SEO (search engine optimization) is really just a sub-portion of SEM (search engine marketing).
The main difference between the two is that SEO focuses on acquiring traffic from organic search, whereas SEM helps you secure a flow of traffic from both organic and paid acquisition channels.
In this article, we will be discussing:
- What exactly is SEO and what are its aspects
- How to conduct keyword research
- What is PPC
- How long does SEM take until you start seeing results
- The costs associated with SEM
Link building cheat sheet
What is SEO?
SEO stands for search engine optimization.
All search engine optimization practices are aimed at helping your pages rank in the top positions of search engine results pages (SERPs) for your target (and related) keywords organically.
SEO is a very broad term that encompasses countless optimization techniques – each one deserving an in-depth guide of its own.
There are three general sides to SEO:
- On-Page SEO
- Off-Page SEO
- Technical SEO
In this section, we will briefly discuss what each one entails and mention some of the most important strategies of each type of SEO.
On-Page SEO
As the name suggests, On-Page SEO refers to all search engine optimization activities that take place on your website.
The main aspects of On-Page SEO are:
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Header tags
- Keywords
Website title tags are the most important on-page SEO element. The title tag tells search engines what the page is about and is the first thing a searcher sees in the search engine results pages (SERP). A title tag should be unique to each page, accurately describe the page’s content, and include the primary keyword for that page.
To optimize a title tag for SEO, make sure to:
- Keep it short: A title tag should be 50-60 characters long, including spaces.
- Use the primary keyword: Include the primary keyword for the page early on in the title.
- Be unique: Each page on your website should have a unique title tag.
A website meta description is a brief description of the content of a web page. The meta description is typically used by search engines to display a brief summary of the page in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
To optimize a meta description for SEO, the following tips can be used:
– Keep the meta description between 150-160 characters
– Use relevant keywords in the meta description
– Make the meta description unique for each page
– Use persuasive language to encourage clicks
Website header tags, or simply header tags, are HTML tags that are used to structure the content on a webpage. There are six different types of header tags, each with its own unique purpose.
The six header tags are:
- <h1> – This is the main header tag and should be used for the most important pieces of content on a webpage.
- <h2> – This header tag is used for secondary pieces of content, such as subheadings.
- <h3> – This header tag is used for tertiary pieces of content, such as sub-subheadings.
- <h4>, <h5>, and <h6> – further break down the content.
To optimize header tags for SEO, it is important to use the correct tag for the correct piece of content. The <h1> tag should be used for the most important content, while the <h6> tag should be used for the least important content.
Most of the time, there is no real need to use any subheaders after <h3>.
It is also important to use keywords in header tags, as this will help search engines understand the content for specific sections on a webpage.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is one of the absolute fundamentals of search engine optimization. And even though it is technically considered an on-page practice, we feel that it deserves a subsection of its own.
In order to show up in search results, you need to know which queries your target audience is searching for.
Keyword research, of course, refers to the process of identifying these queries and optimizing your website for them.
To conduct keyword research, you will need some sort of keyword/rank tracking software.
We use Ahrefs, so in this section, we’ll just guide you through the keyword research process with it.
First, you will need to navigate to Keywords Explorer and type in your parent keyword.
This can be just the general keyword that describes your niche.
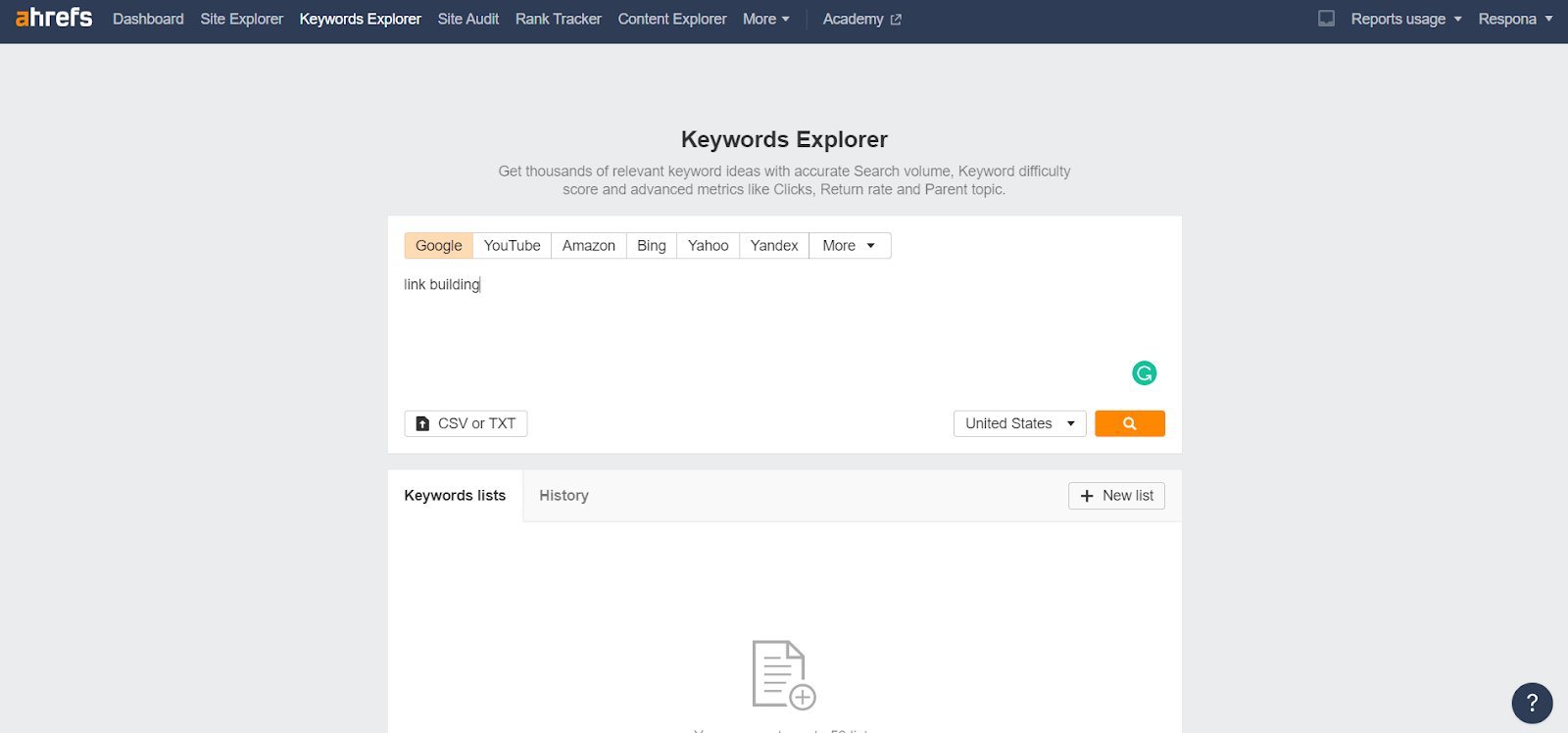
You will then be greeted with an overview of your target keyword, its search volume, related questions, keyword ideas, and other terms that pages that rank for your target keyword also rank.
