Search engine optimization is a huge, ongoing process for any website.
Without it, you will struggle to gain traction, and generate traffic and sales for your business.
Don’t know how to get started with your SEO strategy this year?
In this article, we will be diving deep into:
- What is On-Page, Off-Page, and Technical SEO
- What is an SEO strategy
- How to develop a strong content strategy
- Why link building is important for SEO
- How to perform the most important On- and Off-Page SEO strategies
- Essential SEO tools
As a link-building software, we know about the importance of SEO first-hand, and are more than happy to share our knowledge.
With the help of SEO, we have helped our sister organization, Visme, to over 2.5 monthly organic traffic:
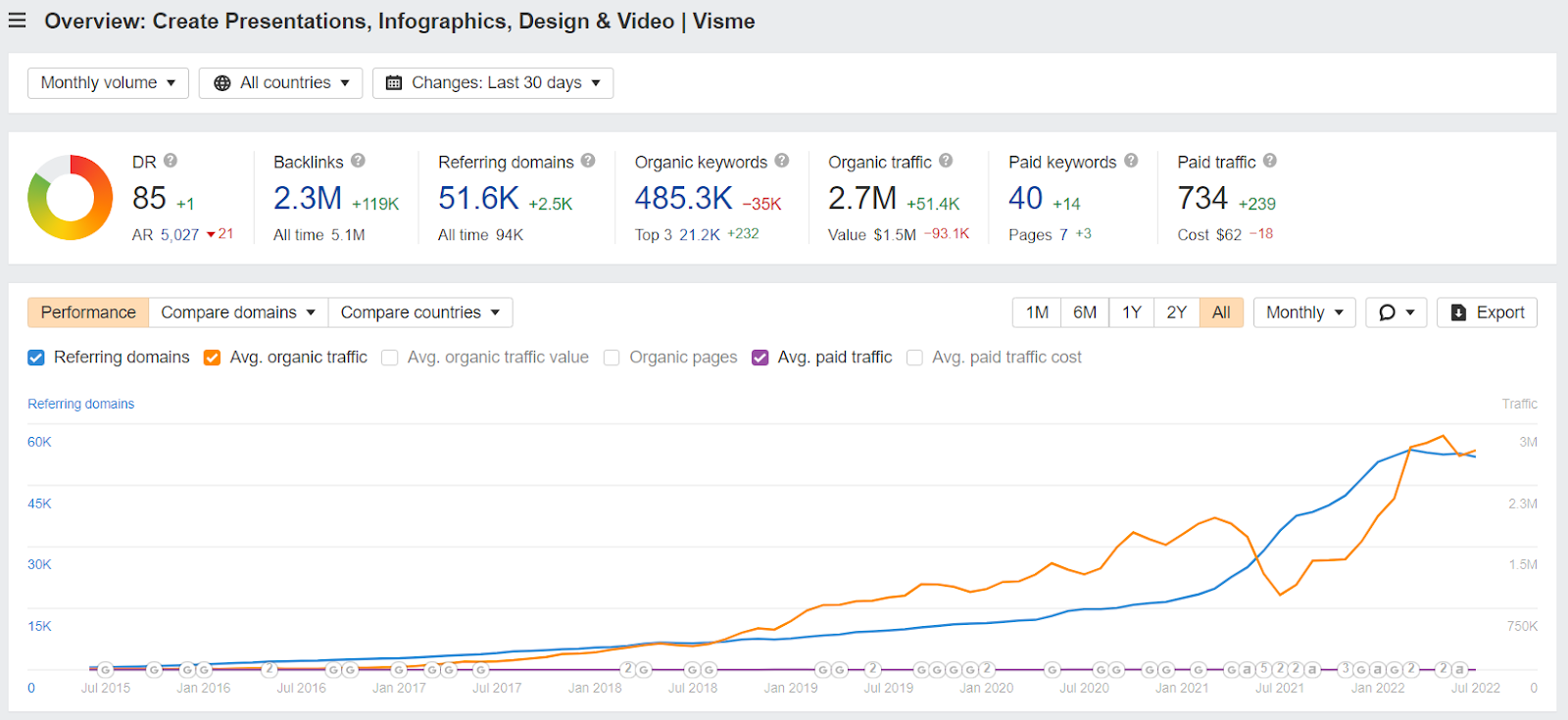
This traffic is estimated to be $1.5 million dollars a month in revenue.
Dying to achieve similar results?
Let’s dive into it.
Link building cheat sheet
What Are the 4 Pillars of SEO?
The 4 pillars of SEO are:
- Content
- On-page SEO
- Of-page SEO
- Technical SEO
Before you can start working on your SEO strategy, it’s important to understand exactly what the four aspects of search engine optimization are, and what they entail.
Content
Content is the foundation of your website.
If you don’t have any content on your site, there is nothing to optimize for search engines.
Developing a solid content strategy and providing your audience with high-quality, actionable content should be the first step of your SEO strategy.
On-Page SEO
As the name suggests, on-page optimization relates to every activity you perform on your own website.
At the core of on-page SEO lies keyword research, creating, and optimizing all of your website content.
This includes everything from your homepage to your blog, service, product, and contact pages.
Image optimization is also a large part of on-page SEO.
Even though meta descriptions and title tags technically appear on search engine results pages and not your website, they are considered on-page SEO as well.
Off-Page SEO
As you might have guessed, off-page SEO is every activity you perform outside of your website.
The majority of off-page SEO is link building, but also includes social media, Google My Business listings, online reviews, and other things that can affect your site’s rankings externally.
In 2012, Google released the Penguin update to combat spammy link building practices.
It was aimed at increasing the importance of high-quality backlinks from actually authoritative resources to reward actually good content and reduce the number of low-quality results that appeared high in SERPs thanks to black-hat tactics.
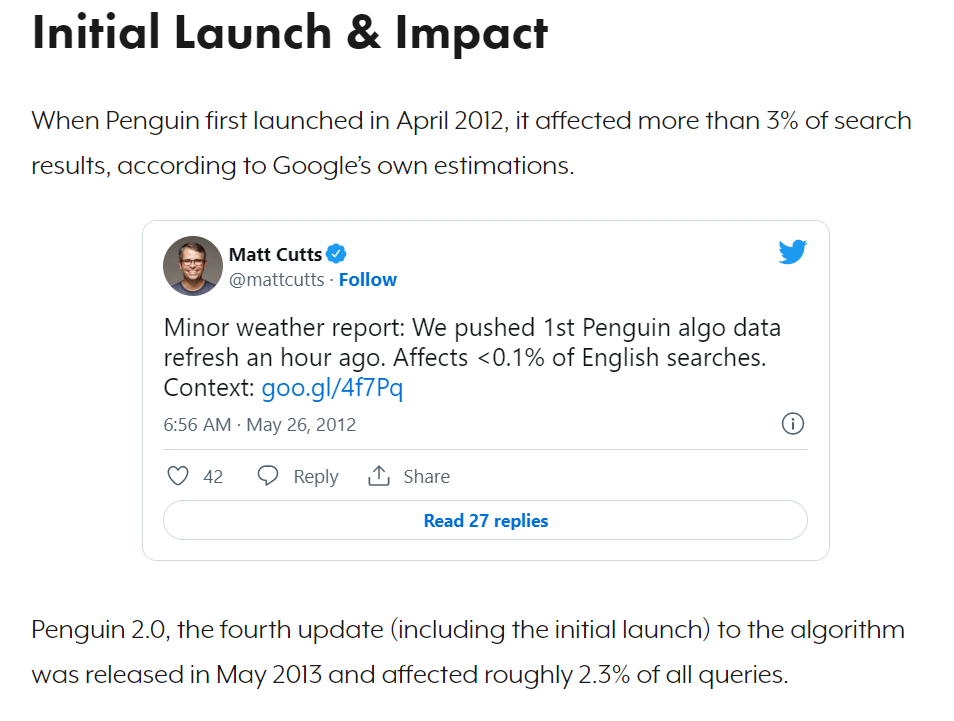
It changed the way SEOs go about link building, completely de-valuing low-quality link schemes, and encouraging people to focus on white-hat link building tactics.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is all about ensuring that your website runs smoothly, and is easily indexable by search engines.
Technical SEO starts before your website even goes online. Whether you develop your site from scratch or use a pre-made template, a big chunk of technical SEO is making sure your website’s code is clean and runs fast.
Everything that ensures your website’s indexability is also considered technical SEO. This includes internal linking, sitemaps, 301 re-directs, and making sure you don’t have any broken links on your pages.
