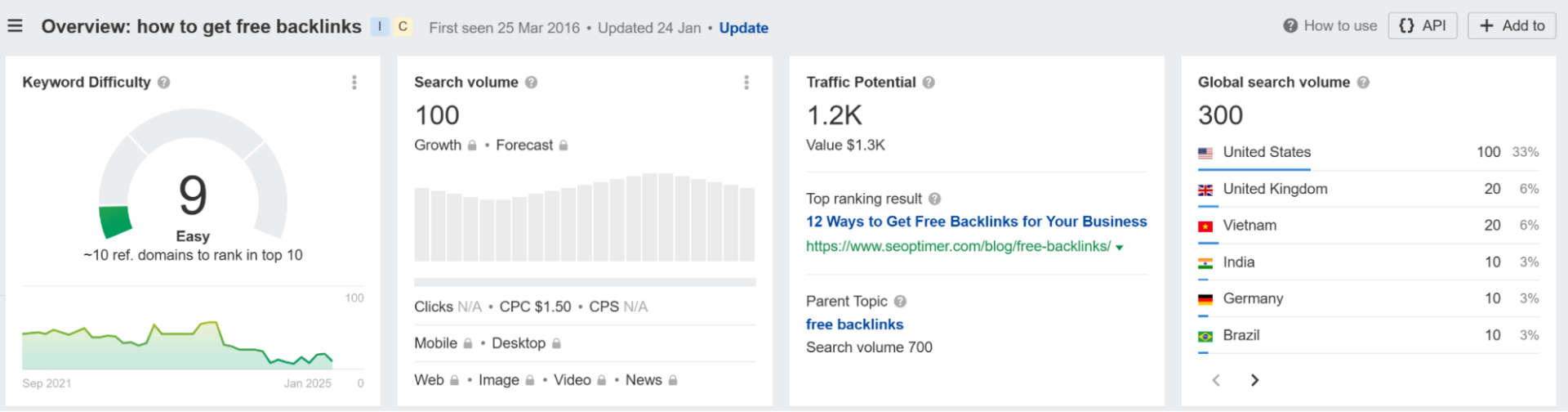
Still, by consistently publishing SEO content that covers them, you’ll be able to relatively easily increase organic traffic – little by little.
Additionally, low-difficulty long-tail keywords usually drive much more targeted traffic than general short-tail ones.
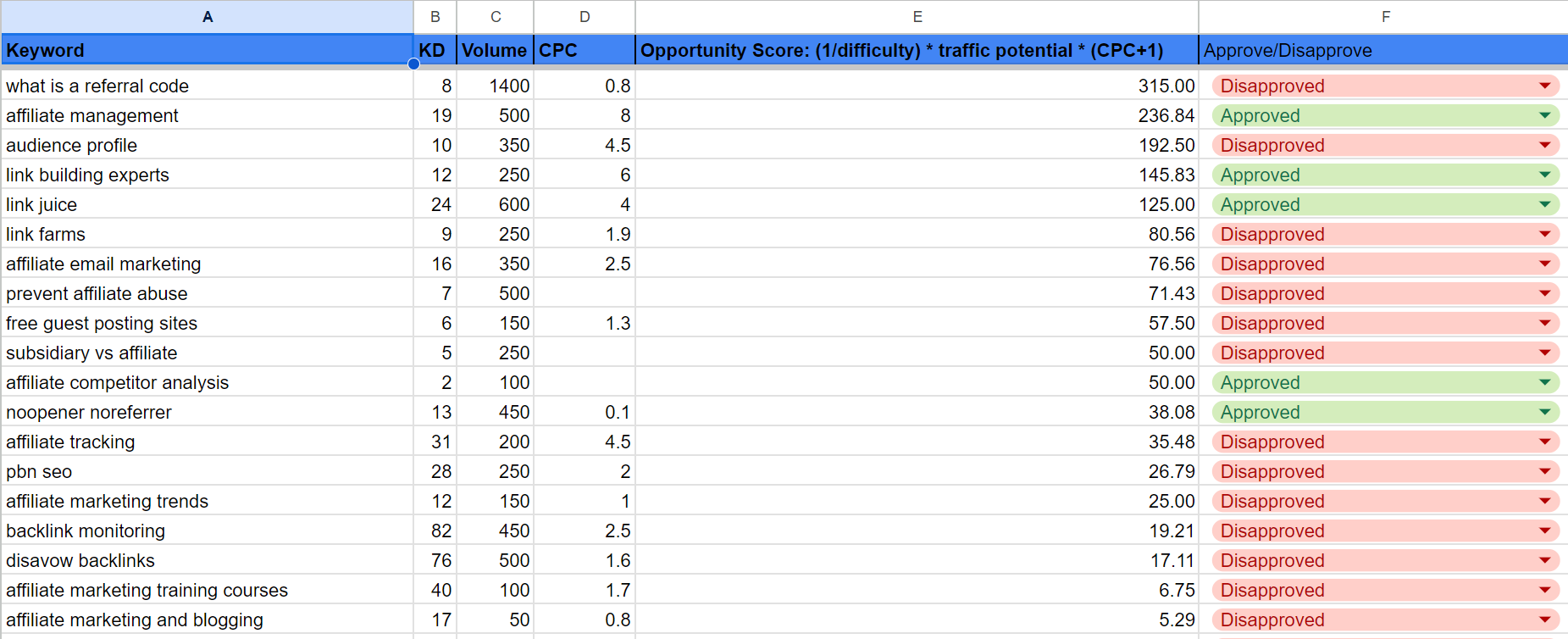
Use our Opportunity Score formula to quickly assess keywords:
(1/difficulty) * traffic potential * (CPC+1) = Opportunity Score
This will help you quickly sift through hundreds of keywords by prioritizing low-difficulty, high traffic potential opportunities.
You’ll still have to manually pick ones that are the most relevant for you, however.
How to Do Keyword Research with Ahrefs
First, identify core terms describing your product (e.g., “link building software”).
Use Ahrefs to evaluate search volume, competition, and relevance.
