Search Engine Optimization
What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO refers to all of your online activities aimed to increase your website’s rankings in organic search results.
There are three types of SEO: on-page, off-page, and technical.
We will dive deeper into the specific SEO strategies of all three types, but for now, let’s answer a simple but important question.
Why is SEO a Big Deal?
SEO is a big deal for a very simple reason: it helps you generate organic traffic to your website and show up high in search engine results pages.
Paid advertising is also a popular way of achieving the same goal but comes with two serious disadvantages: running ads can be a lot more expensive than SEO, and people are naturally skeptical of any links that have an “AD” tag on them.
Taking care of all aspects of SEO can take a tremendous amount of time and resources, but once your website starts getting traction organically, it does so without any additional input from your side – essentially generating free traffic for you.
Getting to that point isn’t free, of course, but once you’re past it, there’s no stopping you.
The Types of Search Engine Optimization
As we already mentioned, there are three sides to search engine optimization: on-page, off-page, and technical.
On-Page
Surprise-surprise, on-page SEO refers to all of your on-page activities.
The bulk of on-page SEO lies in creating high-quality content, identifying and targeting keywords that are relevant to your business, and optimizing images.
Despite technically not being on your page, title and meta tags also classify as on-page SEO.
Off-Page
Off-page SEO mostly revolves around getting backlinks and mentions of your website, on other sites.
Technical
Technical SEO has two goals: ensuring that your website runs well and is easily crawled by search engines.
The process of technical optimization starts even before your website goes live and includes everything from using a good template/coding your own to making sure all of your internal links work properly.
Search Engine Optimization Example
Here is an example of our own page ranking at the #1 spot thanks to proper off-page and on-page optimization:
How to Optimize Your Website For Search Engines?
Now, let’s take a look at the most important SEO techniques you should employ to improve your website’s online visibility.
Site Speed
The speed at which your website loads and runs can have a tremendous impact on your rankings.
Especially mobile optimization ever since Google has switched to mobile-first indexing.
Even if your website has a flawless desktop version but your mobile optimization is lacking, it may lead to diminished rankings in SERPs.
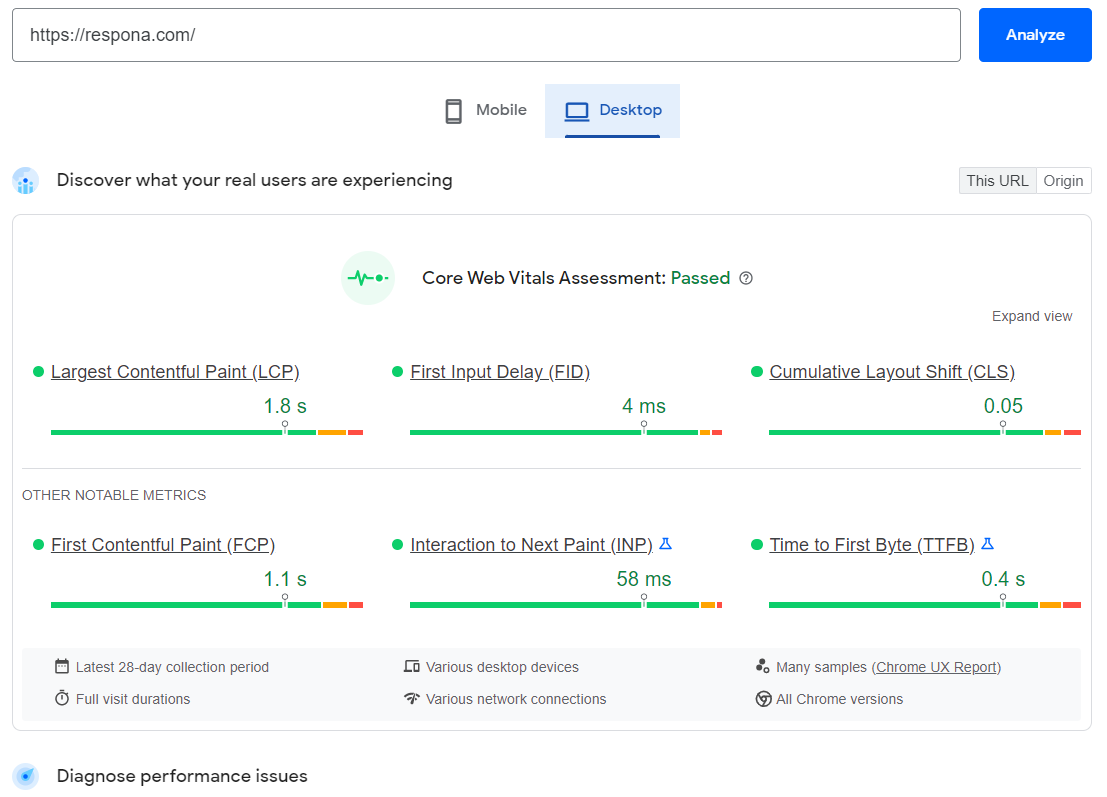
There is no single way to improve site speed as each resource’s architecture and hierarchy is different, but one great tool to measure your site speed and provide suggestions as to which areas could be improved is PageSpeed Insights.
Quality Content
High-quality content should always be at the forefront of your SEO strategy.
After all, what is there to optimize if you have no content?
A website that only has a homepage and a couple of landing pages is unlikely to show up high in search results as opposed to one that has an extensive blog that covers a wide range of keywords and helps the audience solve multiple problems.
Again, there is no be-all-end-all formula for producing high-quality content as each audience’s needs and wants are different.
However, the two most important aspects of a good content piece are:
- It helps your users solve a very real problem
- It targets a keyword that your audience is actually searching for
Which brings us to the next section.
Keyword Research and Optimization
To optimize content, you need to know which keywords and phrases your audience are actually searching for.
You can use a variety of tools for this purpose, but two popular choices are:
- Ahrefs for keyword research
- MarketMuse or SurferSEO for keyword optimization
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are little snippets of text that appear along with your title tags on SERPs and give users a small preview of your page before they actually click on your link.