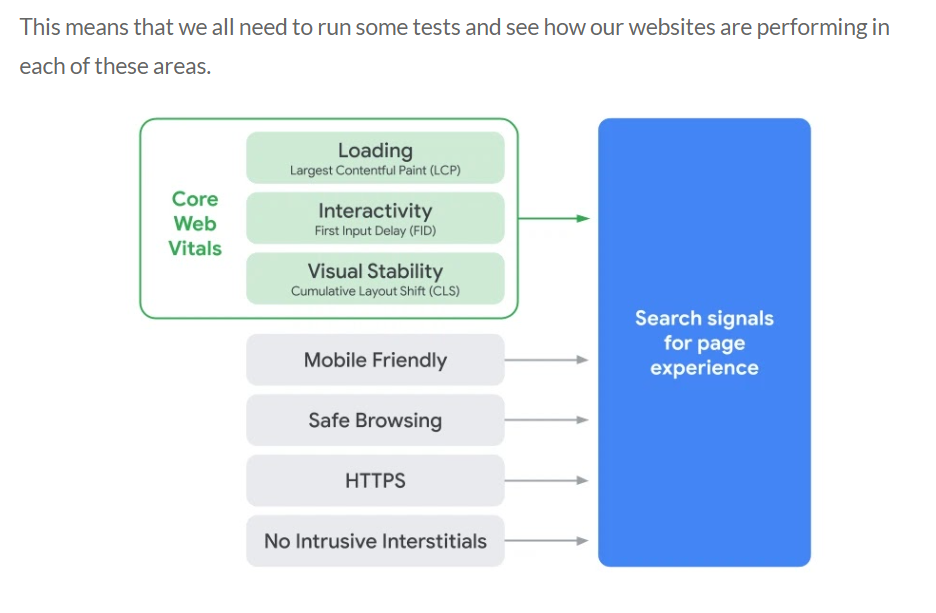
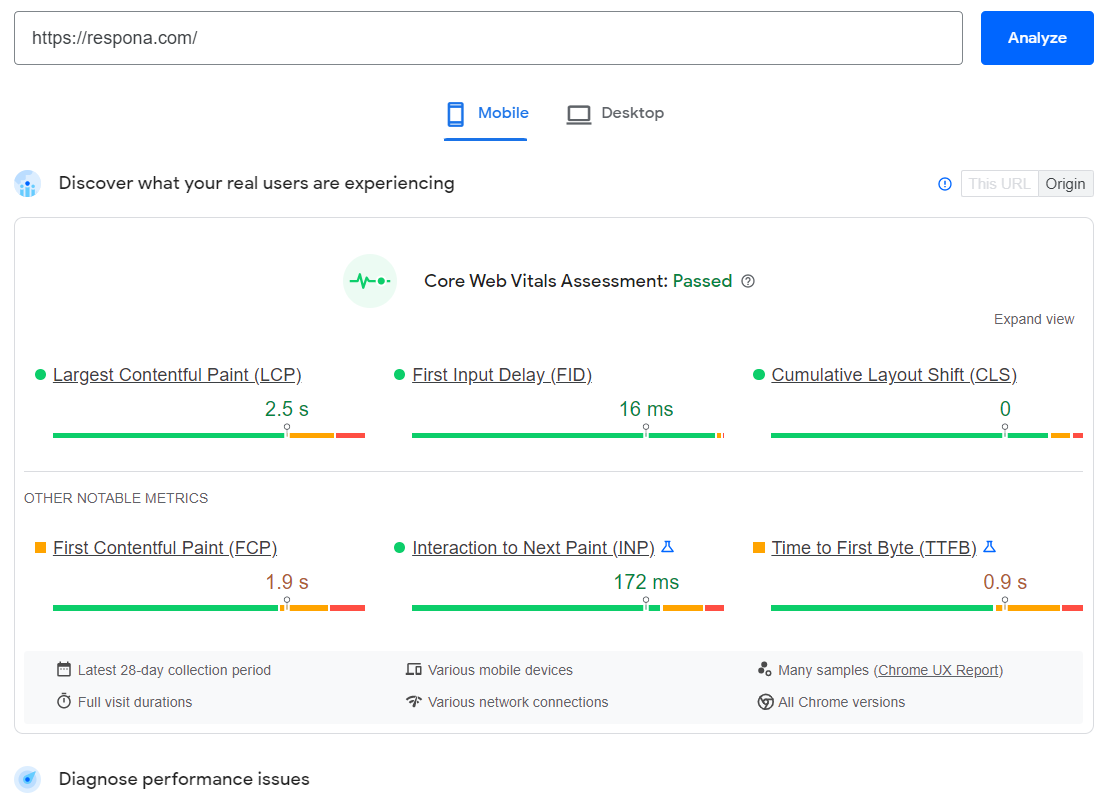
In 2021, Google released the Core Web Vitals update, which emphasized the importance of your Page Experience even further.
Core Web Vitals on their own are an old concept, but since June 2021, they play a major role in calculating your website’s rankings.
They include:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) – how long it takes for your website to load as a whole. An ideal LCP is considered less than 2.5 seconds.
- FID (First Input Delay) – the amount of time it takes your website to react to user input. A “good” FID is less than 100 milliseconds.
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) – how likely your elements are to shift, or change positions on a page, especially during loading. You should strive for a CLS less than 0.1.
What Is an SEO Strategy?
An SEO Strategy is the collection of all your activities aimed at improving your website’s rankings.
It includes everything from developing a website that runs smoothly to producing high-quality content and optimizing it for keywords, building backlinks, and running content audits.
So, you have a website. How do you get started with your SEO strategy?
Well, if you don’t have any content yet, there isn’t really much to optimize. So, the first step is to work on your content strategy.
How to Develop a Solid Content Strategy
Building a website is a lot like building a house, and content is its foundation.
There are four steps to developing a content strategy:
- Identifying the right keywords to target
- Assigning your keywords scores and prioritizing them according to their relevance, traffic potential and competitiveness
- Creating a blog content plan
- Actually producing the content
In this section, we will discuss each step in greater detail.
Conduct Keyword Research
The first step in creating any kind of content strategy is, of course, researching the keywords within your niche.
This can be done with a variety of SEO tools. In our example, we will be using Ahrefs’ Keyword Explorer.
Enter in your niche. We’ll do “link building”, as it’s one of the main keywords we’re aiming for.
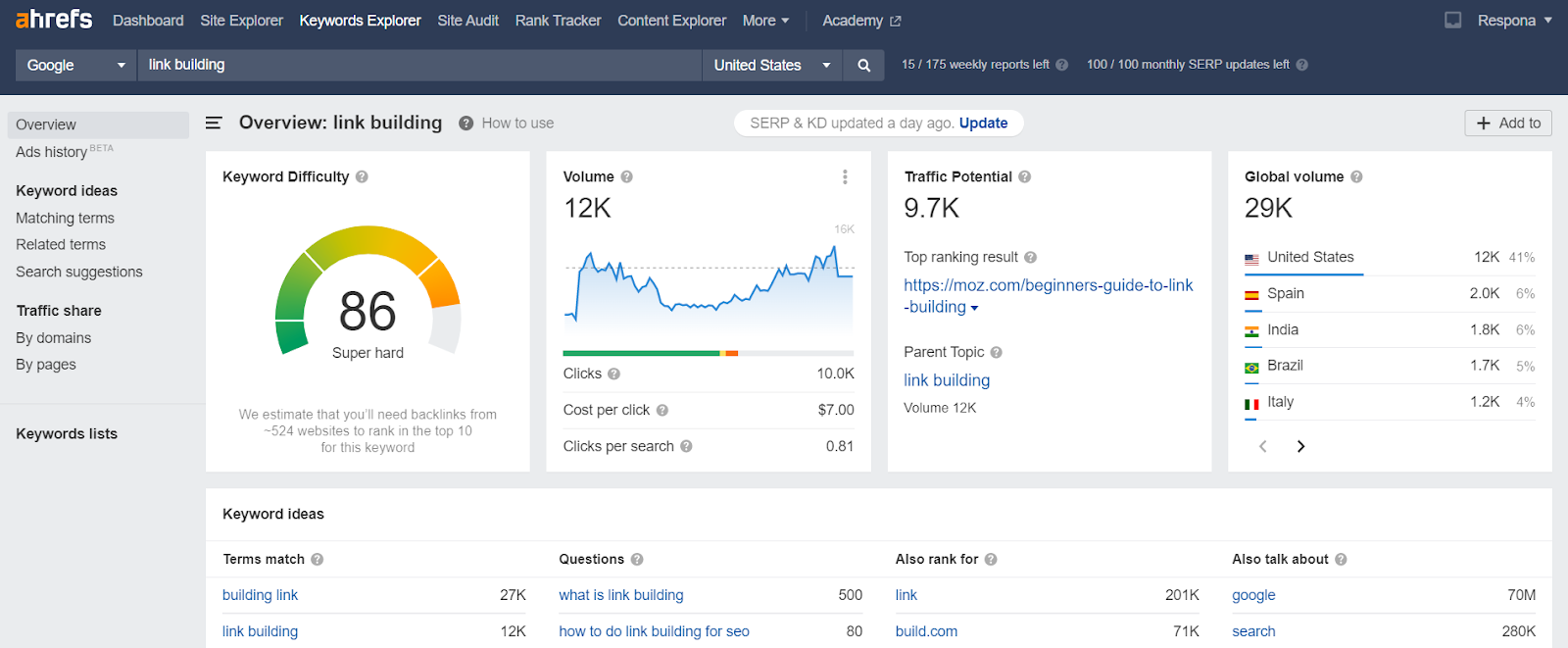
You will see an overview of this specific keyword as well as its most important metrics:
- Keyword Difficulty
- Volume
- Traffic Potential (how much traffic the first result ranking for this keyword gets)
- Cost per click
This will be your parent keyword. Or, at least, one of them.

If you click on “Search Suggestions” in the left side menu, you will be taken to a screen listing other keywords associated with your parent keyword as well as their metrics.