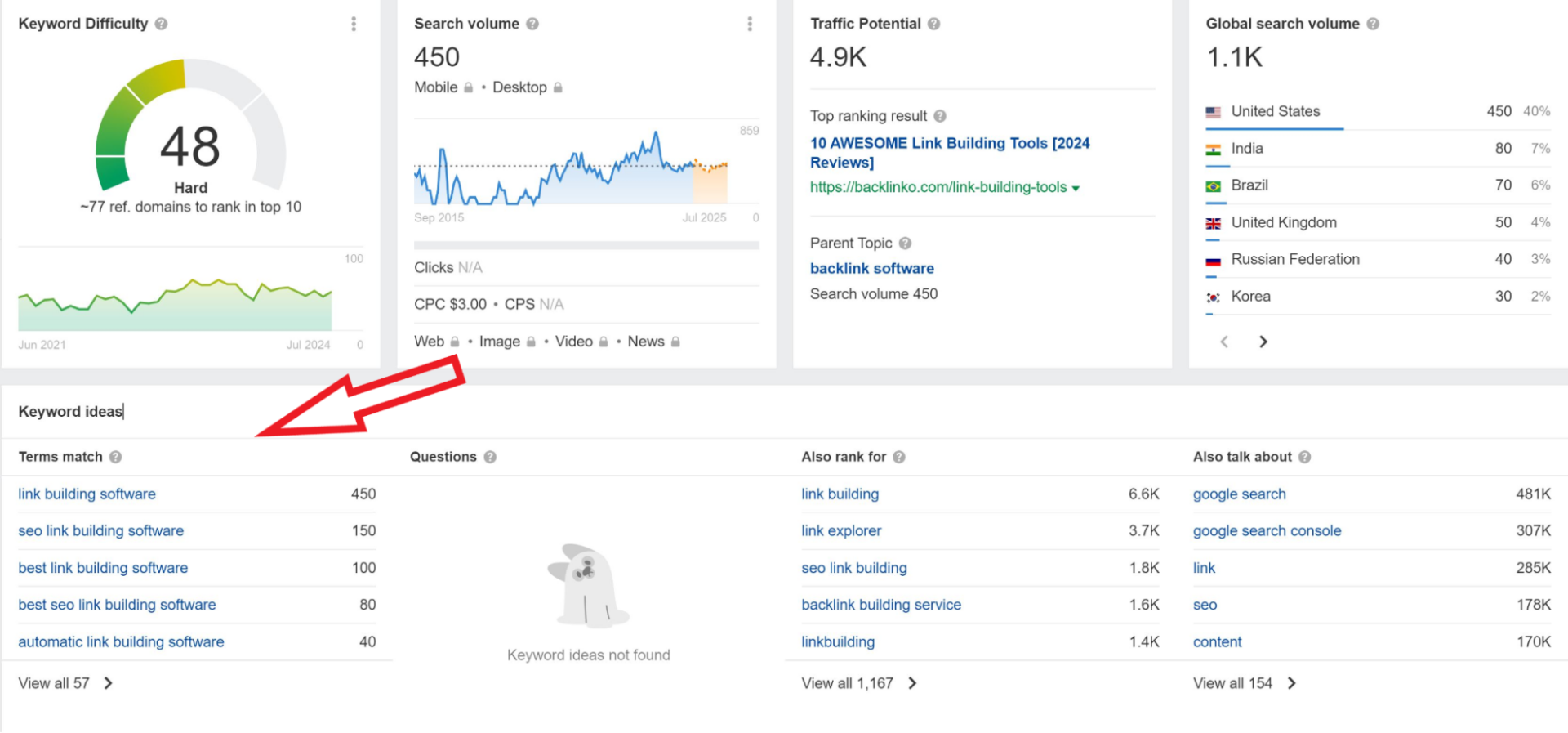
Next, explore related terms to enrich your content (e.g., “link building outreach“).
Use Ahrefs’ keyword explorer for suggestions.
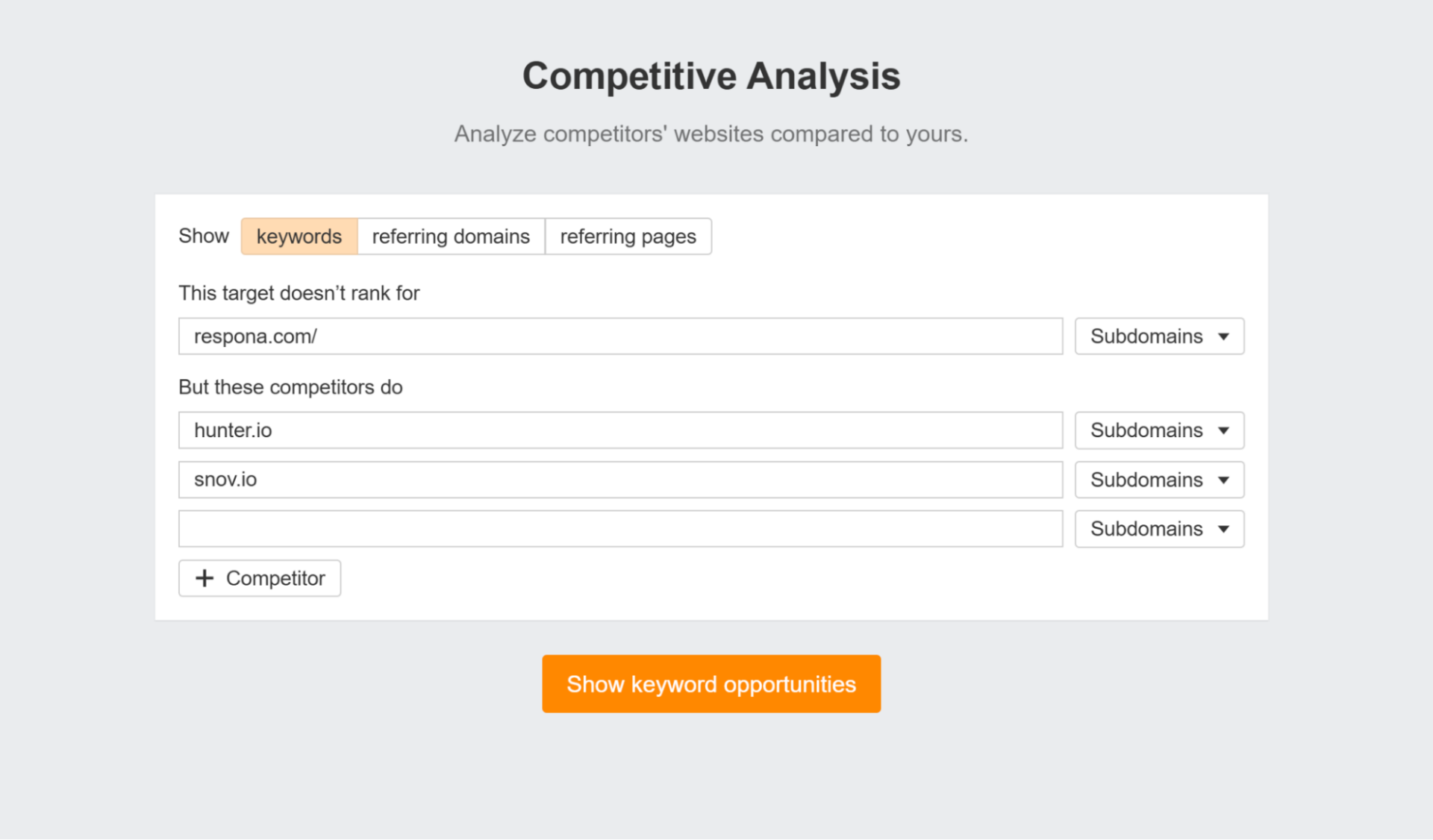
The next step is to find keyword gaps between you and your competitors.