To optimize your meta descriptions for SEO, make sure that they include the primary keyword for your page (or some variation of it), and are no longer than 160 characters in order to avoid truncation.
Title Tags
As the name suggests, the title tag is your page’s title that displays along with your meta description in SERPs.
And much like the meta description, to optimize title tags, you need to make sure that they are short enough to not get truncated (50-60 characters), include your primary keyword, and are unique for each page to avoid duplicate content issues.
Header Tags
Header tags are HTML tags that are used to indicate the headings and subheadings of a web page.
The most important header tag is the <h1> tag, which is used to indicate the primary heading of a web page.
Other header tags include the <h2> tag, which is used to indicate a secondary heading, and the <h3> tag, which is used to indicate a tertiary heading.
These go up all the way up to h6, although anything after h3 is rarely used.
Optimizing header tags is fairly straightforward: all you need to do is make sure there is only one h1 tag per page, and your headers include both your primary and secondary keywords.
Link Tags
Link tags, also commonly referred to as attributes, are HTML elements that change the way links on your site behave.
There are dozens of link attributes that exist, however, we will only discuss the 4 most important ones for SEO.
Dofollow
Dofollow links pass on PageRank, also known as “link juice”.
If a link doesn’t have either the “dofollow” or “nofollow” attribute, it is set to dofollow by default.
It is recommended that you keep all of your internal links dofollow, and nofollow any external ones.
Nofollow
Dofollow’s polar opposite, the nofollow link attribute prevents a link from passing on any PageRank.
These are less desired for link building purposes, but are very useful for situations where you want to link to an external resource, but don’t necessarily want the link to pass on your PageRank.
Sponsored
The “sponsored” link tag exists to mark any backlinks that have been acquired as part of a paid promotion or sponsorship.
Failure to add the “sponsored” tag for any paid links puts you in violation of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
Whether sponsored links pass on PageRank or not can vary on a case-by-case basis, but in general, they either pass on a smaller PageRank value or none at all.
UGC
UGC stands for “User-Generated Content” and is an attribute that should be applied to all links that have been created by your users.
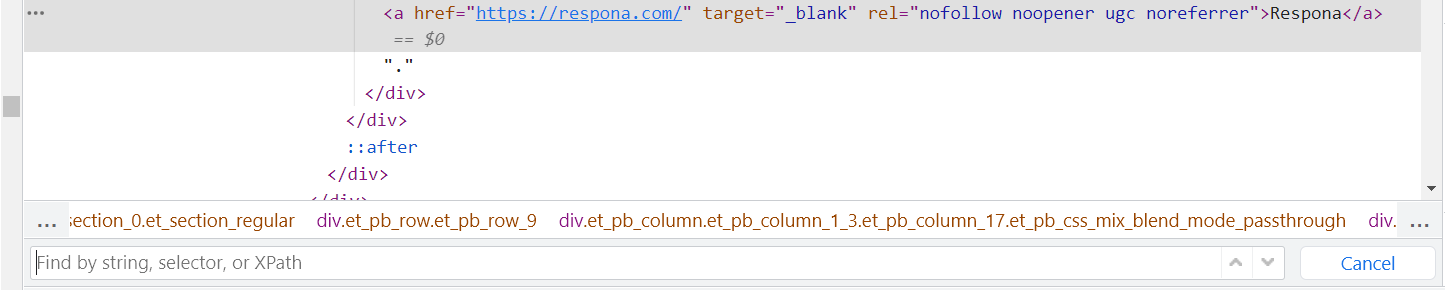
Examples of such links can be blog comments, forum posts, etc.
As a rule of thumb, UGC links do not pass on PageRank, although they can do so on a rare occasion.
Image Optimization
Image optimization refers to several things at once:
- Reducing the size of your images so that they have a lesser impact on your site speed
- Enabling lazy image loading
- Writing alternative texts for each image on your website
The first one is rather straightforward. Larger pictures take longer to load, which affects site speed, especially on mobile.
It is recommended that you use a plugin that helps manage image sizes automatically so you don’t have to manually adjust each image.
Image lazy loading is an option that makes pictures load after other elements, and reducing your time-to-interactive.
It is recommended that your mobile website version also has lazy loading enabled.
Alternative texts are little descriptions of your images.
These are used by screen readers, displayed when image is not loaded, and “read” by search engines to understand what is depicted on the image.
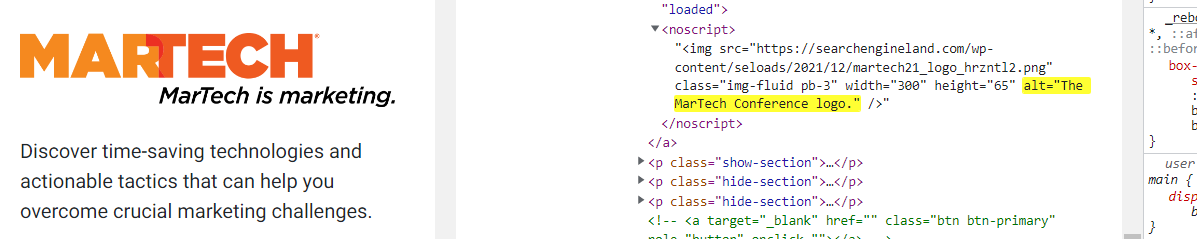
Adding alternative text is simple. If you’re using WordPress, simply click on the image and the alternative text window will appear in the block menu to the right.

Alternative texts need to be brief and descriptive.
Ideally, they should also include your target keyword, but it’s not mandatory.
There are also several occasions when an image does not require an alternative text.
Purely decorative images such as logos do not need alt texts.
Additionally, if the image already includes a caption describing what’s depicted, there is no need to repeat yourself in the alt text.
Link Anchor Text
Believe it or not, the anchor text of your backlinks is actually a ranking factor in its own right.
If you have a lot of backlinks that include a certain keyword in the anchor text, your page will start ranking for that keyword, even if it’s not present anywhere on your actual page.