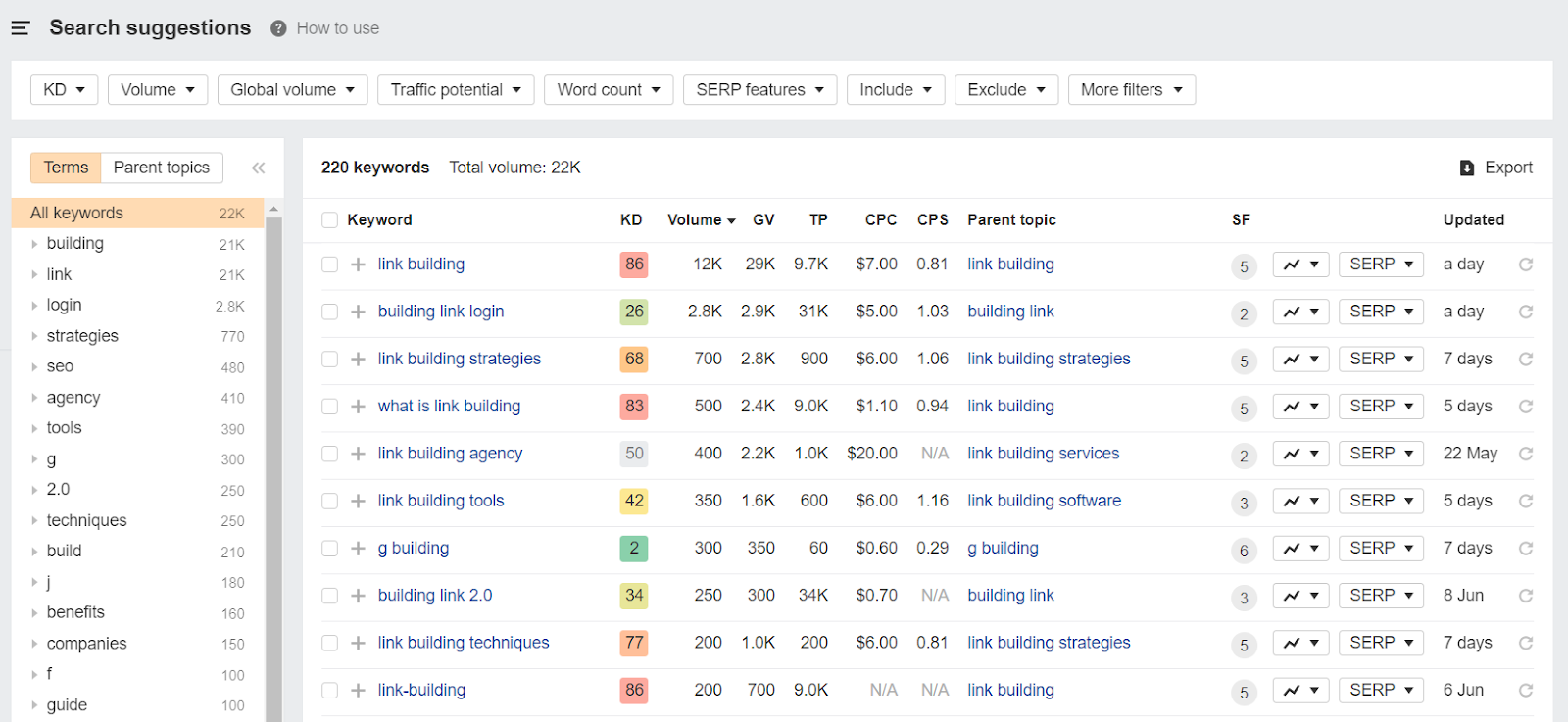
Keyword Difficulty approximates how hard it is to rank for a particular keyword, as well as how many backlinks you will require to rank in the top 10 search results.
Ideally, you want to target with a low difficulty, but high volume to get easy traffic.
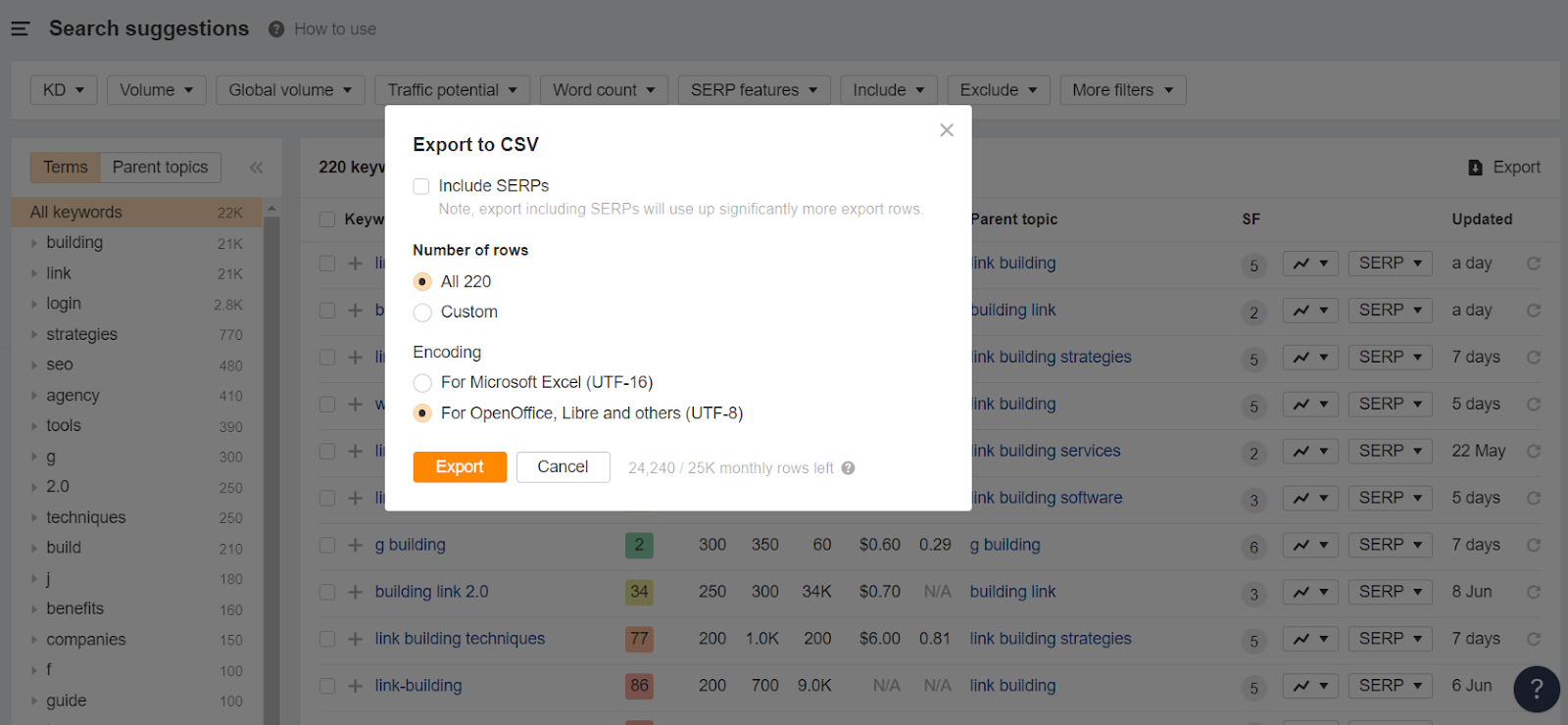
In reality, though, picking good keywords to target can be a little more complicated than that.
How to Prioritize Keywords to Target
Not all keywords that Ahrefs gives you will be relevant to your business.
And even if they are relevant, they might not be great ones to target because of their high competition.
Also, manually sifting through keywords and just guessing which ones are good to target is not the best way to go about this process.
It takes a lot of time, and you might end up with more difficult keywords when there are better opportunities available.
You should always prioritize keywords with the highest traffic potential and commercial intent, and lowest competition.
Luckily, there is a formula that you can use to quickly determine prime keyword opportunities.
The formula is:
(1/difficulty) * traffic potential * (CPC+1) = Keyword Score
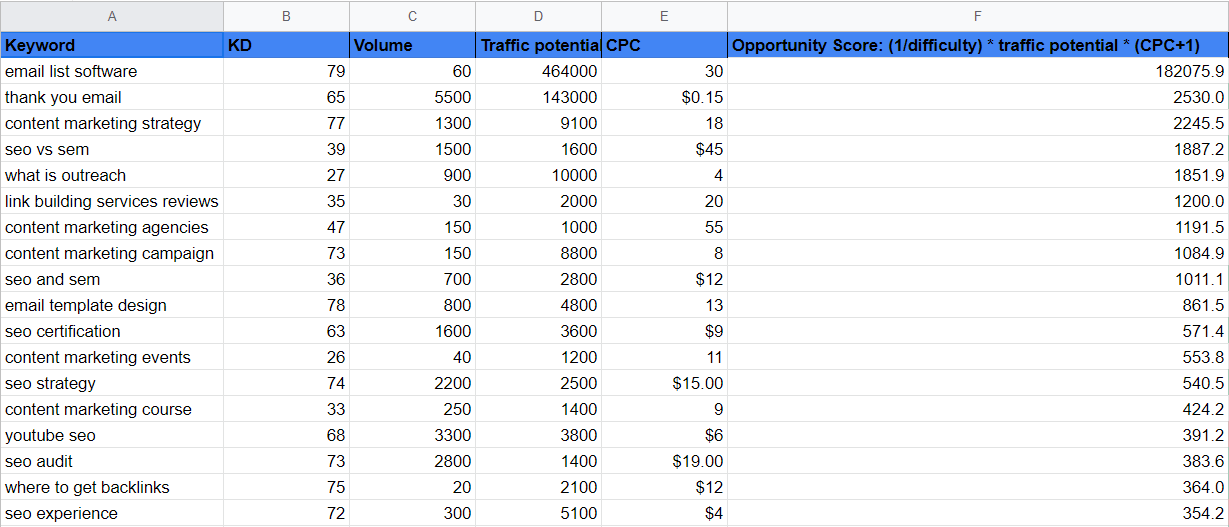
The higher the keyword score you get using this formula, the more relevant and important it is for your blog.
Experiment with different variations of your parent keyword (and other keywords relevant to your niche), and export them from Ahrefs.
Rank your keywords in descending order depending on their Keyword Score to make it easier to prioritize the best ones.
Create a Blog Content Plan
Once you have identified and graded your keywords, it is a good idea to organize them into a content plan depending on the frequency of your uploads.
Another crucial point that you should consider when selecting your keywords is user intent.