Meaning, keywords they are ranking for, but you aren’t.
For this, Ahrefs has a neat competitive analysis feature – besides keywords, it also helps you identify backlink gaps.
Once you have your list of keywords, sort it using the opportunity score formula we mentioned above.
Then, review and refine the list based on relevance and your own judgment.
The next step is to create pages covering these keywords and optimizing them.
Create and & Optimize Content
To optimize on-page content with keywords, you can use SEO tools like SurferSEO and MarketMuse.
They provide suggestions as to which keyword variations need to be included in the content (and how many times) based on every other blog post ranking in the top 10 for the same term.
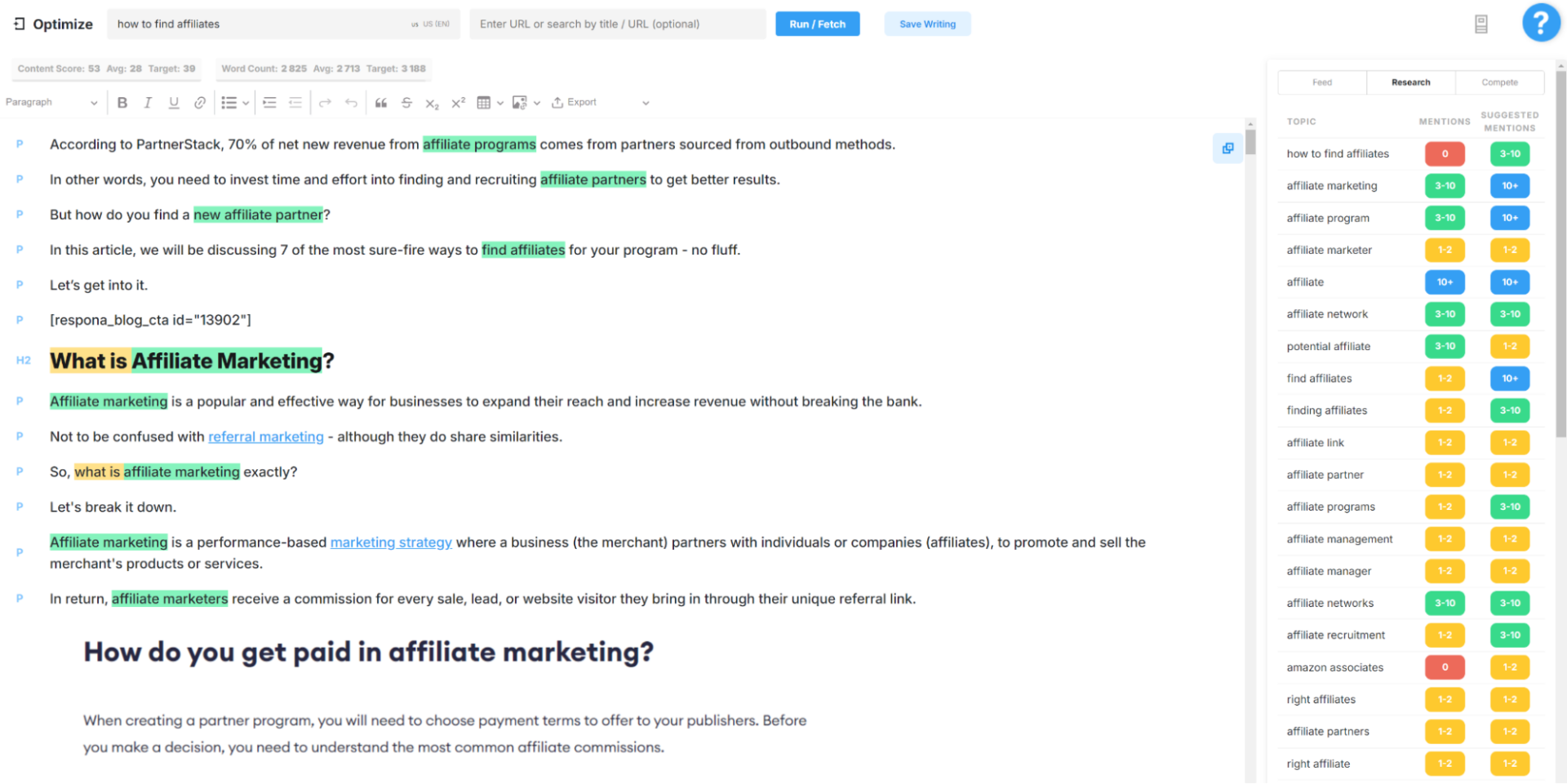
Besides the written content itself, there are other on-page elements that need to be keyword optimized.
This involves:
Header Tags
Header tags structure your content and signal its importance to search engines.
Use your primary keyword or a close variant in your H1 tag.
This is the main title of your page and should clearly communicate what the content is about. Only use one H1 tag per page.
Use secondary keywords and related phrases in your H2 and H3 tags to break down your content into logical sections and sub-sections.
Think of these as subheadings that guide the reader (and search engines) through your content. Use variations of your main keyword, LSI keywords, and related phrases.
Title Tag & Meta Description
The title tag and description are HTML elements that summarize your page’s content in search results.
They are crucial for attracting clicks from search engine users.
- Meta Title: Aim for a concise and compelling title that includes your primary keyword. Keep it under 60 characters to avoid truncation on search result pages.
- Meta Description: Write a brief, informative description (under 160 characters) that expands on your meta title and encourages users to click through to your page. Include your primary keyword and a call to action.
Image SEO
Images can enhance your content and improve SEO.
Always add descriptive alt text to your images.
This helps search engines understand the content of your images and is also beneficial for visually impaired users.

Use your target keyword where relevant, but keep the description natural and accurate.
Use descriptive file names for your images, incorporating your target keyword if possible.
Avoid generic names like “image1.jpg.”
Compress your images to reduce file size and improve page load speed.
Internal Links
Internal links connect different pages within your website.
They help users navigate your site and distribute link equity (ranking power) to different pages.
Link to relevant pages within your site using anchor text that includes your target keyword or a related phrase.