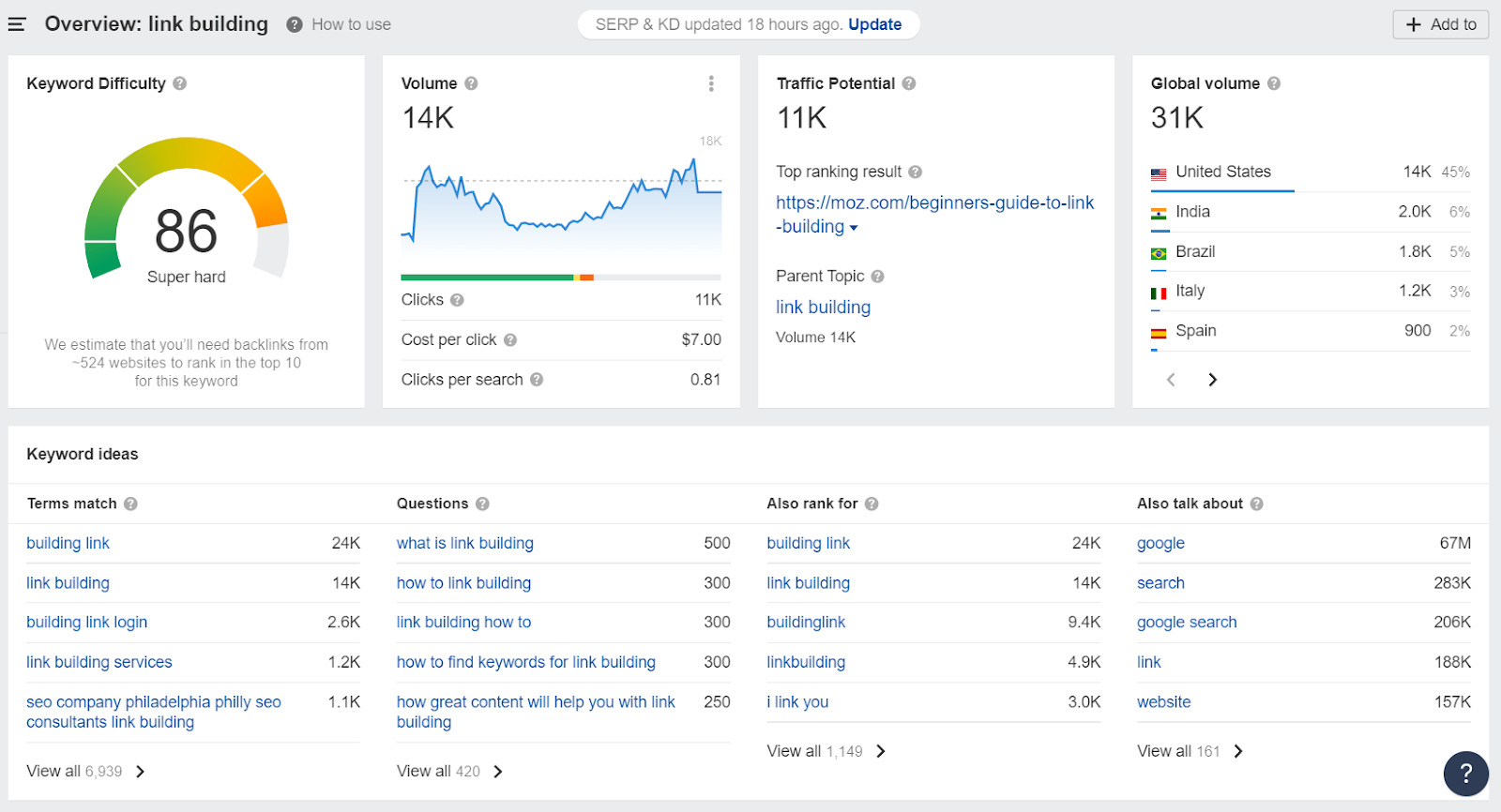
An important attribute of any keyword is its Keyword Density or KD.
It estimates how hard it will be for you to rank for it. It does it by considering the number of other pages ranking for that keyword, how much traffic they’re getting, their Domain Rating, backlink profiles, and much more.
As you can see, “link building” has a KD of 86. This is extremely high and almost impossible to rank for unless you get thousands of backlinks.
An ideal keyword to target would have a low density score, but a high search volume.
Click over to “Search Suggestions” to reveal more keywords, related to your niche, as well as their statistics.
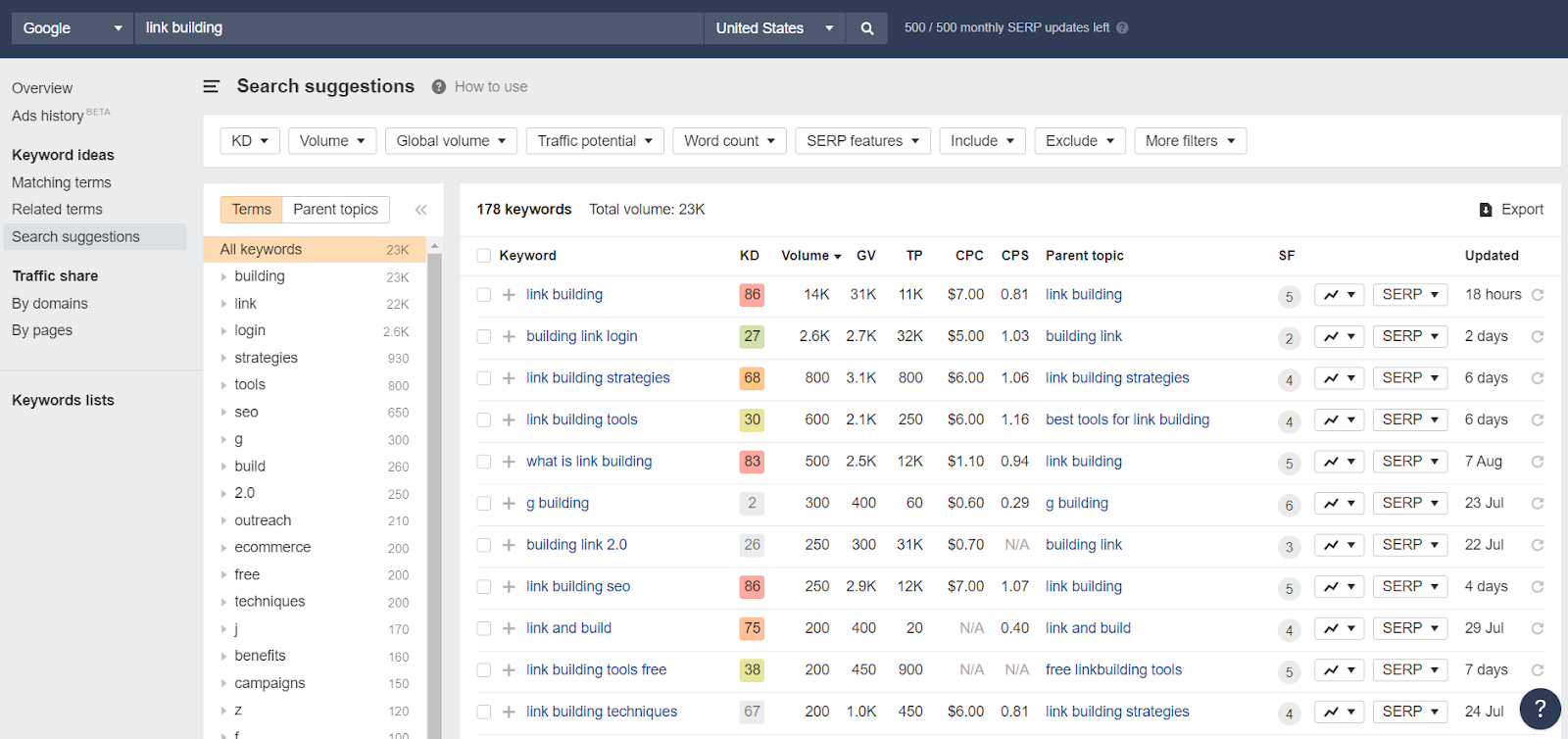
Depending on your niche, you may have hundreds or even thousands of relevant keywords that you could easily rank for.
Manually going through them is a lot of work.
In addition, simply picking keywords that you feel are good fits for your site may not be the best course of action at that moment.
Luckily, there is a formula that can help you eliminate all of the guesswork and quickly assign your keywords scores, depending on how relevant they are to you, their KD, traffic potential, and CPC (cost per click).
This formula is:
(1/difficulty) * traffic potential * (CPC+1) = Keyword Score
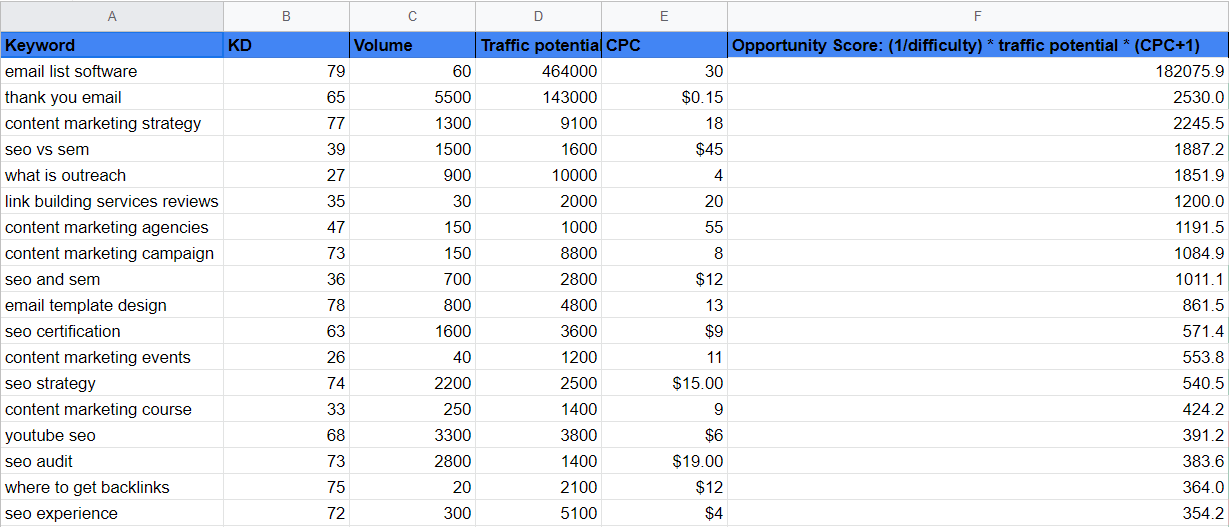
You can export all of your related keyword lists, and combine them into your master keyword sheet in Excel or on Google docs.