User intent is the goal that a person has when they perform a search on a search engine. There are four main types of user intent:
- Navigational: The user is looking for a specific website or page.
- Informational: The user is looking for information on a topic.
- Transactional: The user is looking to buy something.
- Commercial: The user is looking to research a product or service before buying.
To identify the user intent for your keywords, you need to think about what the user is trying to accomplish with their search. For example, if someone searches for “buy shoes online,” their intent is transactional. If someone searches for “shoe size conversion chart,” their intent is informational.
This content plan can take many forms – from a simple sheet of paper with blog post ideas on your table to an in-depth spreadsheet with detailed lengths and outlines of your future content.
It is really up to you how you decide to do it – the whole point of a content plan is to organize your content production instead of looking for new keywords to target every time you decide to write a new piece.
Here is a simple template for a content plan/keyword sheet that you can grab and use.
Produce Quality Content Consistently
Once you have your content plan, it’s time to start working on your blog posts and other pages aimed at your target keywords.
Content production is a multi-stage process as well. It consists of:
- Research
- Gathering expert insights from industry leaders
- Writing
- Editing
Simply re-writing the same article every one of your competitors already has likely won’t do much for your blog.
It will generate a little bit of traffic, but it won’t be groundbreaking.
To get the most out of your blog (and not waste time and resources on something that doesn’t deliver your desired results), you need to make sure every single upload is as good as it can possibly be.
One way to ensure this is by creating 10x, or skyscraper content.
Essentially, this method entails conducting thorough competitor analysis, checking exactly how long their own articles on the same topics are and which angles they covered them from.
Based on that information, you can figure out a way to improve on that content or add another floor to the skyscraper.
For example, as of the time of writing this very article, the top-ranking result for the “SEO strategy” keyword is Hubspot’s guide.
It doesn’t go nearly as in-depth into each individual off-page, on-page, and technical SEO strategy as our article.
Our blog post covers many facets that HubSpot’s one doesn’t, so this article can be considered “10x” content.
Skyscraper content can be extremely time-consuming to create.
So, don’t worry if you’re not able to upload every day or even every week.
It’s better to scale things down and provide consistently valuable content to your readers than to pump out articles just to fill in the keyword gaps.
Simply replicating your competitors’ content is also not going to cut it – they are already ranking for your keyword, and if you don’t have anything unique to put on the table, it’s very unlikely that you will outrank them.
Another type of content that should be part of your plan is evergreen content.
As the name suggests, it’s content that stays relevant for long periods of time, is easily sustainable, and doesn’t require frequent updates.
Common evergreen content formats include:
- How-tos
- Listicles (or top 10 articles)
- Product or service reviews
- Tips and tricks
For example, this guide by Ahrefs on, well, what is evergreen content can be considered evergreen content itself:
While producing your content (especially informational), you should also strive to optimize it for featured snippets.
Featured snippets are portions of your content that appear on search engine results pages without the user even needing to enter your page.
Securing a featured snippet is arguably more important than actually ranking as #1 for your target keyword.
There are five types of featured snippets:
- Simple paragraph
- Numbered or bulleted list
- Table
- Video
And three ways to optimize your content for featured snippets:
1. Keep your content clear and concise.
When creating content, make sure to focus on delivering information in a clear and concise manner. This will make it easier for Google to understand your content and match it to user queries.
For example, if your subheading is “What are the 4 Pillars of SEO?”, the content right below it should immediately answer this question, ideally in a list.
“The 4 pillars of SEO are:
- Content
- Off-page SEO
- On-Page SEO
- Technical SEO”
2. Use keyword-rich titles and descriptions.
Make sure to include relevant keywords in your content’s title and descriptions. This will help Google match your content to user queries that contain those keywords.
3. Format your content using structured data.
Structured data is a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content. It is used to help search engines and other applications better understand the content of a page and provide richer search results.
There are many different ways to add structured data to a page, but the most common method is to use the JSON-LD format. JSON-LD stands for JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data and is a way to encode Linked Data using JSON.
To add JSON-LD to your page, you will need to add a script tag to the head of your page with the type attribute set to “application/ld+json”. Inside this script tag, you will need to add your JSON-LD code.
Here is an example of JSON-LD code that could be used to provide information about a blog post:

Optimize for On-Page SEO
As we already mentioned, on-page SEO refers to the process of optimizing elements that appear on your website for search engines.
Title tags
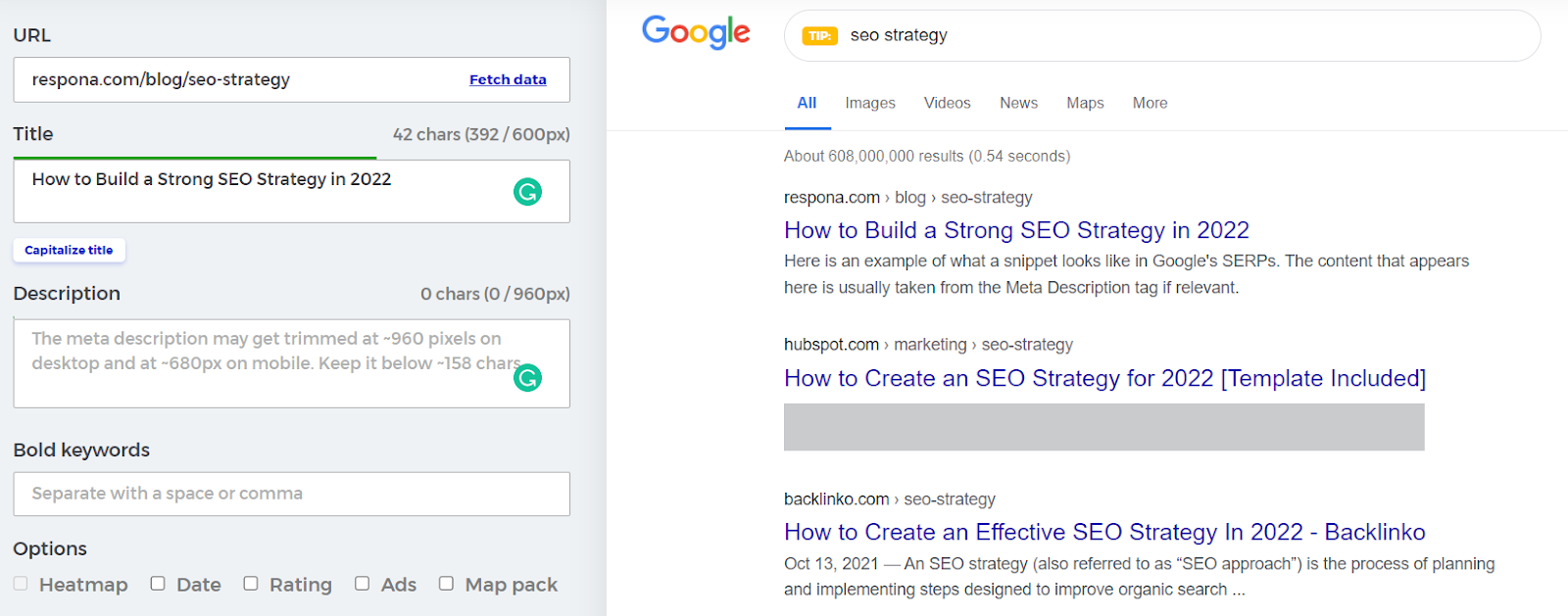
Title tags are the HTML elements that specify the title of a web page. Title tags are typically used to display the page’s title in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
To optimize title tags for SEO, it is important to keep them short, relevant, and descriptive. It is also important to include keywords that are relevant to the page’s content.
Your title tag should be no longer than 60 characters in order to not get truncated.
Additionally, titles that have their target keywords in the very beginning tend to perform better in search engines than ones with their target keyword in the middle or end.
With that being said, you should avoid keyword stuffing and only use your keyword once.
If you’re not sure how your title tag will look on search engine results pages, you can use a SERP preview tool to make sure it doesn’t get truncated.
Meta descriptions
A meta description is a short description of a webpage that is shown in the search engine results pages (SERP).
The meta description is meant to give the searcher a brief preview of what the page is about so that they can decide if they want to click through to the page.
Meta descriptions are important for SEO because they are one of the factors that can influence a searcher’s click-through rate (CTR). A higher CTR can lead to more traffic to your website.
To optimize your meta descriptions for SEO, you should:
– Keep them short and to the point (less than 160 characters)
– Use keywords wisely
– Use compelling language that encourages searchers to click through to your page
– Make sure each meta description is unique
Just like with the title tags, you can use a SERP preview tool to make sure it does not get truncated.
Header tags
Header tags are HTML tags that are used to indicate the header of a section or subsection on a webpage. The header tag can be used to specify the title, subtitle, or other heading for a section of text.
For example, the header just above the previous paragraph is an <h3> header.
There are six different levels of header tags, which are indicated by the number in the tag. For example, the tag <h1> indicates the most important header, while the tag <h6> indicates the least important header.
Header tags are important for SEO because they help search engines understand the hierarchy of information on a webpage.
For example, if a webpage has a header tag <h1> followed by a header tag <h2>, the <h1> tag indicates that the text that follows is more important than the text that follows the <h2> tag.
To optimize header tags for SEO, it is important to use the appropriate tag for the level of importance of the text.
In addition, header tags should include the keywords that you’re trying to rank for. For example, if a webpage is about SEO, the <h1> tag needs to have some variation of “SEO” in it.
On our website, we only use the <h1>, <h2>, and <h3> headers.
The <h1> is, of course, the title, the <h2> headers separate sections in our content, and <h3> headers further separate those sections into sub-sections.
If you want to break up your content even further, you can, but most of the time there is no real need to go past <h3>.