All of your main pages should be accessible from the header or footer.
Ensure that all pages on your website are accessible within three clicks or less from the homepage.
This improves crawlability and user experience.
A shallow crawl depth means search engines can easily find and index all your content.
Regularly check for and fix any broken internal links.
Broken links hurt user experience and can negatively impact your SEO.
Use a tool like Ahrefs, Semrush or the Broken Link Checker to find broken links on your site.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO is focused on securing traffic from other resources.
The lion’s share of off-page SEO is link building, as well as optimizing your site for local searches and getting customer reviews.
Build Backlinks
Backlinks are essential for SEO because they have a massive impact on your rankings.
They pass “link juice” (PageRank), a core part of Google’s search engine ranking algorithm.
More link juice = better rankings.
So, how do you get these valuable backlinks?
Let’s explore.
We recommend a mix of strategies, including guest posting, link insertion, the skyscraper technique, product reviews, and broken link building.
Let’s walk through a guest posting campaign using Respona as an example.
Respona streamlines link building with dedicated campaign templates, automating prospecting, contact discovery, and outreach.
Here’s how it works:
Tell Respona the topics you want to cover and provide writing samples.
This info is used for finding guest posting opportunities and email personalization.
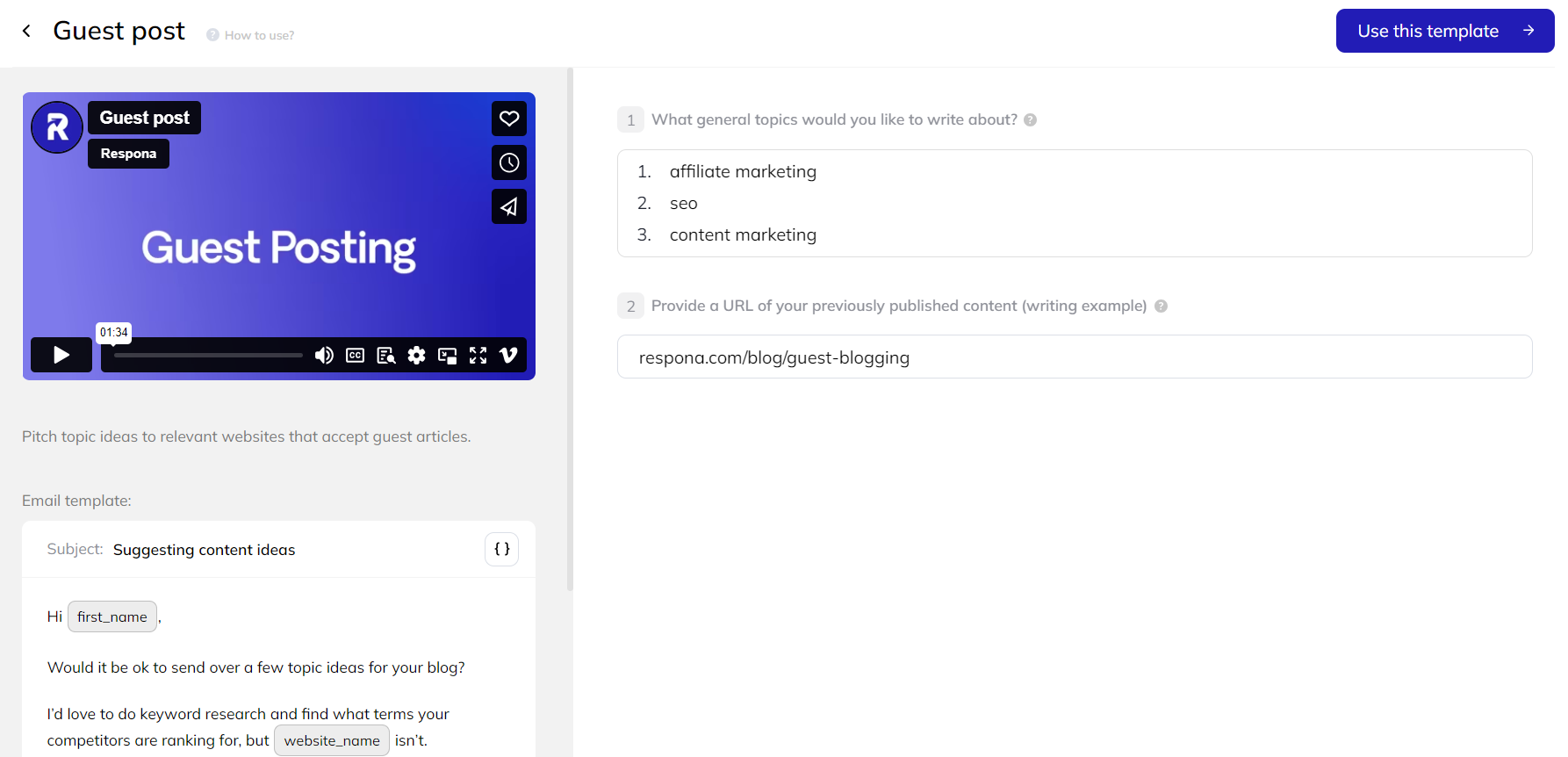
Click “Use this template” to get started.
Respona provides a pre-built sequence you can customize.