There is rarely much control over your links’ anchor texts, but to optimize them for SEO, you should try and ensure that the bulk of your backlinks have exact or partially matching keywords in their anchors.
Canonical Tags
A canonical tag is an HTML element that helps webmasters prevent duplicate content issues on their websites. A canonical tag is placed in the head section of a web page’s code and looks like this:
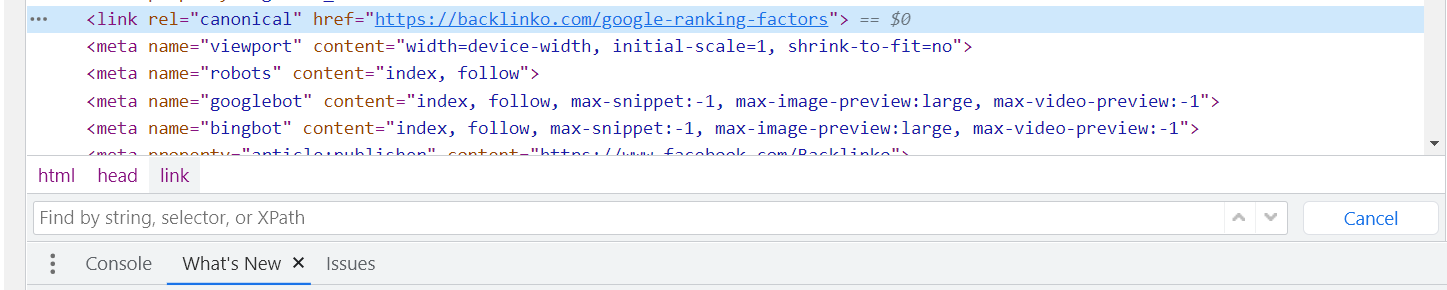
The href attribute of the canonical tag contains the URL of the page that you want to be considered the “canonical” or “master” page.
This URL is usually the original source of the content.
When search engines see a canonical tag on a page, they will index the content of the canonical page and ignore any duplicate content on other pages.
This helps to prevent duplicate content issues from occurring and ensures that only the most relevant and original content is being indexed.
Link Building
Link building is the process of acquiring backlinks that lead to your site from other resources.
Backlinks from high-quality websites or one of the strongest ranking factors to this date.
This is because links pass on what is known as PageRank.
We already mentioned PageRank in the section about link tags, but for those of you unfamiliar with the term, let’s talk a little bit about what it is.
PageRank is a core part of Google’s algorithm, and has been ever since its inception.
In Layman’s terms, it’s a numerical value assigned to each page based on the number and quality of inbound links it has.
The higher the PageRank score of a page is, the higher it will show up in search engines.
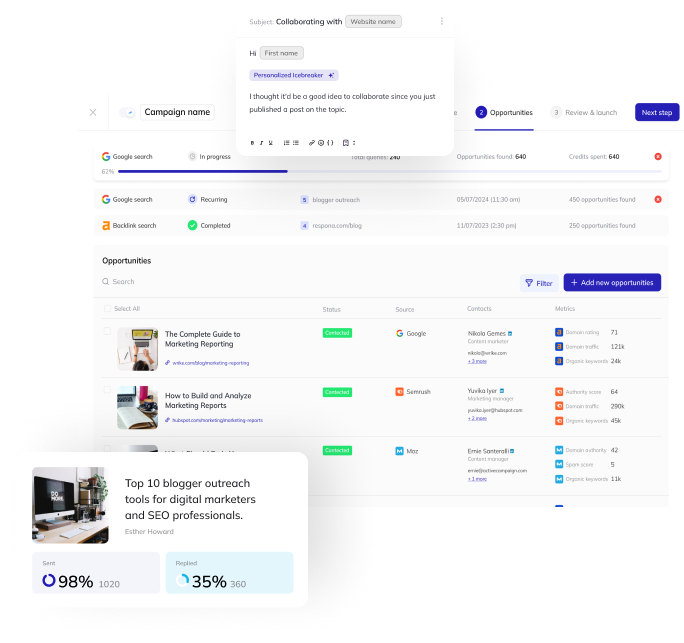
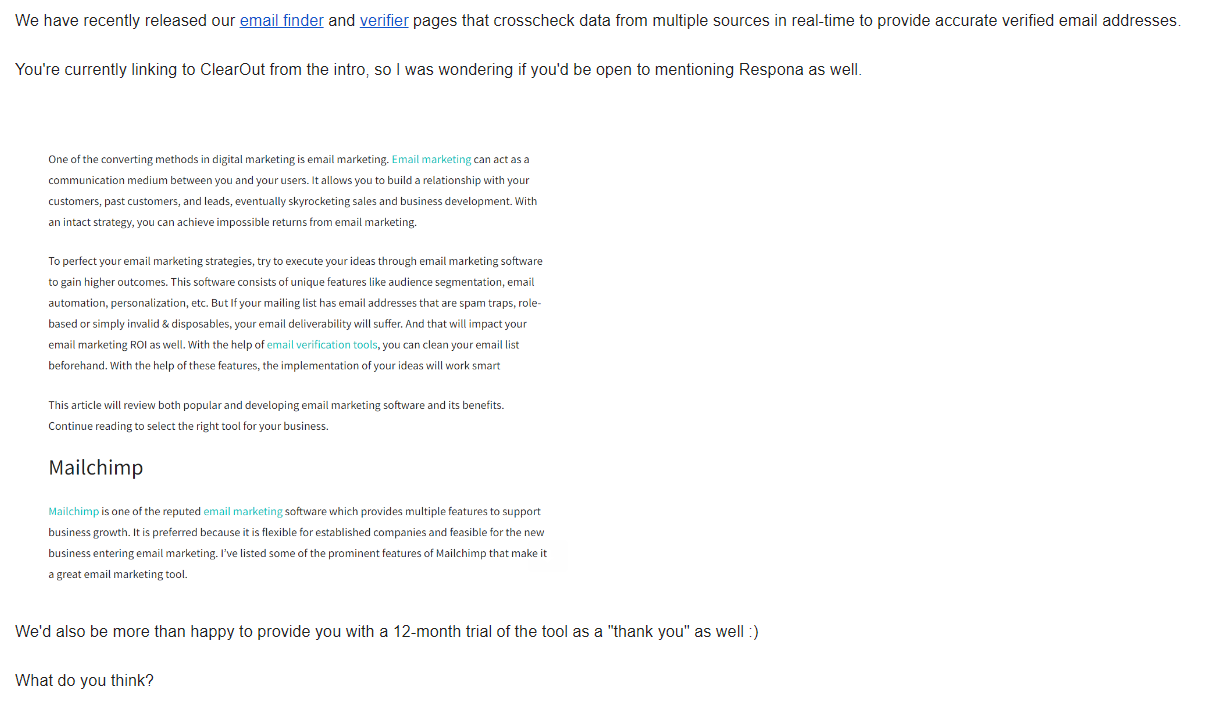
Link building is typically done through cold email outreach, and is actually Respona’s primary use case.