Applying that function to a separate column in your document will allow you to quickly grade the keywords and make more informed decisions when planning out your content, rather than guessing what to optimize for.
When creating your content, pay attention to your keyword density.
You don’t want to stuff your content with keywords, but at the same time, you want to include as many related keywords in it as possible.
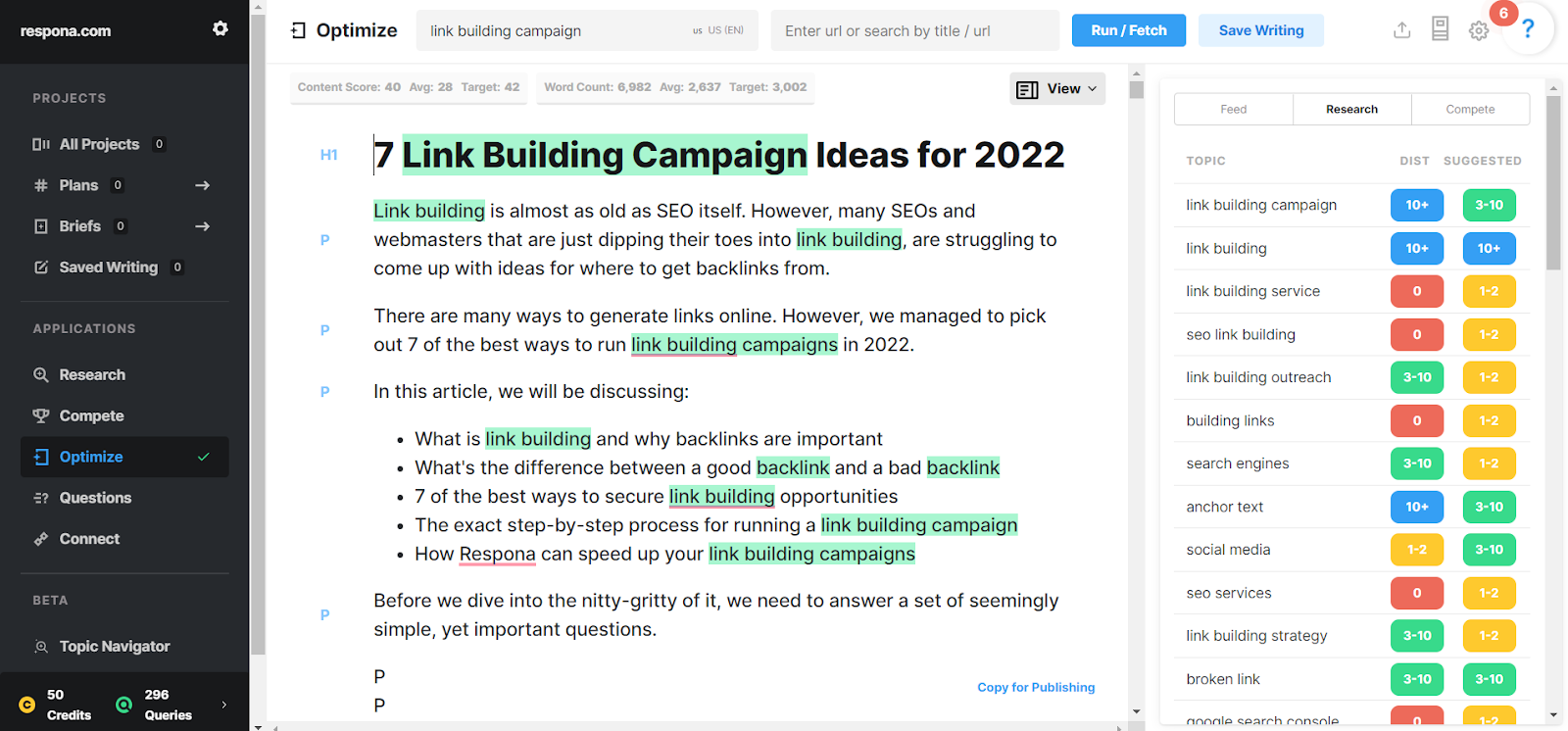
An easy way to do that would be to use a content optimization tool like MarketMuse.
It suggests exactly which keywords should be mentioned in your text, and how many times.
Off-Page SEO
As you may have guessed, off-page SEO refers to optimization techniques that are performed outside of your own website.
The biggest part of off-page SEO is building high-quality backlinks but also includes:
- Social media marketing
- Content marketing
- Brand mentions
- Online reviews
Backlinks are actually one of the most important SEO factors period – not just in terms of Off-Page SEO.
They are so important because of how the Google search algorithm works.
At its core lies PageRank – which is a score that is calculated depending on the number and quality of backlinks pointing to any singular page.
In layman’s terms, the more backlinks from high-quality domains a page has, the higher it will show up in search results.
Over the years, marketers have figured out ways to manipulate PageRank through shady link schemes and purchasing tons of low-quality backlinks.
Google has cracked down on these practices with its numerous algorithm updates, but links from high-quality, authoritative websites remain one of the biggest ranking factors today.
The best way to secure such backlinks is through link building outreach.
Respona’s primary purpose is to cut down on the amount of time required to run successful link building outreach campaigns, so if you’d like to learn more about running them, feel free to refer to the article linked above.
Technical SEO
The technical aspect of your website is equally as important for rankings as high-quality content and a strong backlink profile.
Google rewards pages that provide a good user experience, and quick loading times are a huge part of that.
However, technical SEO involves much more than simply ensuring that your pages load quickly, namely:
- Crawlability and indexability
- Site structure and navigation
- Thin or duplicate content
We will not cover every little detail that technical SEO entails in this section as every one of them deserves a full-length guide of its own, but we will go through the basics.
The very first thing that you should start optimizing is your site structure.
Site Structure
A site’s structure is its overall organization and hierarchy. It’s important because it helps visitors navigate the site and understand its content.
A clear structure also helps crawlers crawl and index your pages more effectively.
The best site structure for both users and search engines is the “flat” structure.
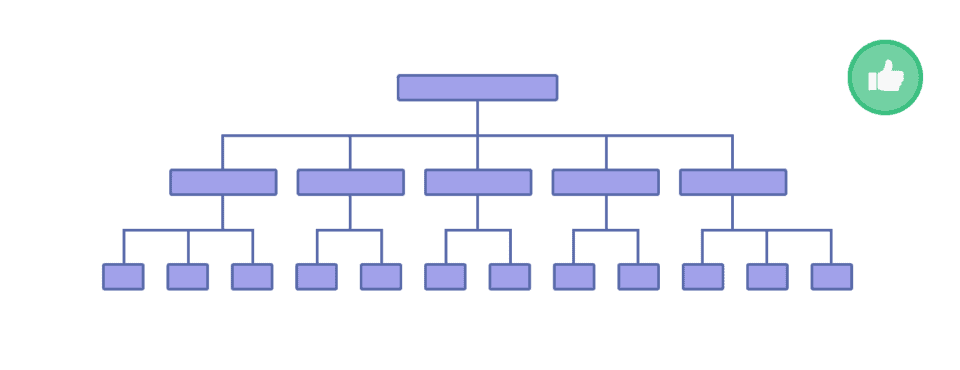
This means that all of your pages are easily accessible and are always only a couple of links away from each other.
The same applies to your URL structure – it should follow an organized and consistent pattern.

The most SEO-friendly navigation style is breadcrumbs.
It automatically adds internal links to your subpages and categories and makes your whole website easy and intuitive to navigate both for users and search engines.
Your internal link structure massively affects your website’s navigation and crawlability as well.
The first step is to understand your website’s current link structure. This can be done by conducting an audit of your website’s internal links.
Once you have a good understanding of your website’s current link structure, you can begin to optimize it for both navigation and crawling.
There are a few things to keep in mind when optimizing your website’s internal link structure:
- Make sure your links are easy to navigate. This means using descriptive anchor text and organizing your links into logical categories.
- Use keyword-rich anchor text to help provide context to each link.
- Avoid using excessive numbers of links on any given page. This can overwhelm users and make it difficult for crawlers to index your content.