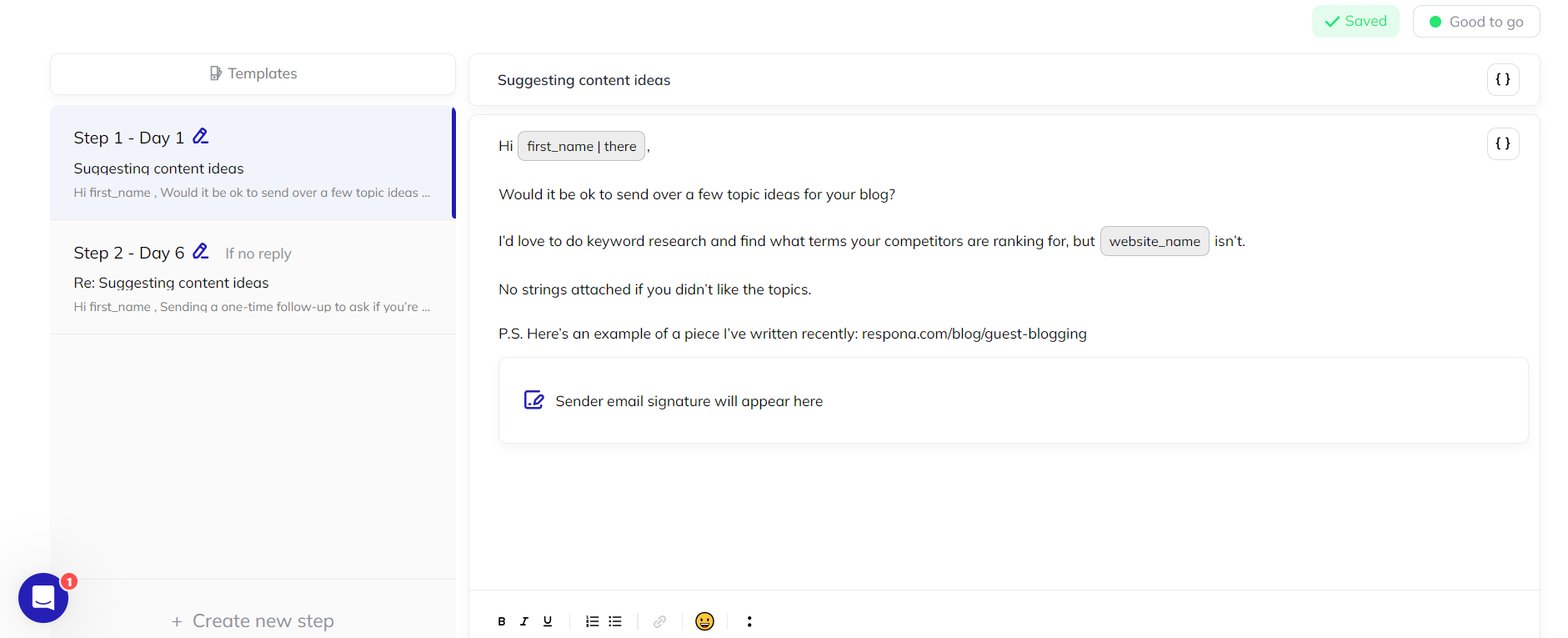
Change the wording, add unsubscribe links, check for spam words, and adjust follow-up timing.
The AI-powered “Icebreaker” variable is a game-changer – it generates personalized opening lines for each email, going beyond a generic “first_name.”
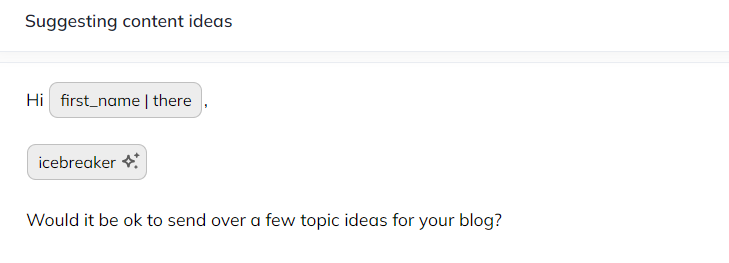
It can even come up with guest post topics all on its own!
The next step is to find guest posting opportunities.
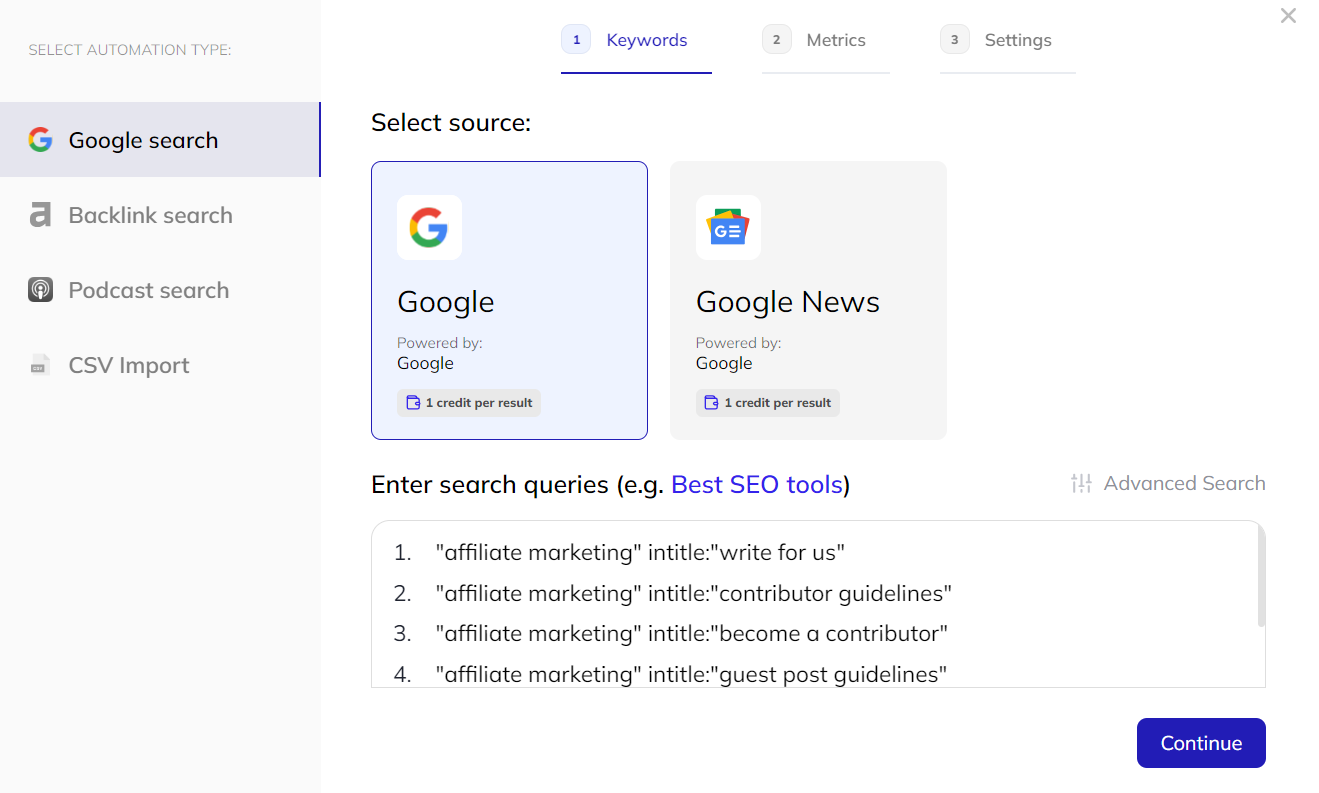
Respona automatically uses search operators with common “write for us” variations and your keywords to run multiple Google searches.
You can refine results with SEO filters.
It also automatically finds contact information for content marketing and SEO managers.