Let’s take a quick look at how you can set up and run a link building campaign of your own with Respona.
It helps automate each step of the process – from prospecting to finding contact information and even personalizing pitches.
Prospecting
Prospecting, or locating the individuals to whom you will be reaching out, is the initial stage of every outreach effort (link building is no exception).
There are several methods, including manual scraping.
Respona, on the other hand, can nearly totally automate this operation.
Our contact search automation retrieves results straight from Google, supports all sophisticated search operators, and can execute several searches concurrently.
A example search is as follows:
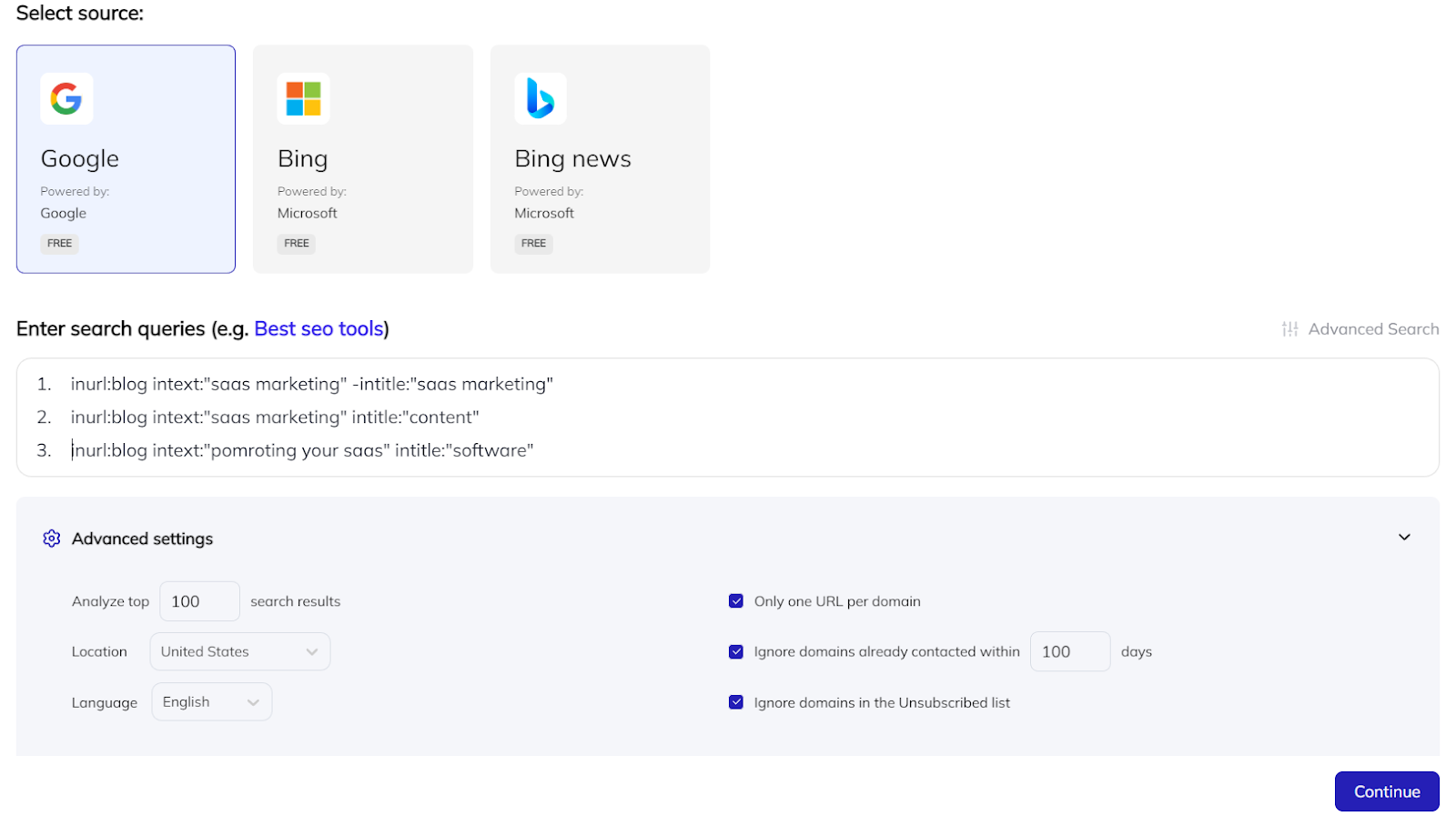
Results will automatically be added to your campaign once the search is done – Respona is purely cloud-based, so there is no need to keep the tab open while you wait.
Email Sequence
Once you’ve identified your prospects, you’ll need to create the email sequence that will be sent to them.
A sequence is typically made up of your first email and a follow-up.
Variables such as @name and @day of week can be included to your Respona sequences to aid with customizing later on.