- Make sure all of your links are working properly. Broken links can frustrate users and prevent your pages from being crawled properly.
One last thing that will help you improve your website’s crawlability is an .XML sitemap.
XML Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that contains a list of all the pages on a website. This list is used by search engines to index the website.
The sitemap can also be used to provide information about the website, such as when the website was last updated, how often the website is updated, and the importance of each page on the website.
You can either write your own .XML file or use a sitemap generator like XML-Sitemaps to do it for you.

You can then upload it to the Sitemaps page of the Index section in Google Search Console.
The next piece of the technical SEO puzzle is thin and duplicate content.
Thin and Duplicate Content
Thin content is generally defined as content that offers little to no value to the reader. It could be a short blog post, an article with very little content, or even a page that consists mainly of images or videos.
Duplicate content is simply content that already exists elsewhere on the internet. It could be an exact copy of an article or a slightly different version of the same content.
Both thin and duplicate content can negatively impact your site’s SEO.
Thin content is often seen as low quality by search engines, which can lead to your site being penalized or even banned from their results.
Duplicate content can also be a problem, as it can confuse search engines and make it difficult for them to determine which version of the content is the most relevant.
This can lead to your site being ranked lower in search results, or even being removed from them entirely.
There are many tools that can help you identify thin and duplicate content, such as Raven Tools.

Site Speed
Finally, let’s talk about site speed. It matters A LOT.
A slow-loading site will cause people to click off and turn to your competitors. It’s no secret that waiting for more than a couple of seconds at a time is frustrating.
Besides basic human psychology, site speed is also a huge ranking factor – Google’s crawlers record exactly how long everything takes to load down to the milliseconds.
A great free tool for measuring your site speed is Google’s PageSpeed Insights:
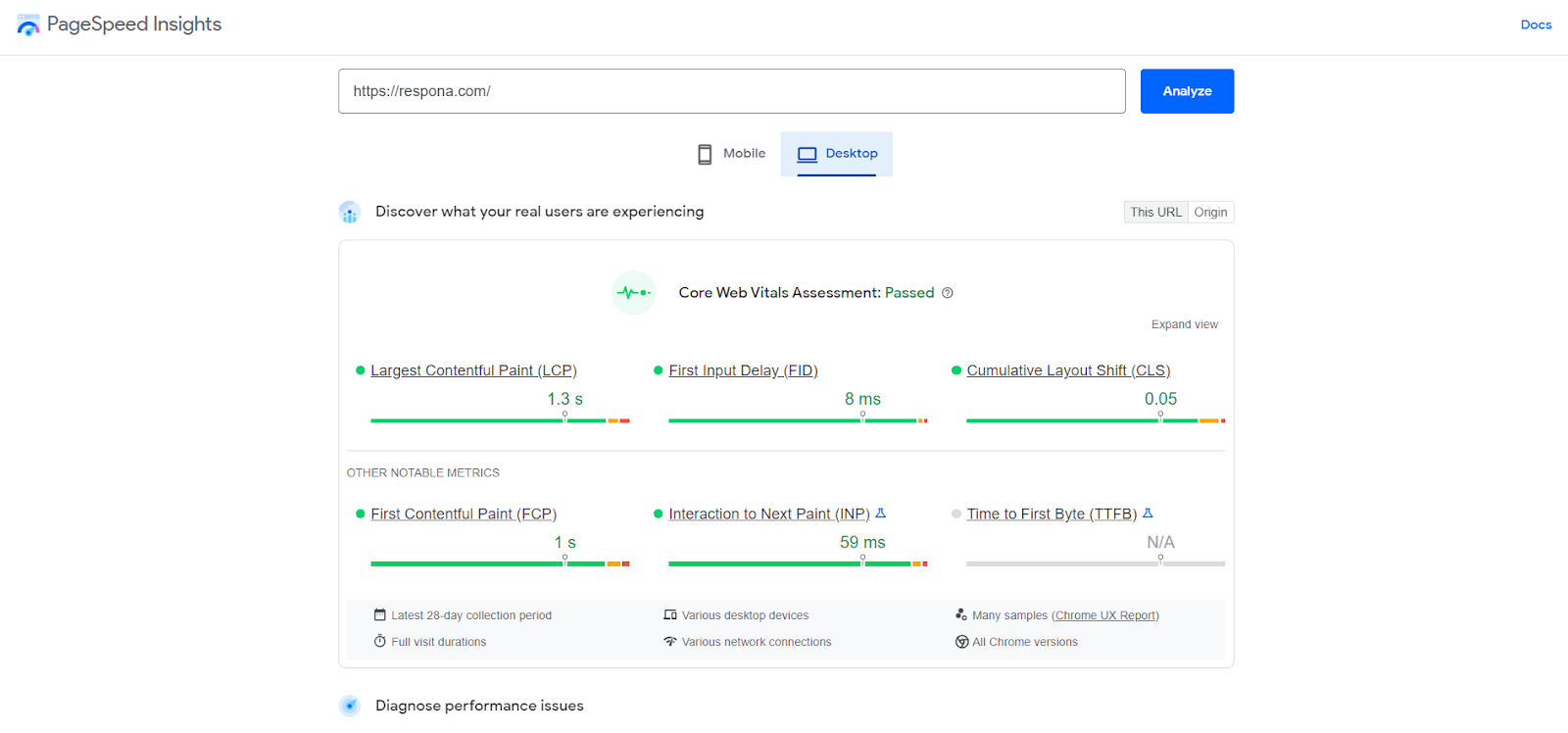
In addition to providing you with accurate data, it also spots loading issues, allowing you to easily identify and eliminate them.
What is PPC?
PPC (or Pay-Per-Click advertising) is a subsection of search engine marketing that’s focused on generating traffic and leads through paid channels.
There are many PPC channels, but one of the most popular (and effective) is Google Ads.
If you have the budget, pay-per-click ads can be a great way to generate lots of qualified leads, considerably boosting your sales.
PPC Advantages
Pay-Per-Click advertising has many advantages over search engine optimization:
- You see results quicker.
SEO is a long-term strategy that takes months and years until it starts to really kick in.
In comparison, setting up a PPC only takes a few hours – bringing you to the top of search results instantaneously.
- You can rank for your competitors’ names.
An overwhelming number of PPC campaigns are run for the names of competing businesses.
For example, if you Google Ahrefs right now, the first ad result that you’ll get is actually SEMRush:
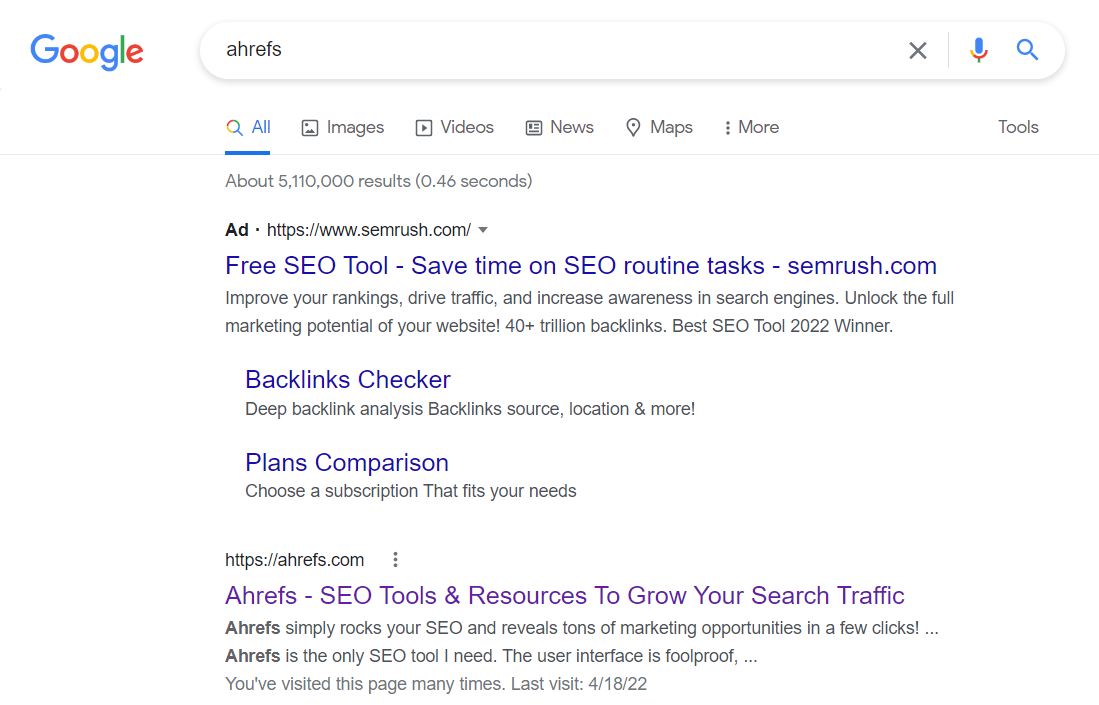
So, if you can’t outrank your competition, you can simply pay to show up higher than them.