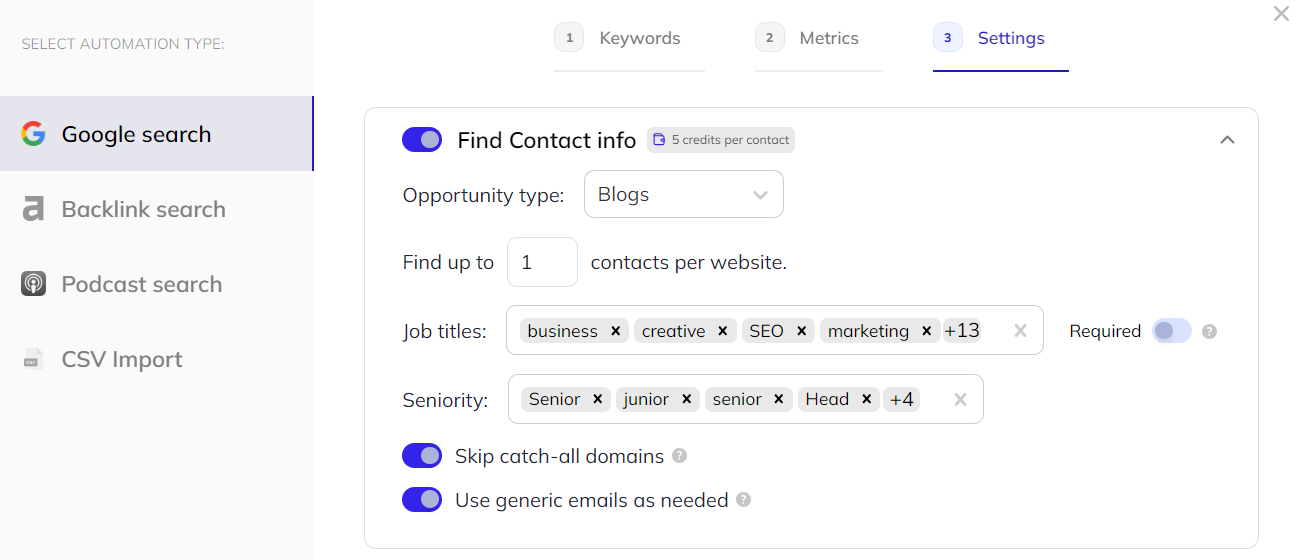
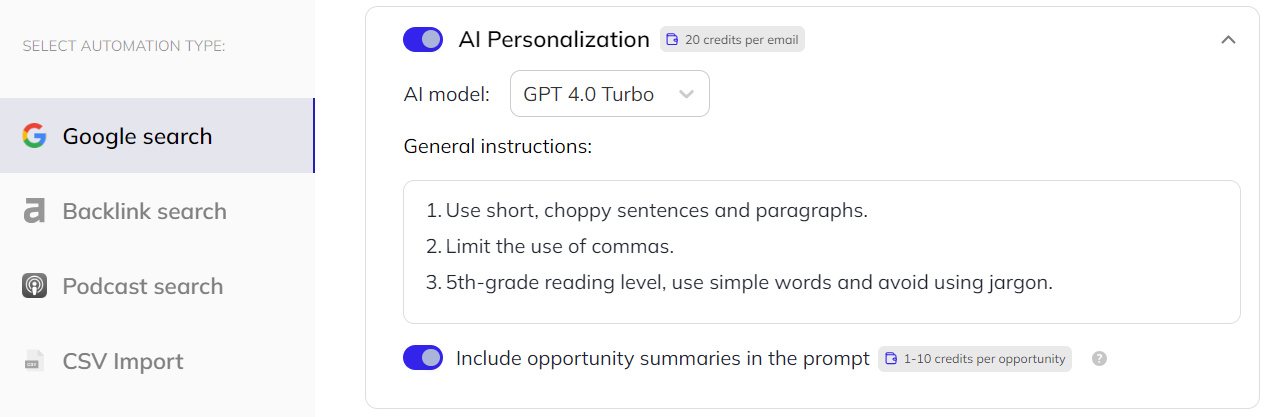
This screen is also where you can provide guidelines for the AI variables, specify the desired tone, feed it examples, and outline requirements for each personalization.
It can also “read” your prospects’ pages and pull something from their content into personalizations.
Once you start the search, Respona will find opportunities, contact details, and personalize emails using AI, in real-time.
Once it’s done, all you have to do is review & launch the campaign.
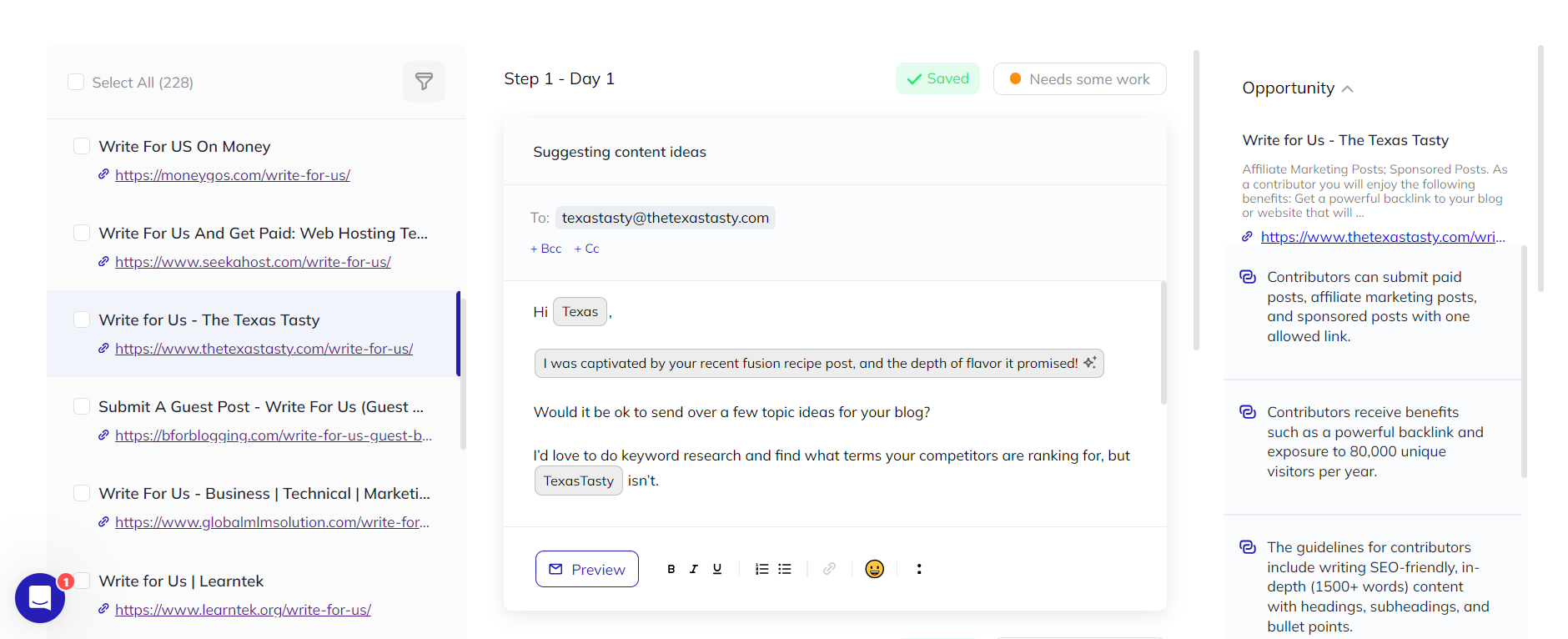
Carefully examine all variables (standard and AI-generated), and add manual personalizations where necessary.