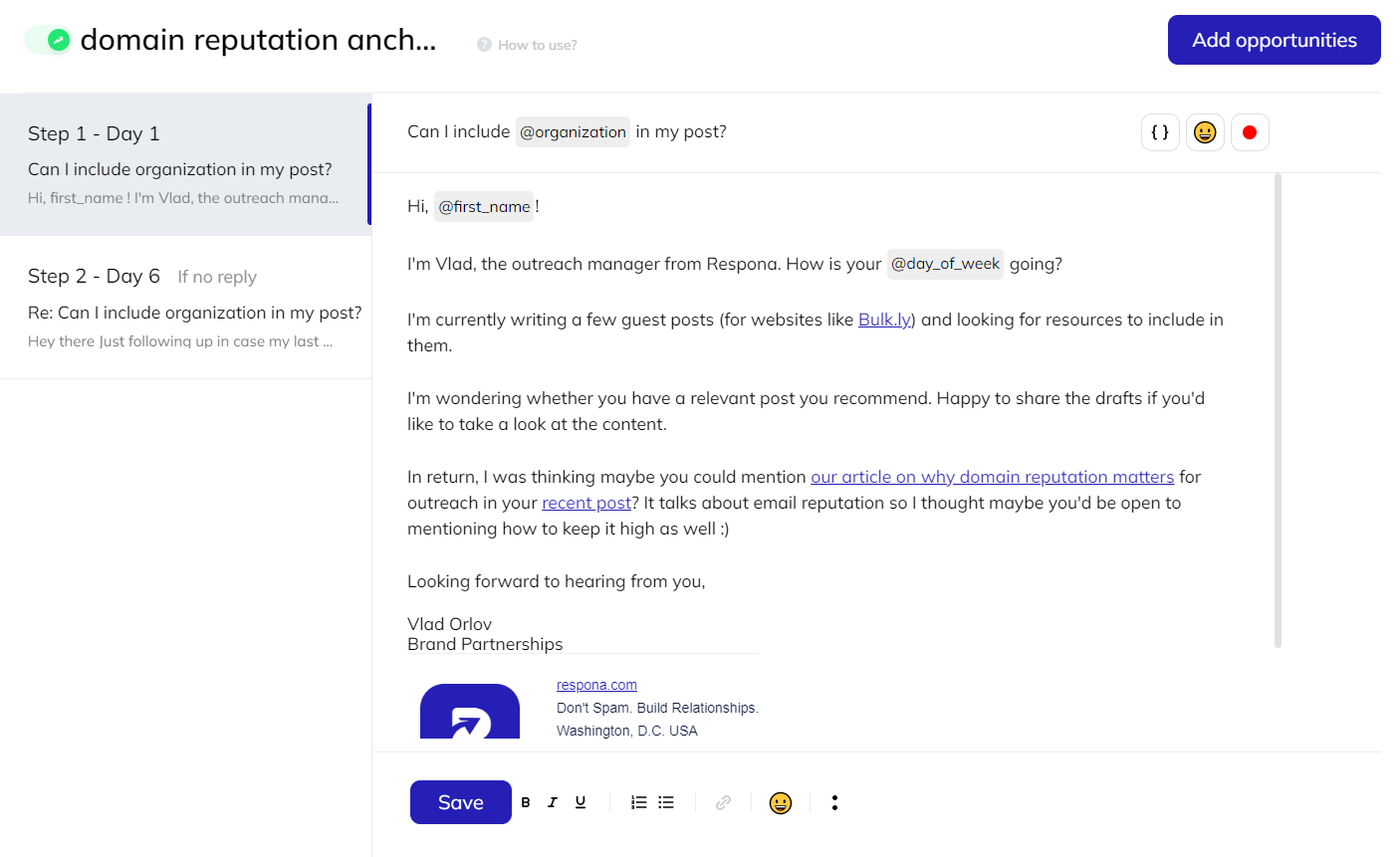
To learn more about crafting top-tier link building pitches, feel free to visit our A-Z link building outreach guide.
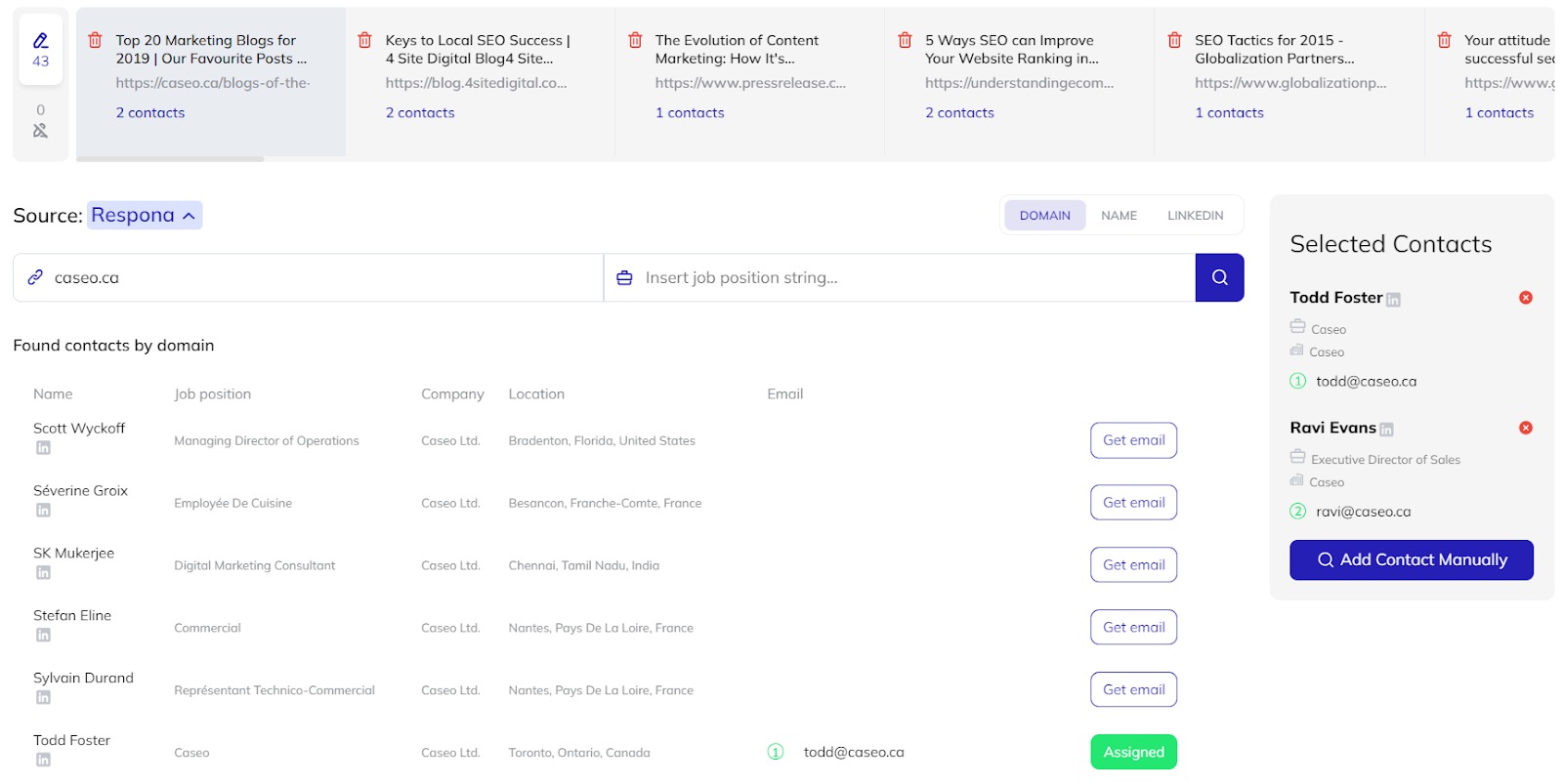
Finding and Confirming Contacts
It may appear that locating contact information is difficult. However, this does not have to be the case.