- PPC ads are much more predictable than SEO.
Google is constantly changing the way its algorithm works, and strategies that are extremely important right now might lose their value just a couple of months down the line.
Pay-Per-Click ads aren’t nearly as volatile as SEO, and once you figure out what works for you, it’ll likely stay that way for a long time.
You can A/B tests on your advertisements to ensure you get the highest possible return on your investment.
- PPC ads are much more targeted.
With PPC advertising, you can effectively skip a couple of steps of the conversion funnel and market your products/services to an audience that is already ready to make a purchase.
- With PPC, you can rank high even if your actual SEO isn’t top-notch.
You don’t need a high Domain Rating, thousands of backlinks, or even great content to start ranking high in search engines with PPC.
Even if you have literally just launched your website, you can occupy the #1 spot right off the bat.
Sounds fantastic, doesn’t it? Well, what about the disadvantages?
Disadvantages of PPC
- Most people skip over search ads.
There are a few reasons why people might not trust search ads.
First, people might feel like they are being tricked into clicking on an ad because it is mixed in with the search results.
Second, people might not trust the advertiser and feel like they are being sold something that they don’t need.
Finally, people might worry that clicking on an ad will take them to a website that is not safe, or that contains malware.
- PPC heavily relies on third-party cookies.
PPC campaigns heavily rely on third-party cookies in order to track conversions and target audiences.
Guess what happens if the user blocks or wipes their cookies regularly?
That’s right, you can’t track your campaign effectively.
- Ad Blockers exist.
Adblockers do exactly what they’re advertised to do.
If a person is using an adblocker, they’re not going to see your ad – as simple as that.
- PPC is expensive.
To really get started with PPC, you need a decent budget.
Especially if you’re trying to advertise for competitive keywords, you need to be ready to bid a lot of dollars for each click.
If you don’t know what you’re doing, it’s easy to burn through your budget without really getting much out of it.
- SEO can have a much higher ROI.
SEO takes much more time to start appearing in search results, but its potential return on investment is much higher than that of PPC.
Once you start appearing on the first page, you will essentially be generating free traffic, which will only snowball as you get closer to the fabled #1 spot.
Now, let’s take a look at the exact, step-by-step process of setting up your own PPC campaign.
Setting Goals
There are many different goals you can have with a PPC campaign, but the most common ones are generating leads, generating traffic, and generating sales.
The best PPC channel for each goal will vary depending on your specific business goals, but generally, the best channels for generating leads are Google AdWords and Bing Ads.
The best channels for generating traffic are generally the same as the best channels for generating leads, but you may also want to consider using social media advertising platforms like Facebook and Twitter.
The best channel for generating sales will again vary depending on your specific business goals, but typically, the best platform for this is Google AdWords.
Targeting
Selecting an audience and keywords to target is the backbone of any PPC campaign.
You can do this by targeting specific keywords that relate to the products or services that you offer.
There are three different types of search intent keywords that you can target:
- Transactional
- Informational
- Navigational
Transactional keywords are keywords that are related to a specific transaction that a user is looking to make. For example, if you are selling shoes, a transactional keyword would be “buy shoes online.”
Informational keywords are keywords that are related to a specific topic that a user is looking to learn more about. For example, if you are selling shoes, an informational keyword would be “how to clean shoes.”
Navigational keywords are keywords that are related to a specific website that a user is looking to visit. For example, if you are selling shoes, a navigational keyword would be “www.shoestore.com.”
When you are targeting a specific search intent keyword, you should be targeting keywords that are relevant to your products or services. You should also be targeting keywords that are relevant to the audience that you are trying to reach.
There are different types of audiences that you can target:
- Affinity audiences
- In-market audiences
- Life events
- Custom intent audiences
- Remarketing
Affinity audiences are people who have a specific interest in a particular topic. For example, if you are selling shoes, you could target an affinity audience of people who are interested in fashion.
In-market audiences are people who are actively searching for a particular product or service. Again, if you are selling shoes, you could target an in-market audience of people who are actively searching for shoes.
Life events are people who are experiencing a particular event in their life. If we follow the shoe example, you could target a life event audience of people who are getting married.
Custom intent audiences are people who are looking for a specific product or service. For shoe sellers, you could target a custom intent audience of people who are looking for shoelaces.
Remarketing is when you target people who have visited your website in the past.
When you are picking an audience for your own PPC campaign, you should consider who your target market is and who your ideal customer is. You should also consider what type of keywords you want to target.
Landing Page Optimization
There are many reasons to optimize your landing pages for your PPC ads.
One reason is that it can help to improve your quality score, which in turn can lead to lower costs per click and higher ad positions.
Additionally, optimizing your landing pages can help to increase your conversion rate, and ultimately lead to more sales or leads.
Finally, by optimizing your landing pages you can improve your overall ROI from your PPC campaigns.
There are a number of different ways that you can optimize your landing pages for your PPC ads.
One way is to make sure that your landing page is relevant to the keywords that you are targeting.
Another way is to make sure that your landing page is clear and concise, and that it has a strong call to action.
Additionally, you may want to consider testing different landing pages to see which ones convert best.
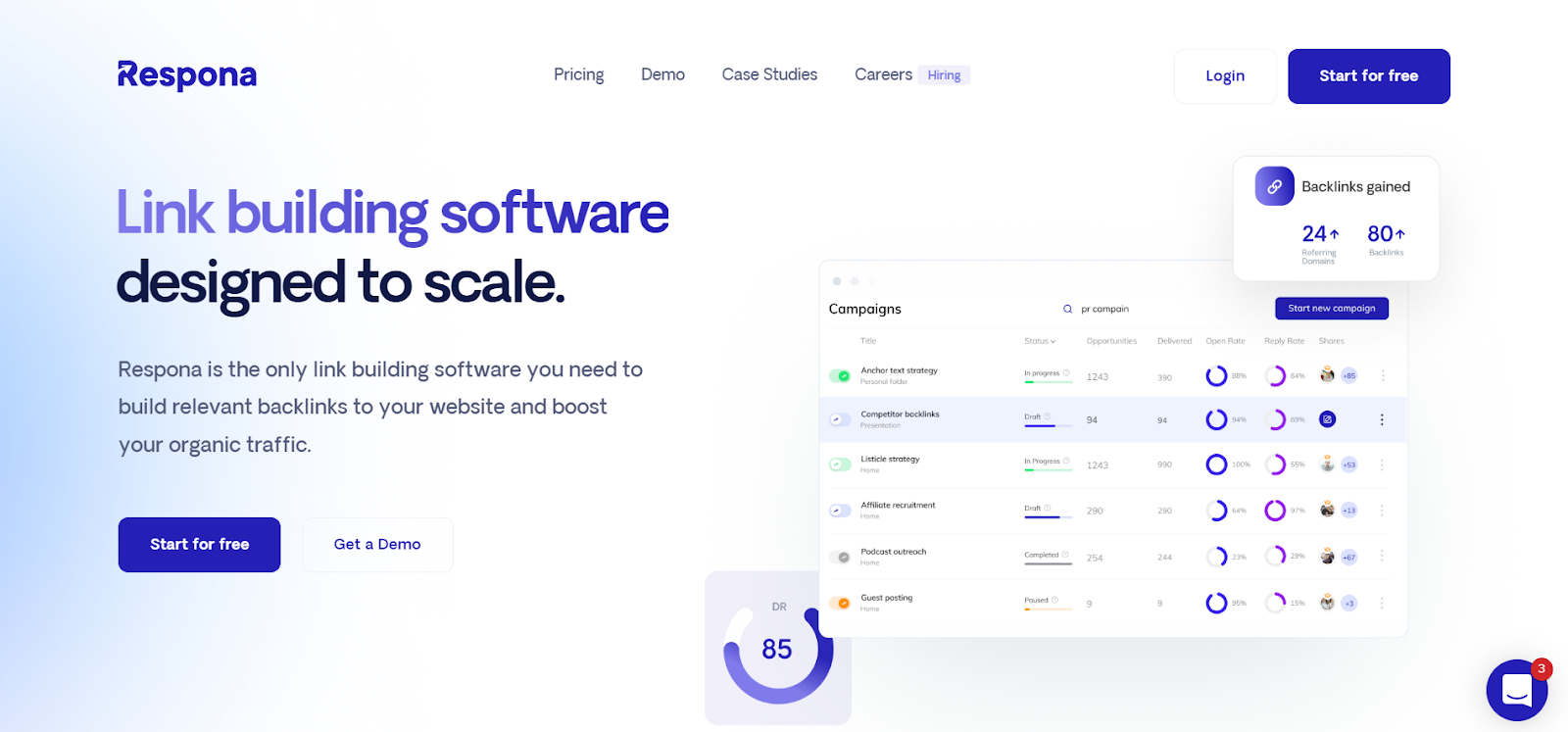
For example, here is our own “Link Building Software” landing page.