Link tags
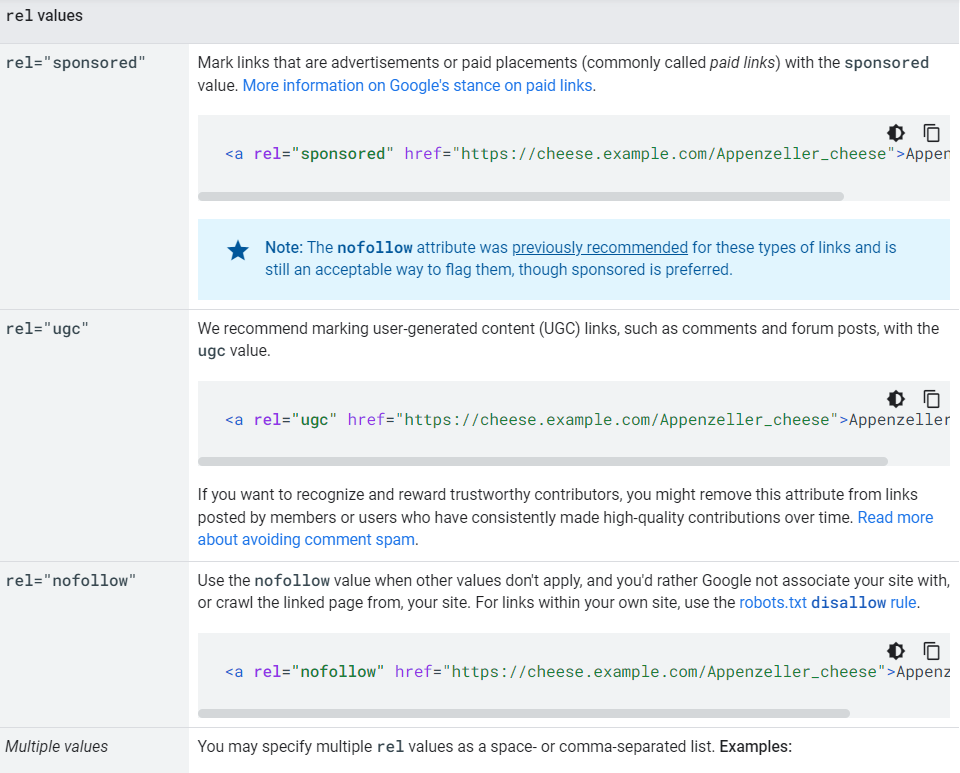
There are many different tags links can have, but the most important three are:
- Dofollow
- Nofollow
- Sponsored
The dofollow link tag is an HTML tag that tells search engines to follow the link to the page. This is the default setting for most links, and is important for SEO because it allows search engines to find and index the pages linked.
The absence of either a “dofollow” or “nofollow” tag makes the link “dofollow” by default.
Dofollow links also pass on link equity.
The nofollow link tag is an HTML tag that tells search engines not to follow the link to the page. This is used for links that are not trusted, or for sponsored links.
Nofollow links do not pass on link equity and so do not have any SEO impact.
However, they still direct traffic to the linked website, so they should not be ignored.
Sponsored links are links that are paid for by a company, and are usually marked as nofollow so that they don’t affect the search engine ranking of the page they’re linking to.
All paid links are required to have the “sponsored” tag by Google.
Keyword density
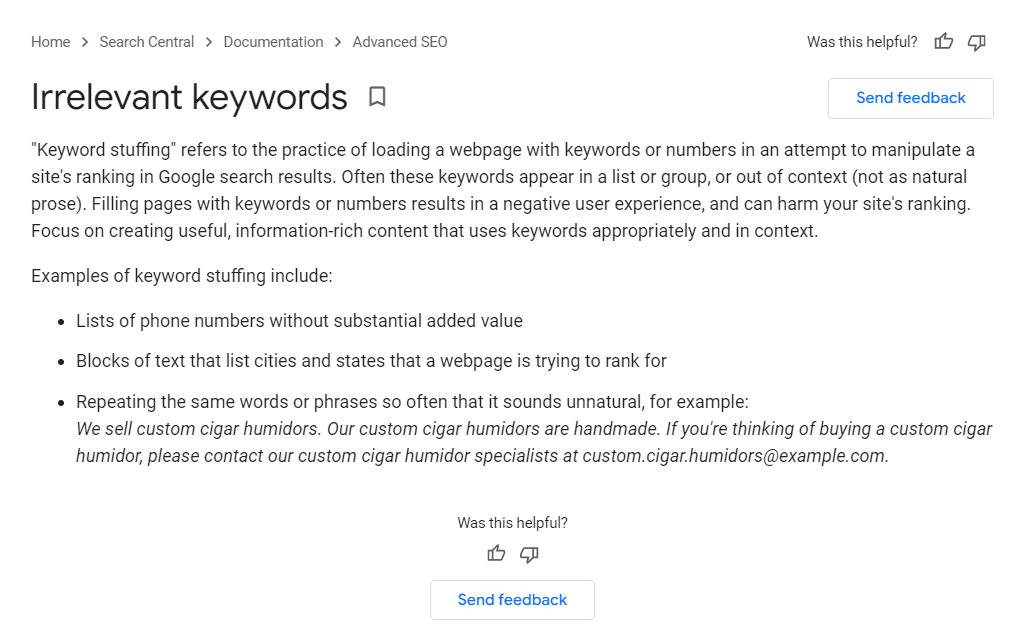
Keyword density used to be a big ranking factor and many SEOs stuffed their content with keywords to try and manipulate their rankings.
In 2024, it is enough to have your main keyword included in the page’s URL slug as well as its title.
However, including different variations (especially longer-tail ones) in your content can help your page rank for multiple keywords at the same time.
You should only target keywords that are relevant to your content, and space them out naturally, without stuffing them in big chunks.
There are many different tools that can help you optimize your content for keywords.
Two good examples are SurferSEO and MarketMuse.
Personally, we use MarketMuse in-house. Once you enter the main keyword you wish to target with your article and paste in the content, it will highlight exactly which keywords need to be mentioned and how many times throughout the post.
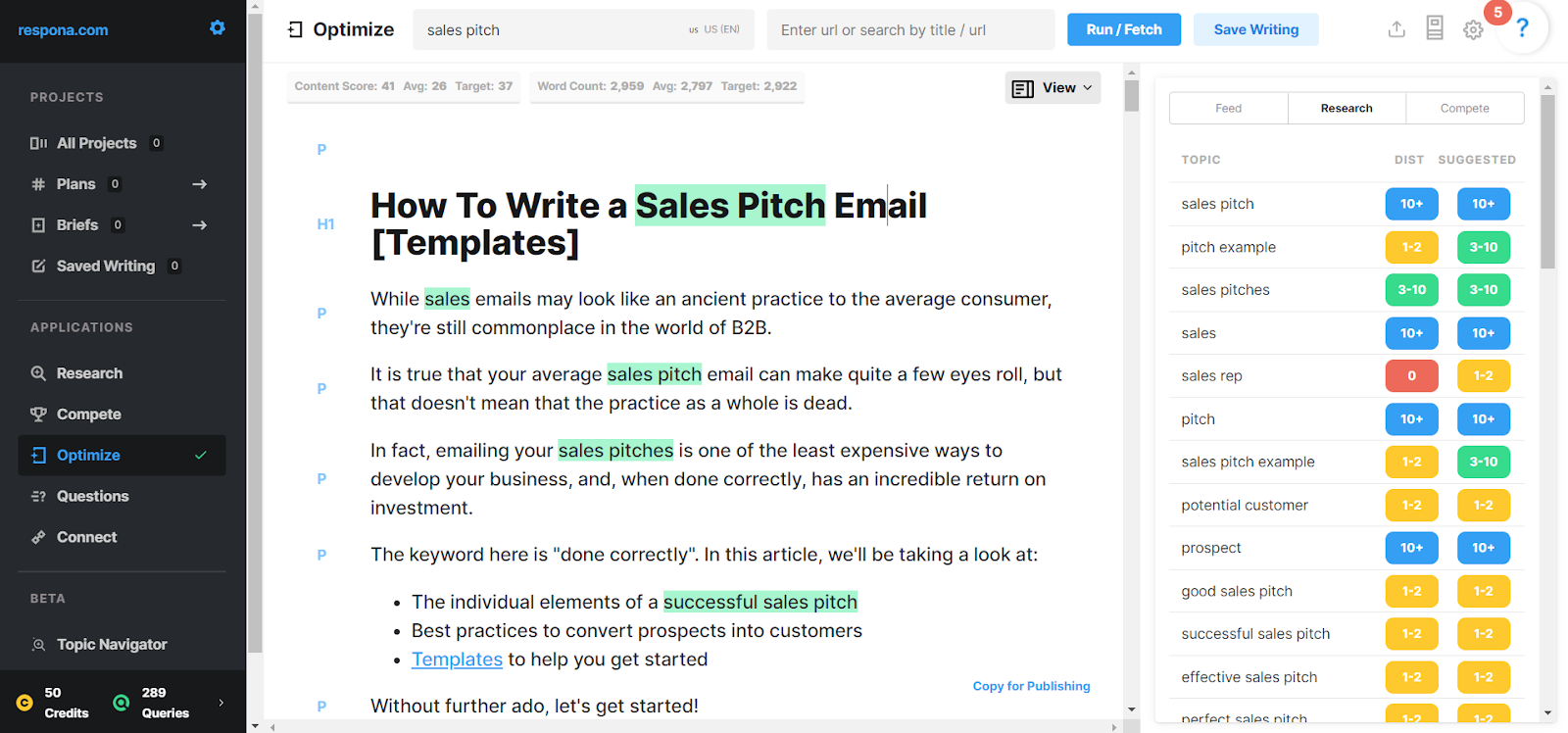
Image optimization
Image optimization is the process of optimizing an image to make it smaller in file size while still maintaining its original quality.