This process has been practically abolished by Respona. All you need to do is tell the tool who you’re looking for, and it will take care of the rest.
Please allow us to explain.
You’ll see this window after finishing your email sequence in Respona and moving on to Step 3 – Find Contacts:
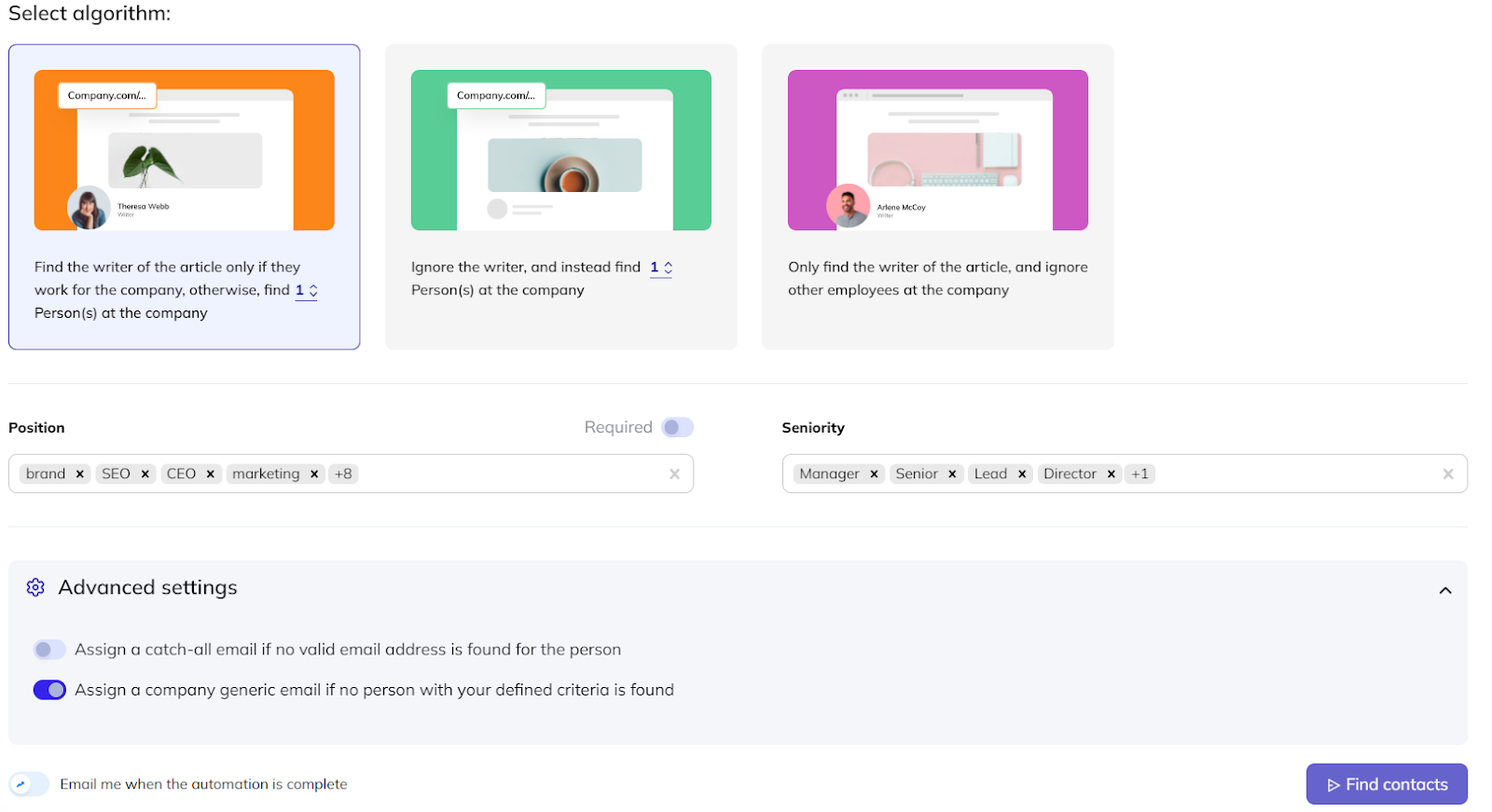
As you can see, the contact search algorithm has three modes:
- Find the article’s author if they work for the company; otherwise, find x person(s) at the company.