We’re not currently running any PPC campaigns, but the landing page is optimized for conversions – and actually is ranking at #2 in Google for the keyword “link building software”.
Besides being perfectly optimized for related keywords, the page is extremely informative, walking you through the campaign creation process with Respona, providing potential customers with the exact information they’re looking for.
It also has a powerful call-to-action, “Start for Free”. Anybody can register and start using Respona right now, with no payments required until the end of a 7-day free trial.
Ad Creation
Creating a PPC ad with AdWords is a simple process that can be completed in a few steps.
First, log in to your AdWords account and click on the “Create Ad” button.
Next, select the type of ad you want to create. There are four different types of ads that you can create with AdWords: text, image, video, and rich media.
Once you have selected the type of ad you want to create, you will need to enter some basic information about your ad, such as the headline, description, and destination URL.
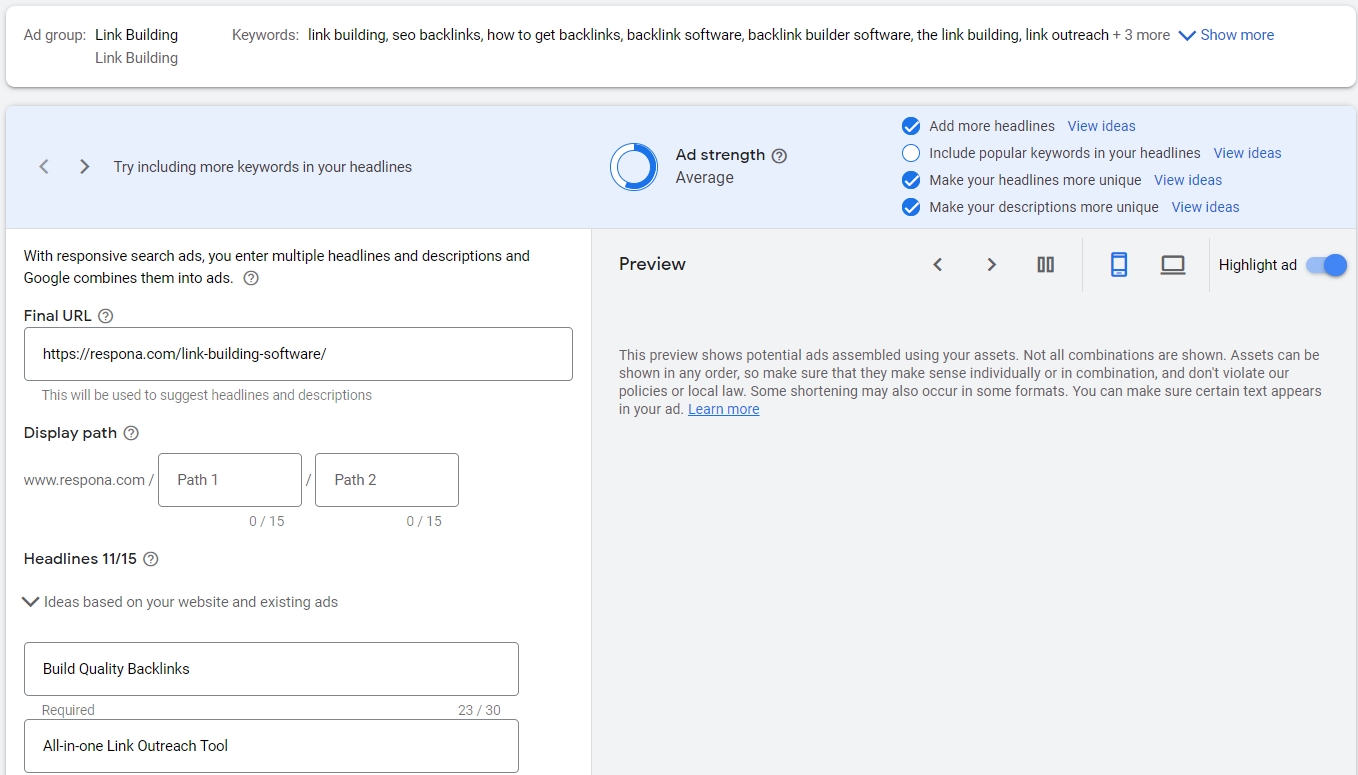
After you have entered all of the required information, you will need to select your ad’s target audience. You can target your ad to people based on their location, language, and interests.
Once you have selected your target audience, you will need to choose your ad’s budget and bidding strategy. AdWords offers two different types of budgets: standard and accelerated. Standard budgets are best for most advertisers, while accelerated budgets are best for advertisers who want their ads to be shown more frequently.
After you have selected your budget and bidding strategy, you will need to choose where you want your ad to be shown. AdWords offers two different types of ad placements: search and display.
Finally, you will need to review your ad and make sure that all of the information is correct. Once you have reviewed your ad, you can click on the “Submit” button to submit your ad for approval.
Analyze and Optimize
There are many factors to consider when analyzing and optimizing your PPC campaigns. Some important factors include:
–Click-through rate (CTR): This is the percentage of people who click on your ad out of the total number of people who see it. A high CTR means that your ad is relevant and appealing to your target audience.
–Cost per click (CPC): This is the amount you pay each time someone clicks on your ad. A lower CPC means that your campaign is more efficient and is generating more clicks for your budget.
–Conversion rate: This is the percentage of people who take the desired action on your website after clicking on your ad. A high conversion rate means that your campaign is effective in driving relevant traffic to your website.
–Average position: This is the average position of your ad on the search engine results page (SERP). A higher position means that your ad is more visible to potential customers and is more likely to be clicked on.
By analyzing these and other factors, you can identify areas where your campaign is performing well and areas where there is room for improvement. Based on your analysis, you can then make changes to your campaign to improve its results.
What is SEM?
Search engine marketing (SEM) is a strategy that helps you drive search engine traffic from both organic and paid channels.
Both SEO and PPC are types of SEM.
So, is there really a difference? Nope.
Which Type of SEM is Most Effective?
There isn’t really a straight answer to this question: some business owners will swear by SEO, while others will say it’s a complete waste of time when you can jump straight to the top of search results with a good PPC campaign.
Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
SEO can take a very long time to actually kick in, but once you reach a higher DR, your website will start appearing high in search engine results organically, essentially providing you with free traffic from that point.
However, the amount of time and effort it takes you to reach that point can vary from website to website greatly.
PPC, on the other hand, is a surefire way to show up in SERPs for your desired keywords, as long as you have the budget for it.
SEO isn’t really more effective than PPC, or vice versa.
In reality, for the best results, you should use both SEO and PPC.
Generally speaking, there is one thing that both SEO and PPC are best at.
SEO can help you establish yourself as an authority in your field by capturing lower-density informational keywords.