This can be done in a number of ways, such as by reducing the resolution, compressing the file, or using a different file format.
By optimizing your images, you can improve your website’s performance and speed, as well as its SEO.
Another side to image optimization is alternative text.
Alternative text, also known as “alt text” or “alt tags,” is the text that appears in place of an image on a web page if the image fails to load on a user’s screen.
The alt text serves several purposes, including helping users who are visually impaired understand what is on a web page and helping search engines index the content of a page.
When it comes to optimizing alt text for SEO, the key is to make sure that the text is descriptive and keyword-rich.
This will help ensure that your images are properly indexed by search engines and that users will be able to find them when they search for relevant keywords.
Every single image on your website should have an alternative text.
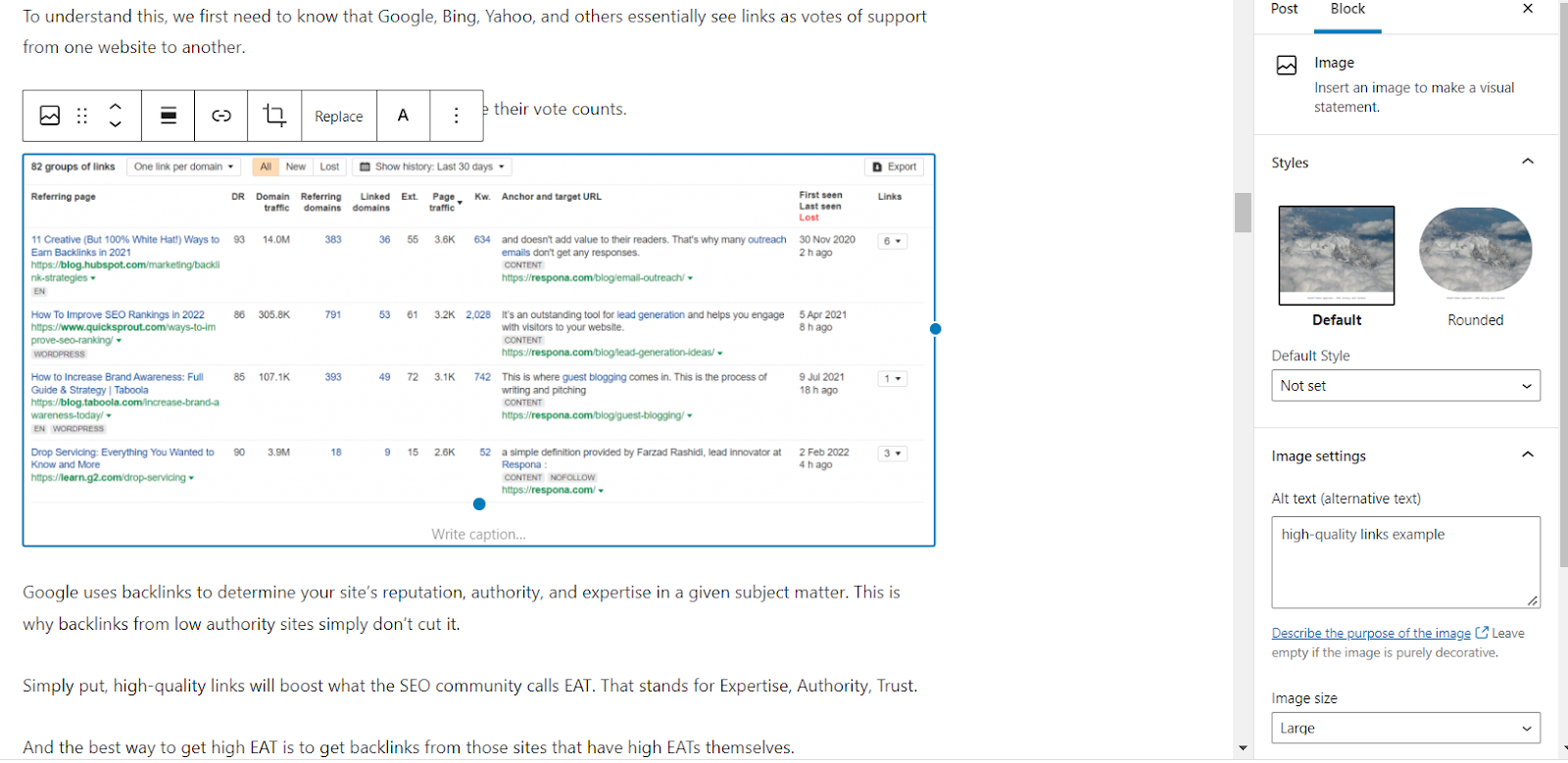
If you’re using WordPress (like us), adding alternative text to your images is very simple.
All you have to do is open the post with your desired image, click on the picture, and enter the alternative text in the image settings window that pops up in the right sidebar.
It is also recommended to use a plugin that automatically compresses all of your on-site images without sacrificing too much quality as manually scaling every picture down can get tedious.
Anchor text
Anchor texts are the pieces of text that are clickable on a webpage.
They can be either internal links, which take the user to another page on the same website, or external links, which take the user to a different website.
The anchor text is the part of the link that is visible to the user and is usually underlined.
Anchor texts are important for SEO because they are one of the factors that search engines use to determine the relevancy of a website.
If a website has a lot of links with anchor texts that are relevant to the website’s content, then the website is more likely to rank higher in search results.
Conversely, if a website has a lot of links with anchor texts that are not relevant to the website’s content, then the website is less likely to rank high in search results.
A good, relevant, and seo-optimized anchor text is one that is keyword rich and descriptive of the page that it is linking to.
It should be short and to the point, and should avoid using generic terms like “click here” or “more information”.
For example, the links on the following screenshots lead to our articles on, you guessed it, the types of links, and white-hat SEO techniques.

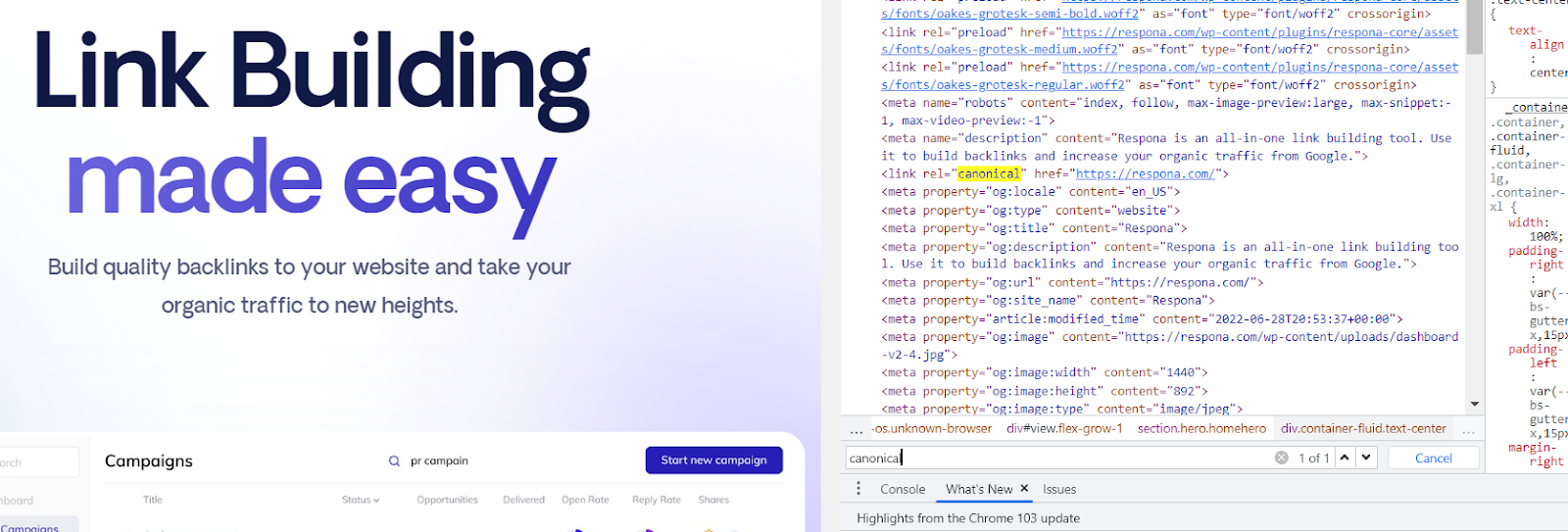
Canonical Tags
A canonical tag is an HTML element that helps webmasters prevent duplicate content issues on their site.
It does this by telling search engines which version of a page is the “canonical” or “master” version.
This is important for SEO because it helps search engines index and rank your content more accurately.
To use a canonical tag, you simply add the following HTML element to the head section of your page:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” />
Replace “http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” with the URL of your canonical page.
You can also use the “canonical” link tag to point search engines to the canonical version of a page that is on a different domain.
For example, if you have a page on your site that is also available on another site, you can use the following canonical tag to tell search engines that the version on your site is the canonical version:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” />
Replace “http://www.example.com/canonical-page.html” with the URL of your canonical page.
The “canonical” link tag is just one of many ways to tell search engines about the canonical version of a page.
Other methods include using the “rel=canonical” HTTP header, and using the “301 redirect” status code.
robots.txt file
A robots.txt file is a text file that tells search engine crawlers which pages on your website they should index and which they should ignore.
This is important for SEO because it allows you to control which pages are included in the search engine index, and therefore which pages are eligible to rank in search results.
To use a robots.txt file on your own website, you will need to create a text file and upload it to your website’s root directory.