- Ignore the author and instead look for x person(s) at the company.
- Find only the author of the article and ignore other employees.
The first one is the best for link building.
Clicking “Find Contacts” runs the automation in the background, after which you’re also able to double-check its results.
Personalizing Pitches
All of the variables that you selected in Step 2 – Create a Sequence will be automatically adjusted here.
Simply providing their name and website however, is only half the fight.
You could also talk about something unique from their article in your email to make it look as though it was sent by a genuine person who read their blog post rather than just another link building pitch.
This can significantly increase the time it takes to personalize your campaigns, though, especially larger ones.
To help with this, we have created an AI that automatically pulls five snippets right from your prospects’ articles that you can simply copy and paste into your emails, making it seem as if you actually read their content.
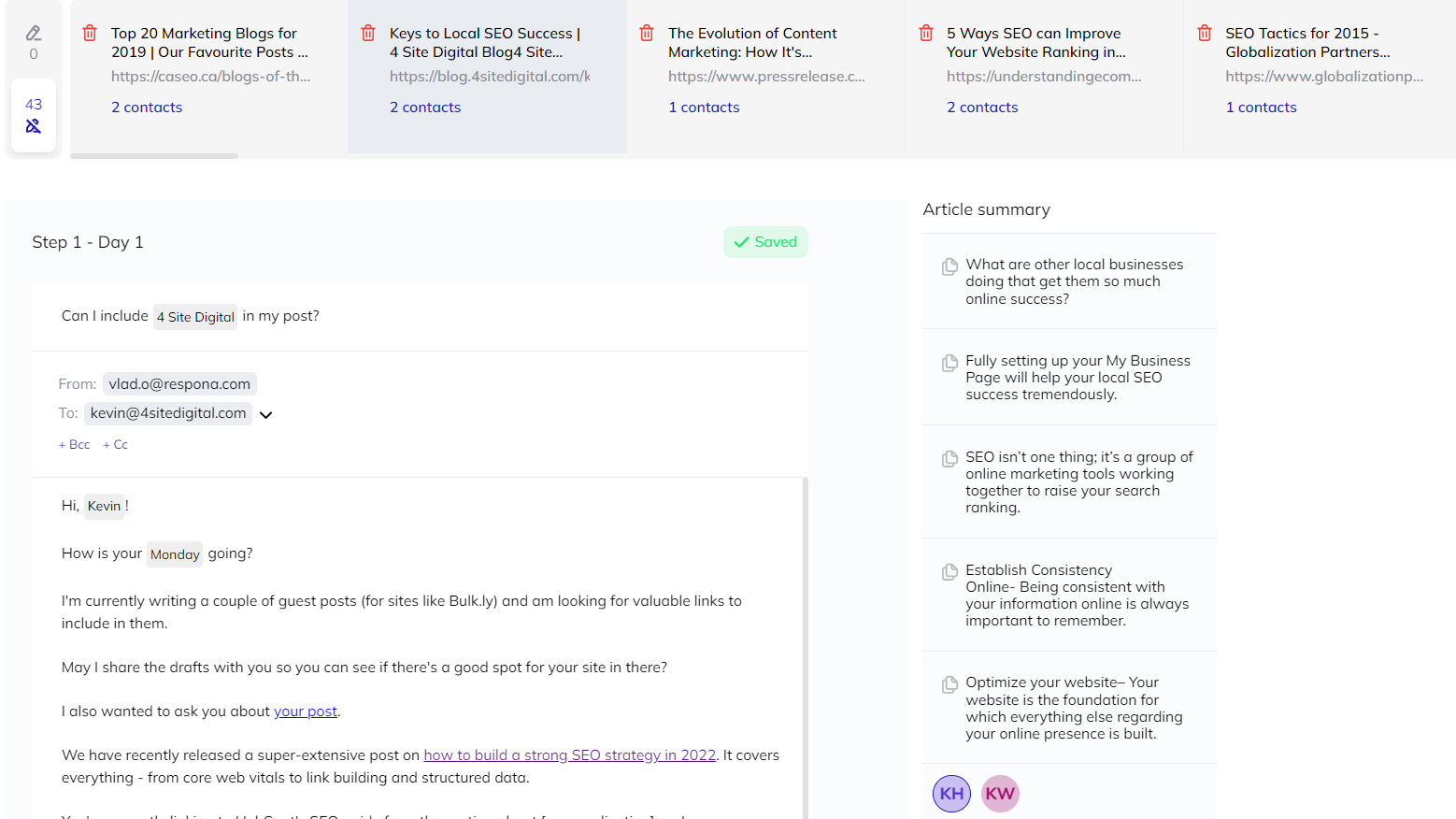
You’ll find the article summaries on the right portion of your screen.
Another strategy for giving your link building pitches an extra touch of humanity is to attach screenshots highlighting where you think your link would fit.
These cannot be automated, so it implies that someone actually went through the effort of crafting the pitch before sending.
Social signals
Social signals are a bit of a nebulous term, but at its heart, it refers to the idea that social media can have an impact on search engine rankings.
In general, the more engaged a piece of content is on social media, the more likely it is to rank well on search engines.
This is because engagement is a signal to search engines that people find the content valuable, and so it should be given more weight in search algorithms.

There are a number of ways to measure social engagement, but some of the most common metrics include things like shares, likes, and comments.
The more of these that a piece of content receives, the more likely it is to rank well on search engines.
Local SEO
As the name impies, local SEO is geared towards helping your website show up in local searches.
There are many aspects of local SEO, but some of the most important ones include:
- Local link building
- Listing your business on the map
- GMB
GMB stands for Google My Business and helps you manage your business’ appearance in search results, as well as Google Maps.
This isn’t really as relevant for SaaS businesses, but if you have an actual office or store, it’s important to fill out your GMB profile with contact information, directions, etc.
Review sites
Review sites like G2 are a huge part of off-page SEO.