For example, let’s take a look at the keyword “link building campaign”:
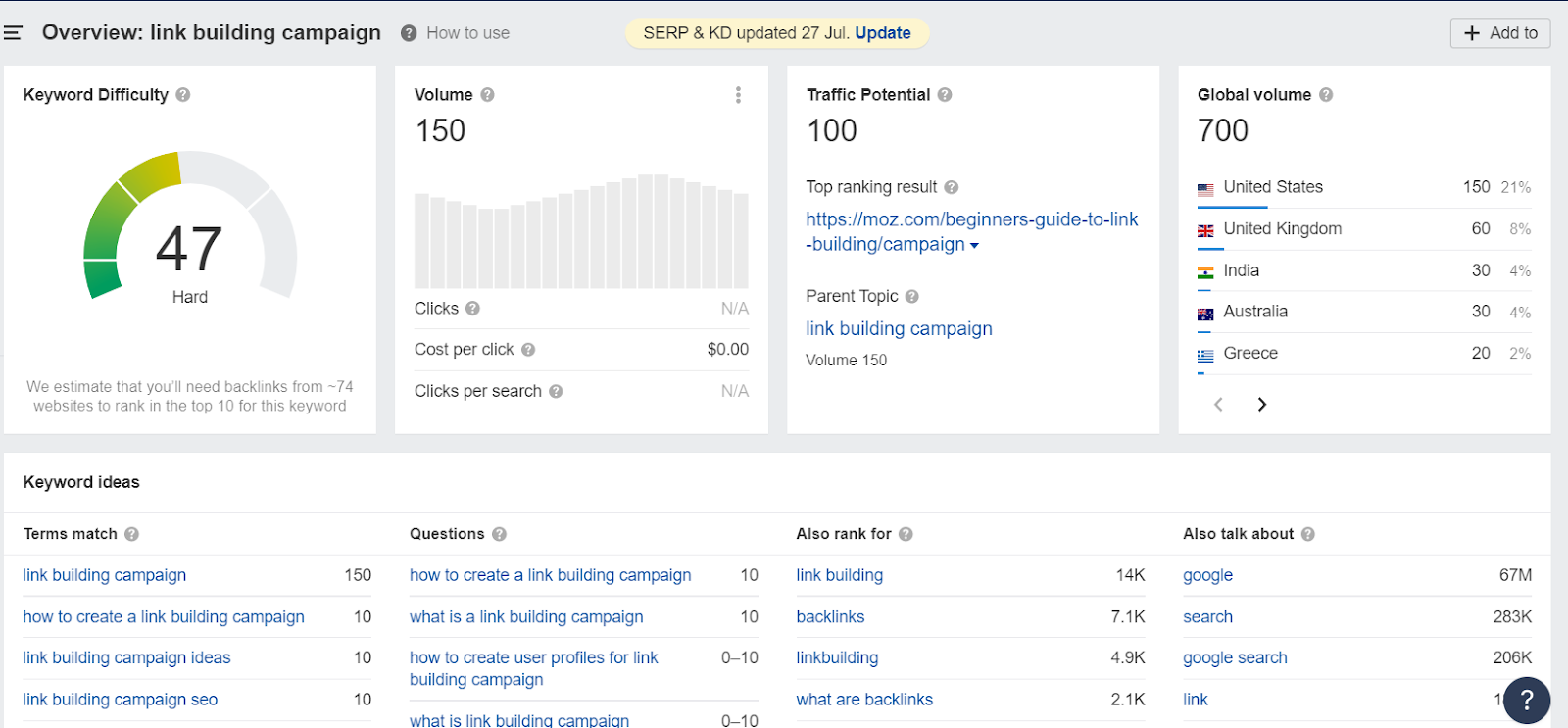
With a density score of 47 and a global search volume of only 700, it isn’t really that difficult to rank for.
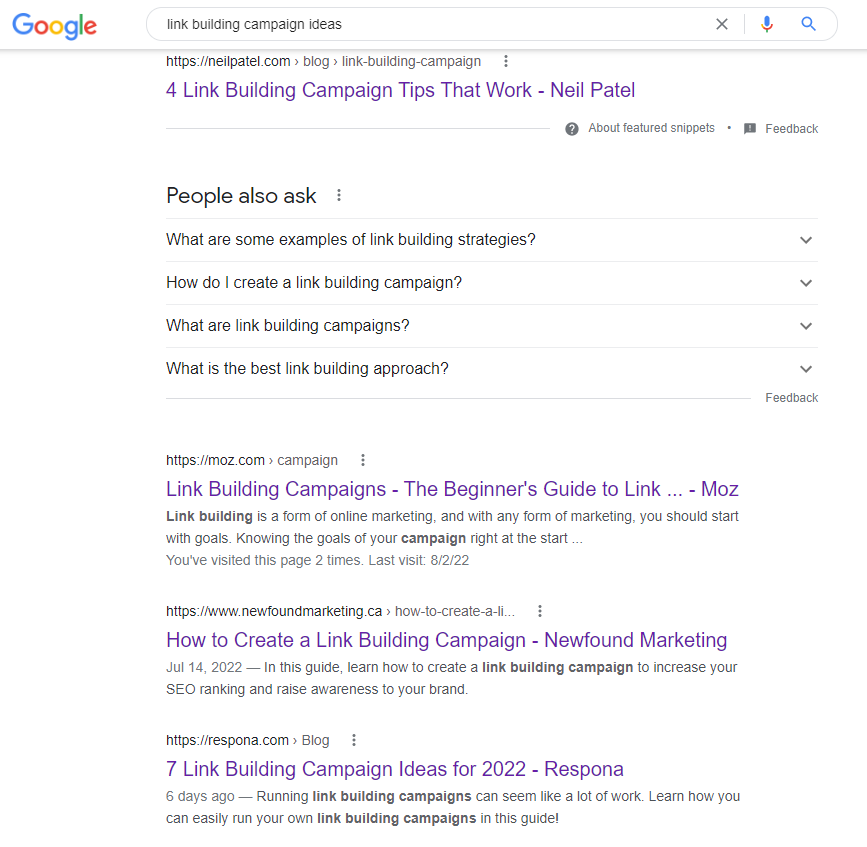
And indeed, our own article targeting that keyword (at the time of writing this article) is ranking at #4 in Google only 6 days after publication:
If we take a look at a more transactional keyword, for example, “link building service”, you’ll notice that it has both a higher density and search volume, making it much higher to rank for with SEO alone:
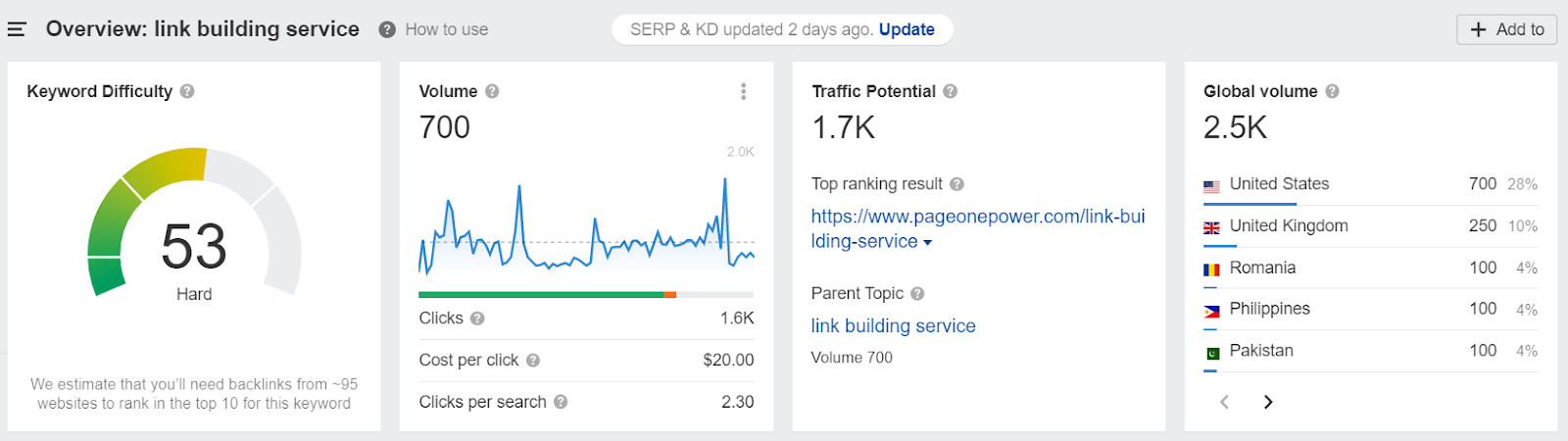
If you look at the actual search results for this keyword, you’ll notice that most of them are advertisements and landing pages:
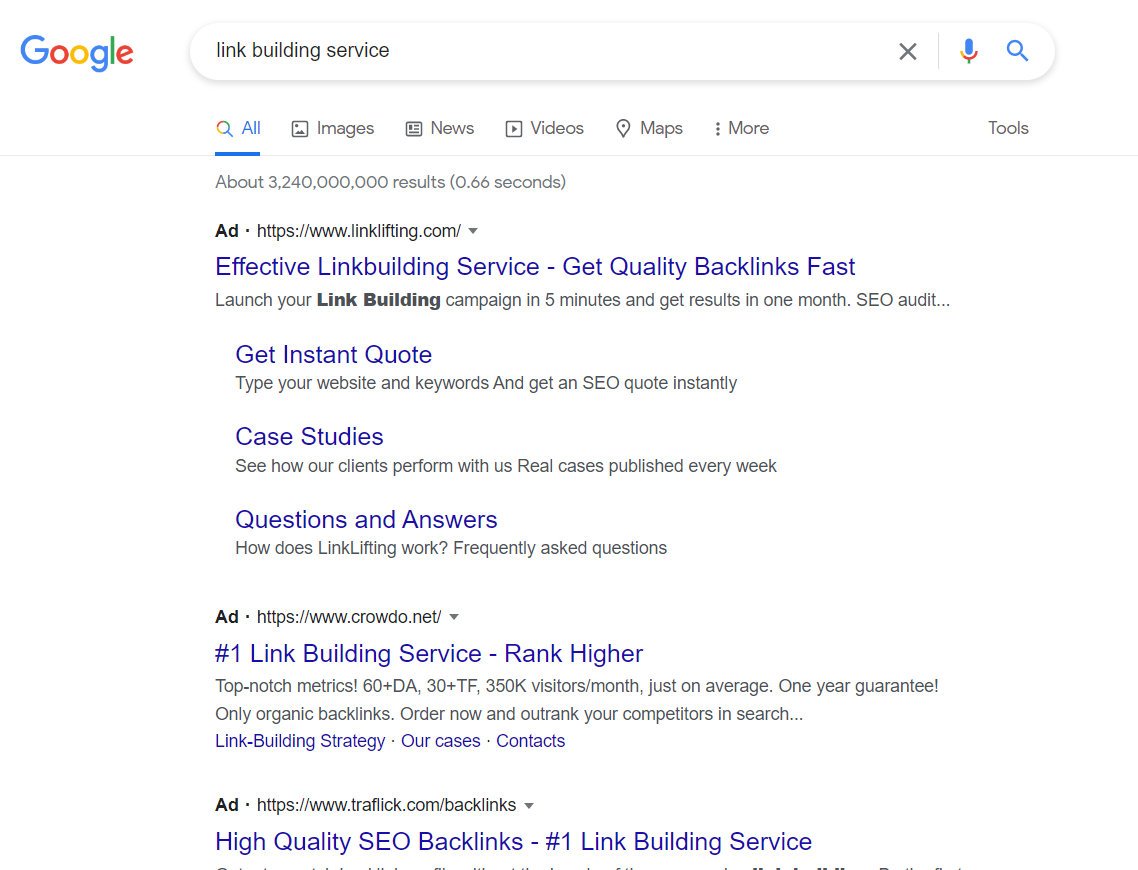
Meaning that if you were to launch your own landing page trying to target that keyword, it would most likely get drowned out by the competition, unless you’re the highest PPC bidder.