Before sending, the tool also performs pre-launch checks for unsubscribes, recent contacts, and empty placeholders.
Once your campaign is live, monitor responses and start writing those guest posts!
Link building can be a huge time investment, but Respona makes it indefinitely easier.
Local SEO
This section is more applicable for businesses with a physical location.
Local SEO you appear in local search engine results and on Google Maps, connecting you with nearby customers actively looking for what you offer.
Think about it: when someone searches “coffee shops near me,” you want to be one of the results.
Your Google Business Profile is the cornerstone of local SEO efforts.
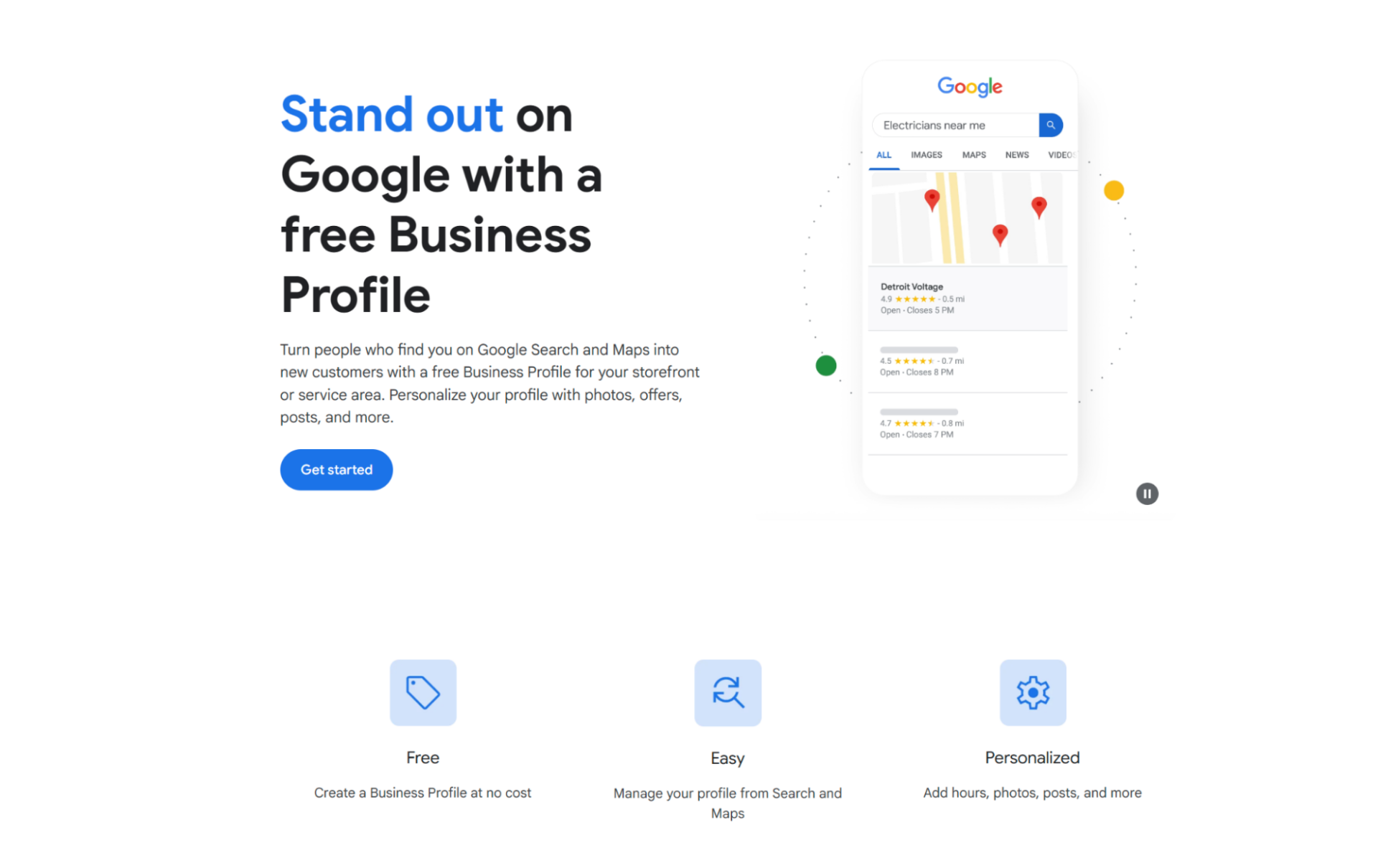
Claim and fully complete it.
Accuracy and detail are important: name, address, phone number , website, hours, categories, and a well-written description.
Use relevant keywords naturally within your description.
Customer Reviews
Customer reviews are essential for building trust and influencing purchasing decisions.
While Google reviews are important, explore other relevant platforms like Yelp, G2, industry-specific review sites, and even social media.
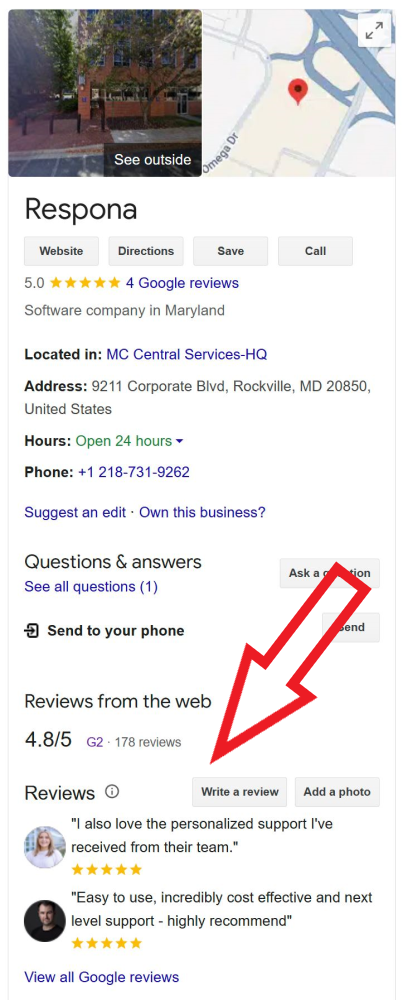
Make it as easy as possible for customers to leave reviews.