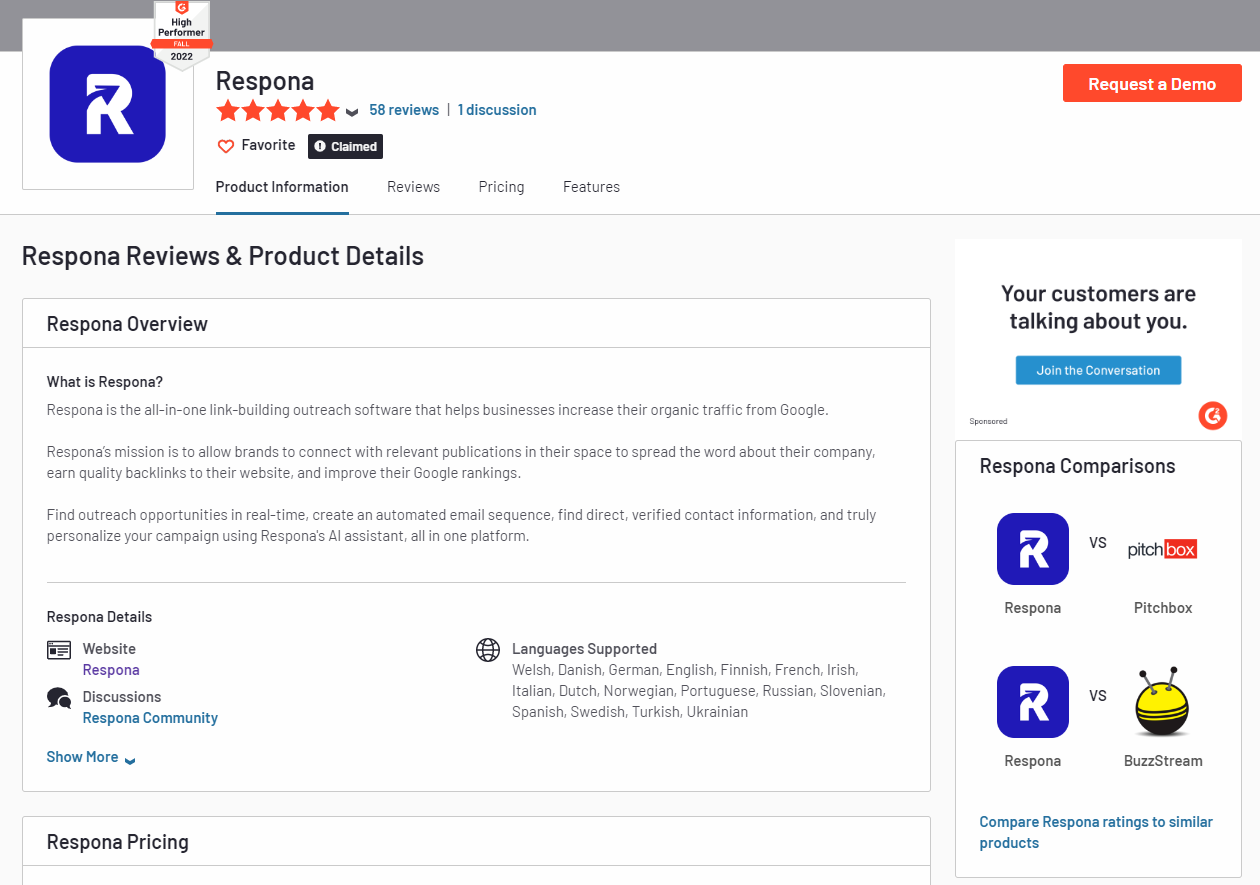
First of all, they allow you to generate additional traffic and attention to your business, since they have hundreds of thousands of people already visiting them.
Second of all, getting your business listed on one of those can drastically improve your trustworthiness in the eyes of new potential customers, especially if you amass a number of positive reviews.
It doesn’t take a lot of time or effort to get yourself registered on these resources, and the benefits you will be getting in the long run are too good to pass up.
Site Architecture
Site architecture is the overall design of a website, including the structure of the website’s pages and the way those pages are linked to each other.
Site architecture can have a significant impact on SEO because it affects how easily search engines can index and crawl a website.
A well-designed website with a good site architecture will be easier for search engines to crawl and index, and will therefore tend to rank higher in search results.
The best type of site architecture for crawlability is known as “flat”.
In a “flat” website, all pages are accessible within only one or two clicks of the homepage.
As a good rule of thumb, you should always try to make sure your crawl depth is less than three, meaning that the crawler never has to follow more tahn three links to index a page.
Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that contains a list of all the pages on a website. This list is then used by search engines to index the website.
Having a sitemap is important for SEO because it allows search engines to find all the pages on a website, and index them properly.
Without a sitemap, Google might struggle to find and index all of your pages, especially if your internal linking is subpar, crawl depth is too big, or if you have some orphaned pages.
You can create a sitemap manually or take advantage of one of the numerous sitemap generators available for free.
Internal and Broken Links
Internal links are important for two reasons.
The first one is that, of course, they help guide your users through your pages.
But, from an SEO perspective, internal links serve as a way for Google’s bots to crawl through your website.
We already mentioned that your crawl depth should never be over three to avoid indexing issues.
For best indexing, it’s worth the effort to make sure that each of your pages has at least 5 internal links pointing to it from other pages.
We don’t need to tell you that broken links are bad for business – they make your site look unprofessional, and may even hurt your rankings.
Luckily, you don’t have to manually audit your pages for broken links as there are many tools available for this, mainly Ahrefs’ Broken Link Checker.
Redirects
A redirect is a way to send both users and search engines to a different URL from the one they originally requested.
Redirects are important for SEO because they can help to ensure that users end up on the correct page on your website, and they can also help to pass along any link equity from the original page to the new page.
Redirects can be useful in a number of different situations, such as when you move a page to a new URL, when you change the format of a page (e.g. from HTML to PDF), or when you want to redirect users from an old page to a new page.
Bottom Line
So, to sum it up, there are three sides to search engine optimization:
- On-page
- Off-page
- Technical
Each type includes dozens of different strategies, but some of the most important are quality content, keyword research and optimization, link building, and site speed.