So, to sum it up:
- SEO works better for informational keywords
- PPC makes it easier to rank for “difficult” transactional keywords
How Long Does SEM Take?
Again, it really depends on which route you decide to take.
If you try to rank for high-density and volume keywords, SEO can and will take you a long time.
Ranking for your target keywords can take months, but generally, SEO is a much more sustainable and evergreen practice than PPC.
In contrast, if you’re able to identify low-density, but highly relevant keywords within your niche, you can start ranking on the first page of Google within as little as a week.
PPC can get you ranking on the top spots of search engine results pages within just hours of launching your campaign.
SEM Cost
Both SEO and PPC can get quite expensive.
On average, hiring an in-house SEO specialist will cost you around $52,000 in the U.S., according to Glassdoor.
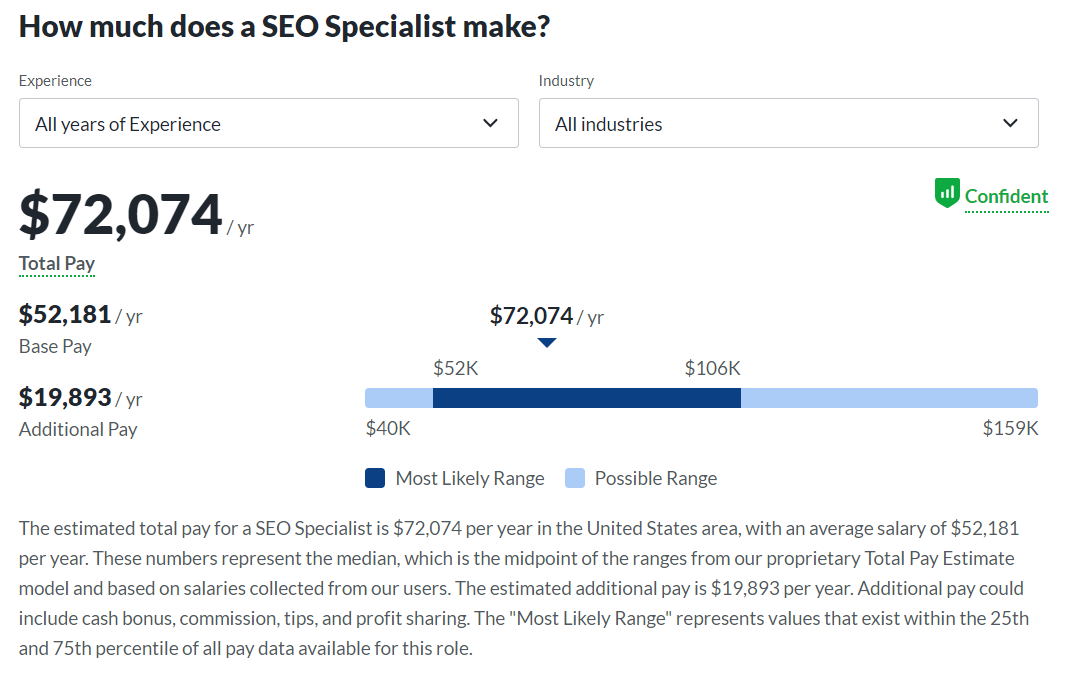
However, a single SEO specialist likely can’t cover all of your search engine optimization needs simply because of how expansive SEO really is.
Just take a look at link building – to have any real success with it, you will need at least one person doing it full-time for you. At the very least (if you outsource link building overseas), you will be looking at around $1000/month, just for link building alone.
However, once you get past the point where you need to actively invest in SEO to show up in search results, you will be getting what is essentially free traffic.
As for PPC, the cost per click will vary greatly depending on your keyword of choice.
For example, if you were to pay for a thousand clicks for the “link building” keyword, you would be down $7000, since its CPC is #$7:
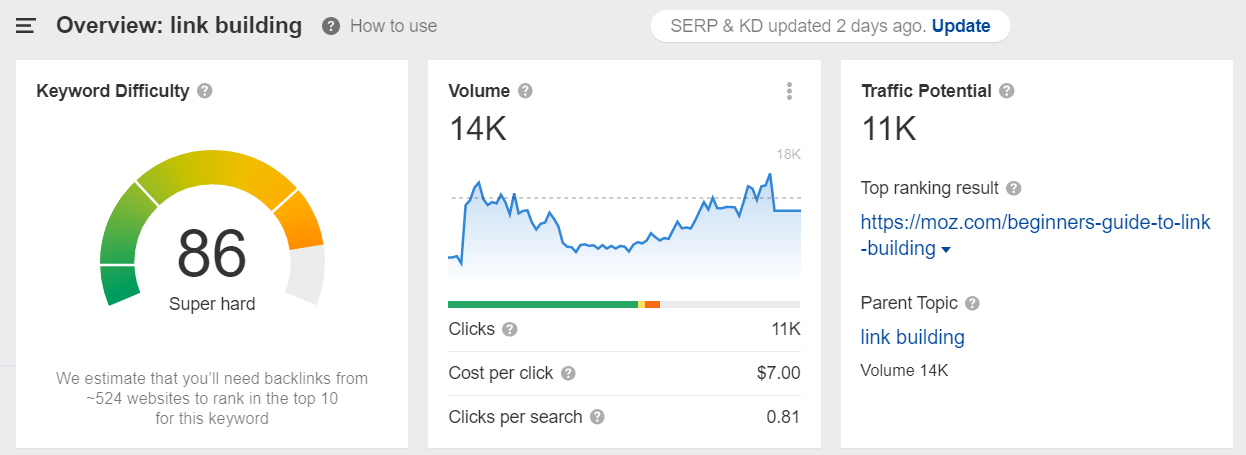
This is $7,000 for every thousand clicks until you stop paying for it.
If you only rely on PPC to generate traffic, this sum will really stack up from month to month.
Link building cheat sheet
Now Over To You
So, is there really a difference between SEO and SEM?
Kind of – SEO is just a subsection of SEM that focuses on generating traffic from organic search.
If you’re deciding whether you should invest in SEO or PPC for your own business – we’d recommend trying both.
Just think of PPC as more of a short-term strategy to boost yourself to the top of search results (as long as you have a budget), and SEO as a way to conquer less competitive informational keywords and start establishing yourself as an authority in your field.
SEO can be an enormous venture, especially if you start to dip your toes into link building.
So, if you ever need help running your own link building campaigns, don’t hesitate to start your free trial with Respona and start building links to your own website in no time!