Provide direct links to your review profiles on your website, in email signatures, and on receipts.
Respond to both positive and negative reviews in a professional and timely manner. Thank customers for their feedback and address any concerns they raise. T
Technical SEO
Now, I know I mentioned that there won’t be any technical mumbo-jumbo – but bear with me.
Yes, there are some areas of technical SEO that require deeper knowledge and even coding.
But I only included the most important – and simplest parts of it.
After all, you can’t completely forego technical SEO as its speed is also a major ranking factor.
Core Web Vitals & Mobile Optimization
These metrics measure how quickly your web pages load and how stable they are.
Fast loading times and a good user experience are important for both visitors and search engine rankings.
Google provides a free tool called PageSpeed Insights that analyzes your Core Web Vitals.
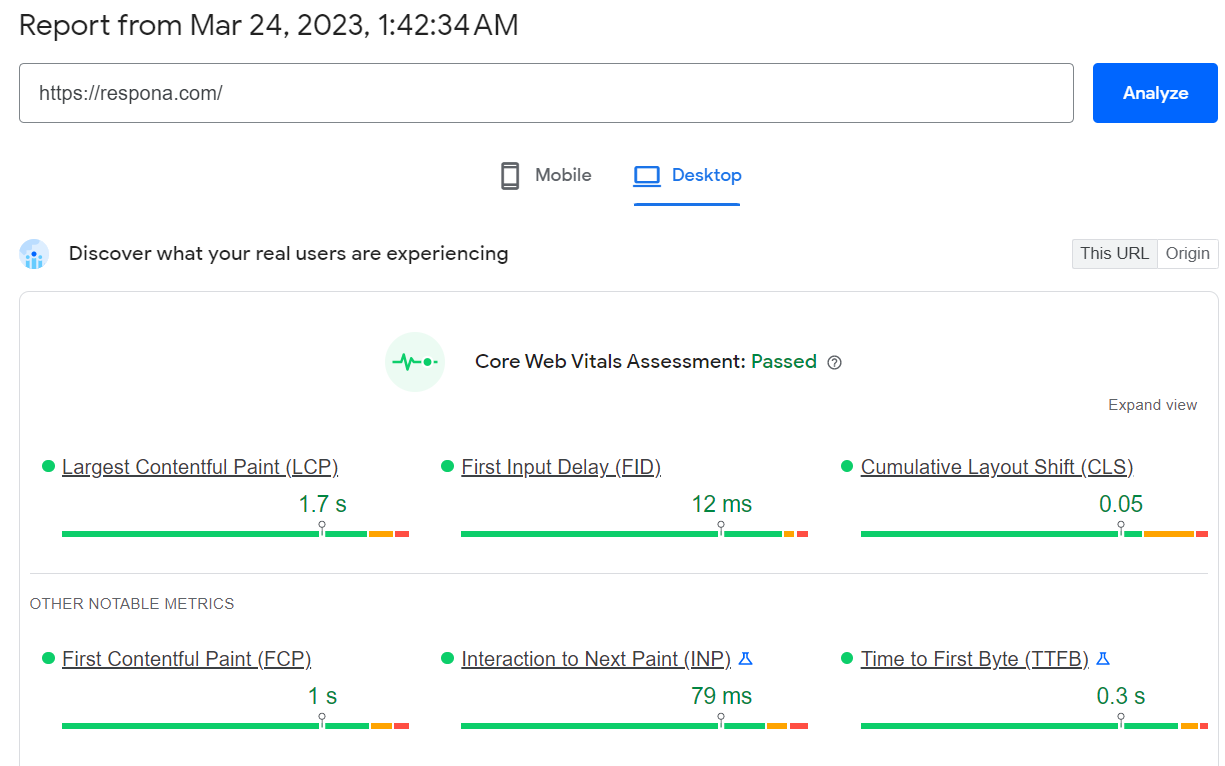
It tells you exactly what’s wrong with your site’s speed and how to fix it.
Your website must also work well on mobile devices.
Google also offers a Mobile-Friendly Test to check if your website meets mobile requirements.
Crawlability
Crawlability refers to how easily search engines can access and index the content on your website.
These elements help:
Sitemap: A sitemap is a file that lists all the important pages on your website. It helps search engines discover and index your content more efficiently. There are many free tools available that can automatically generate a sitemap for you.
Robots.txt: This file tells search engines which parts of your website they should not crawl. This is useful for excluding duplicate content or private pages.
Canonical tags: If you have multiple pages with similar content, canonical tags tell search engines which version is the primary one, preventing duplicate content issues.
Manual indexing requests: each time you publish a new page, you can submit it for indexing in Google Search Console manually. This way, you don’t have to wait for the next time your site gets crawled.
Redirects
Redirects send users and search engines from one URL to another.
They are necessary when you change a page’s URL or delete a page.
Redirects prevent “page not found” errors and ensure users are taken to the correct content.
Link building cheat sheet
Now Over to You
By this point you have a pretty good idea on how to do SEO on your own as a small business owner.
The most time-consuming aspects of it are constant content production, and, of course link building – because these tasks never truly end.
You must always be on the hunt for new keywords and backlink opportunities to keep getting that sweet, sweet traffic.
Need help growing your link profile?
Don’t hesitate to start your 14-day free trial with Respona to see it in action.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I really do SEO optimization on my own?
Yes, absolutely!
While SEO success can seem difficult to achieve, the basics are manageable for anyone willing to learn.
Consistent effort and patience are key to seeing results.
What are the most important things to focus on for DIY SEO?
SEO best practices include keyword research, content creation, on-page optimization, link building, and technical SEO tactics.
These are the core elements for improving your website’s visibility.
What tools do I need for DIY SEO?
Use Google Search Console and Google Analytics for website monitoring.
Ahrefs or Semrush (paid) are great for keyword research and running a site audit.
PageSpeed Insights and the Mobile-Friendly Test are also helpful.
How long does it take to see results from DIY SEO?
Search engine optimization is a long-term game.
Expect to see noticeable improvements after several months of consistent work.
Where can I learn more about SEO?
Explore online guides from Google Search Central Moz, Search Engine Land, and Backlinko.
Follow SEO blogs and consider online courses for deeper knowledge.