The file should contain a list of instructions for the crawlers, telling them which pages to index and which to ignore.
Creating a robot.txt file is a two-step process.
1. Decide which pages on your site you want to be crawled and which you don’t. This is done by creating a “disallow” list of pages you don’t want crawled.
2. Upload the robot.txt file to your website’s root directory.
Here is an example of a robot.txt file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /cgi-bin/
Disallow: /tmp/
Disallow: /admin/
This file tells all web robots to stay out of the cgi-bin, tmp, and admin directories.
Optimize for Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO includes activities such as white-hat link building, brand mentions, or digital PR with the main purpose of improving the rankings of a particular website or web page on the search engine results pages (SERPs).
To put it simply, it consists of actions taken outside of your website that help you gain more online visibility, which is why it’s also known as off-site SEO.
Some of its most prominent actions that you should keep in mind are Link building, Guest blogging, Social bookmarking, and Digital PR
Those are all important off-page SEO techniques and while each plays a major role, link building is usually where marketers tend to focus their efforts.
Why?
Even though Google is constantly updating its algorithm to deliver better results to searchers, backlinks seem to hold their value as a prominent ranking factor.
That’s why gaining high-quality backlinks from relevant and trustworthy sources can increase your own domain authority and, as a result, your organic traffic too.
After all, an important factor for Google when ranking a website is its online reputation and whether it’s considered high-authority in its field.This is why so many companies develop link-building strategies.
These are usually set up by creating great content and developing relationships with influencers and bloggers through email outreach. In fact, 38.4% of professionals in digital marketing spend between $1,000 and $5,000 a month on link building.
Especially if you’re a relatively new business, there are several reasons why off-page SEO will be useful to you.

If we want to understand why backlinks are important, we have to take it back to the 90s, before Google was the king of search engines.
Backlinks came into play with the creation of PageRank, invented by one of Google’s founders Larry Page.
Before Larry Page, search engines would rank pages based mostly on keyword density and on-page factors that many marketers would take advantage of.
With the introduction of PageRank, Google would put an emphasis on backlinks as being an indicator that one page found another page as a valuable resource.
Over time, Google became a pioneer in determining search rankings which led to many many updates that stress the importance of backlinks.
And as marketers started taking advantage of backlinks aka buying them or link stuffing, Google has continued to tighten rules on how sites can legitimately build their backlink profile.
We are talking about, of course, the Penguin update.
Currently, the only reliable and legitimate way to acquire high-quality backlinks to your website is by link building, which leads us to the next section.
Link building
Link building is the process of acquiring backlinks to your website, from other sites. This is mainly achieved through cold email outreach.
High-quality backlinks from relevant, authoritative resources are one of the biggest ranking factors for a website, even in 2024.
As we already mentioned, Google Pengin was released to only reinforce these types of links as a ranking factor.
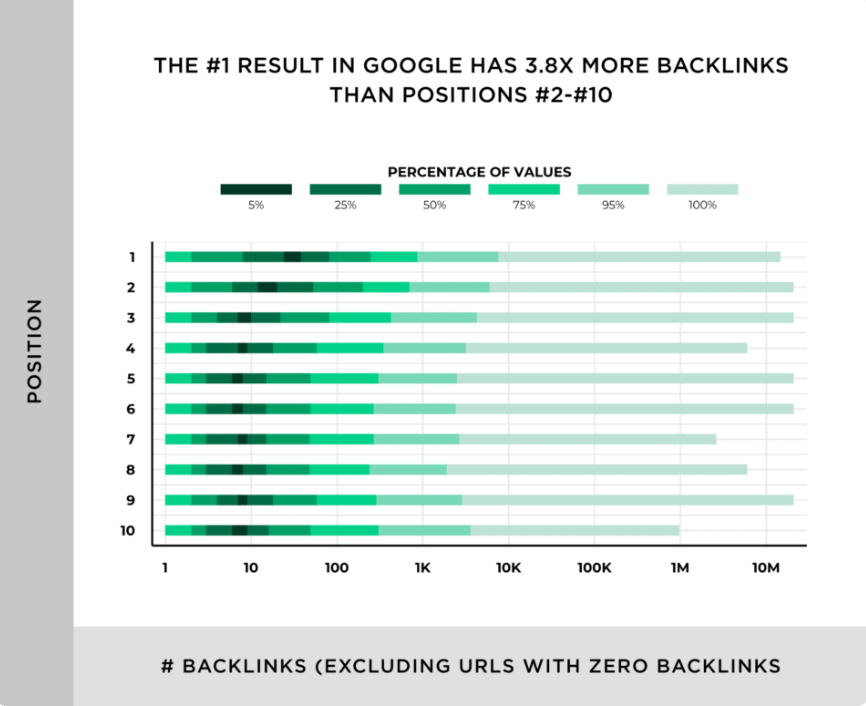
There is a clear correlation between the number of high-quality backlinks a website has and high rankings in search engine results pages:
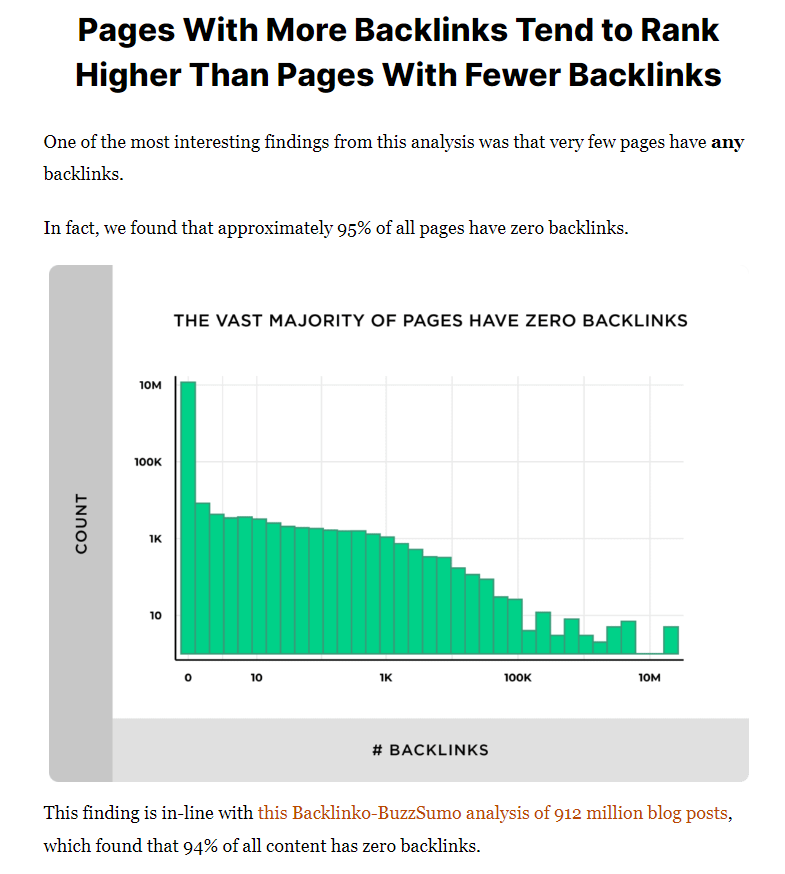
In fact, the average first result on Google typically has almost 4x as many backlinks as next results:
We have already covered the individual link building strategies as well as their step-by-step processes, so we’re just going to list out a few in this section:
- Anchor text strategy
- Competitor backlinks
- Guest posting
- Broken link building
- Unlinked mentions
- Link reclamation
- Listicle outreach
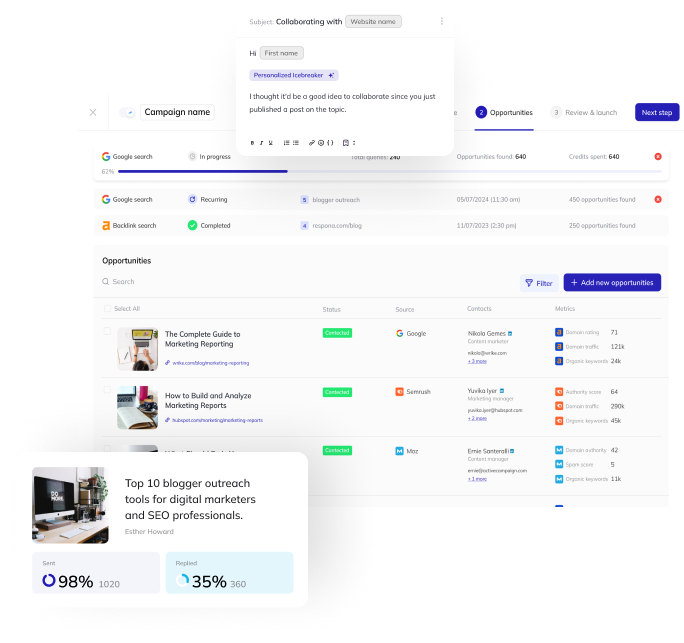
Primarily developed as a link building outreach tool, Respona can help you build backlinks to your website, regardless of the strategy you choose.
Social media
While social media does not directly affect the rankings on your website, it can be a great way to generate traffic, build relationships with your audience and share your content.
Your social media presence can affect your website in several ways:
- By increasing the number of inbound links to your website.
When you post content on social media, make sure to include a link back to your website.
This will help increase the number of inbound links pointing to your site, which is a key ranking factor for SEO.
- By boosting your brand awareness and visibility.
The more active you are on social media, the more people will become aware of your brand.
This can lead to more website visitors, which can in turn improve your SEO.
- By providing fresh and relevant content.
Social media is a great platform for sharing fresh, relevant content that can help improve your website’s SEO.
For example, if you blog regularly, you can share your blog posts on social media to help drive traffic back to your site.
- By building relationships and engaging with others.
Social media is all about building relationships and engaging with others.
The more active you are in these interactions, the more likely people are to visit your website and link to your content.
Local SEO
Local SEO is the process of optimizing your website for Google searches that are made within a certain geographical area.
This can be done by optimizing your website’s title and meta tags, as well as your website’s content, to include keywords that are relevant to your business and that are likely to be used by people who are searching for businesses like yours in your area.
Google My Business is a free tool that allows businesses to manage their online presence across Google, including Search and Maps.
By verifying and editing your business information, you can help customers find you, contact you, and learn more about your business.
It’s important to register your business on Google My Business because it helps you control how your business appears on Google Search and Maps.
When customers search for your business on Google, they’ll see your business name, address, and phone number, as well as your business hours, website, directions, photos, and customer reviews.
Registering your business on Google My Business is easy.
You’ll need to create a Google account if you don’t already have one.
Then, follow the on-screen instructions to add your business information.
Once your business is verified, you can start managing your online presence.
Review sites
Review sites are third-party websites where customers can leave reviews about their experiences with businesses.
Review sites are important for off-page SEO because they provide an easy way for customers to leave reviews about your business, which can help improve your business’s search engine ranking.
Additionally, many review sites allow you to respond to customer reviews, which can show potential customers that you are responsive to customer feedback.
To get your business featured on review sites, you can create a profile on popular review sites or sign up for directories that list businesses in your industry.
You can also encourage customers to leave reviews by providing links to review sites on your website or in your email signature.
Optimize for Technical SEO
Technical SEO is perhaps the hardest and most tedious part of search engine optimization.
Site Architecture
Site architecture is the organization of a website’s content. It includes the structure of the website’s pages and the way in which they are linked together.
A well-organized website will have a clear hierarchy and a logical structure. The most important pages should be easy to find, and the website should be easy to navigate.
Site architecture affects SEO in two ways.
First, it can help search engines understand the structure of the website and index the site’s pages more effectively. Second, it can help visitors find the information they are looking for, which can improve the website’s click-through rate and conversion rate.
There are a few simple rules to follow when optimizing your website’s architecture:
- Make sure the most important pages are easy to find.
- Use descriptive titles and keywords in your URLs.
- Use breadcrumb navigation to help visitors find their way around the website.
- Use internal linking to help search engines index your website more effectively.
- Use redirects judiciously to avoid 404 errors.

Site Speed Optimization
Site speed is the speed at which your website loads. It is measured in seconds and it is important for both SEO and user experience. A slow website can negatively affect your SEO rankings and cost you potential customers.
There are a few key things you can do to optimize your website for fast performance:
- Use a content delivery network (CDN)
- Optimize your images
- Minimize HTTP requests
- Use caching
- Minimize redirects
- Optimize your code
- Use a faster hosting provider
- Use a content management system (CMS) that is optimized for speed
- Monitor your website speed regularly and make improvements as needed
Mobile Optimization
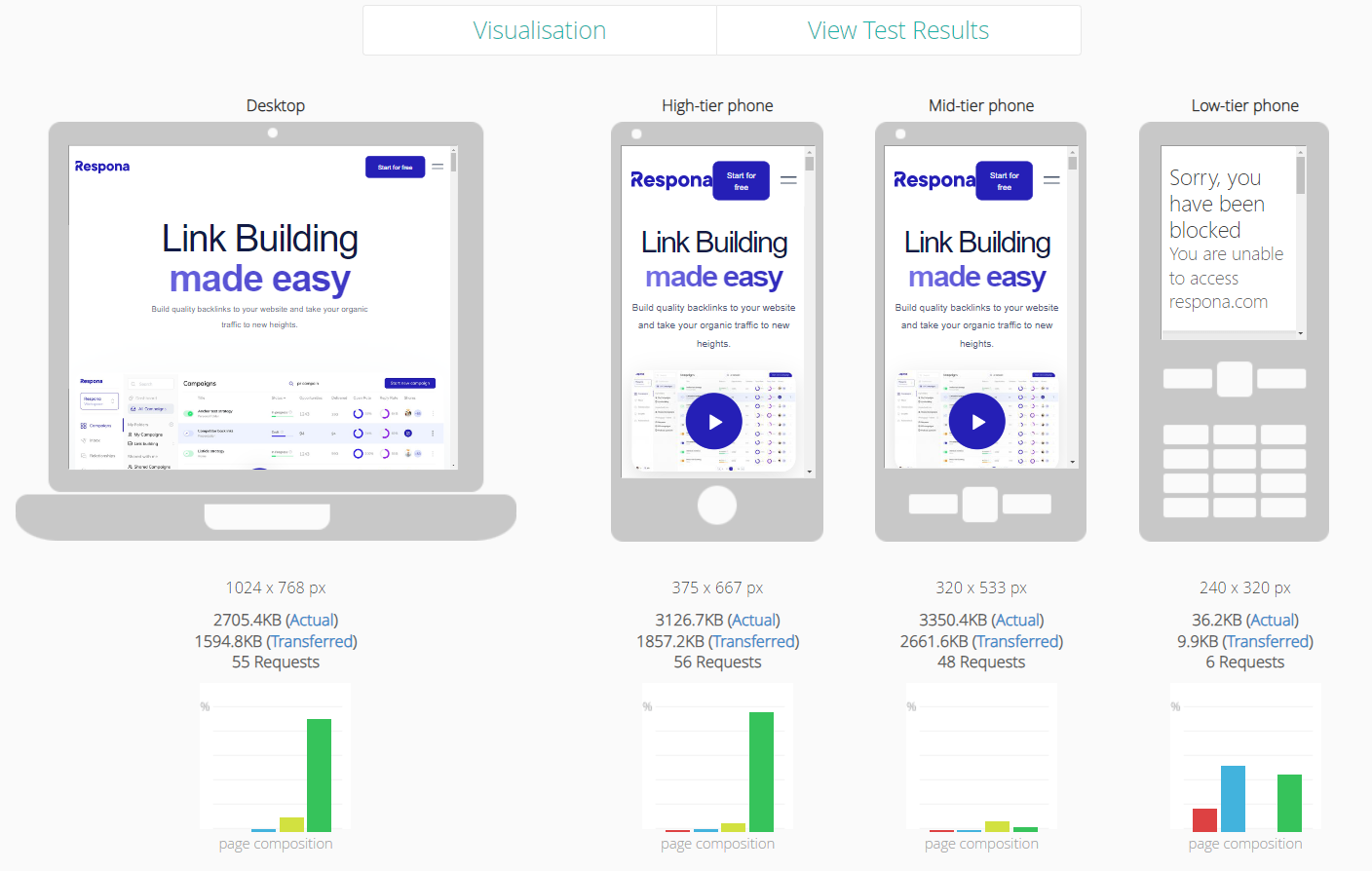
Mobile optimization is the process of making your website more accessible and user-friendly for users on mobile devices.
This includes optimizing your website for different screen sizes, improving load times, and making sure your site is easy to navigate on a touch screen.
Mobile optimization is important for SEO because it can help improve your website’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs), and simply because of the number of people browsing the Internet on mobile devices.
There are a number of different strategies you can use to optimize your website for mobile, but some of the most important things to keep in mind are:
- Make sure your website is responsive. This means that your website should automatically adjust to fit the screen size of the device it’s being viewed on.
- Improve your website’s load time. Users are less likely to stick around on a website that takes too long to load, so make sure your website is as fast as possible.
- Use large, easy-to-tap buttons and links. Small buttons and links can be hard to click on a mobile device, so make sure your website’s design is mobile-friendly.
- Simplify your website’s navigation. Too many menu items can be overwhelming on a mobile device, so keep your website’s navigation clean and simple.
- Optimize your images. Large images can slow down your website, so make sure to compress your images before uploading them to your website.
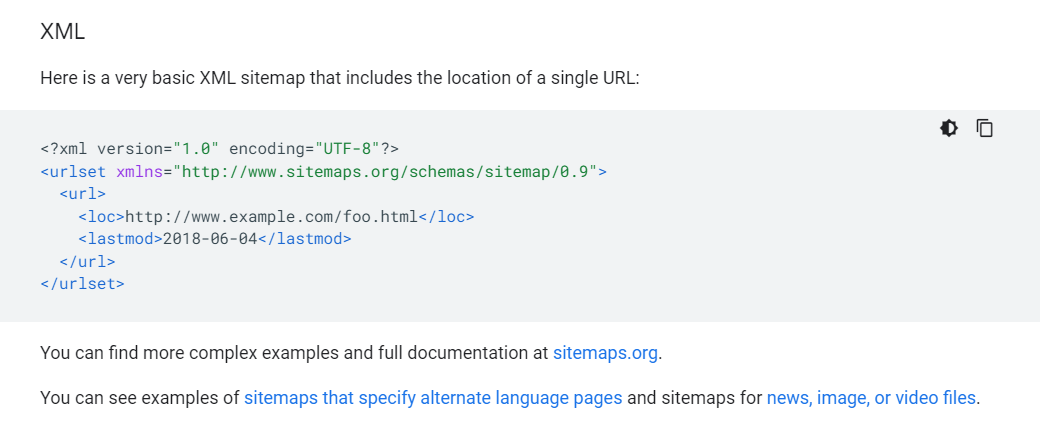
sitemap.xml file
A sitemap is a file that contains a list of all the pages on your website. This file is then used by search engines to crawl your website and index all of your pages.
Sitemaps are important for SEO because they help search engines find and index all of your website’s pages. This makes it easier for your website to rank in search results.
Creating a sitemap is simple. Just create a file called sitemap.xml and place it in the root directory of your website. Then add the following code to the file:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
<urlset xmlns=”http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9″>
<URL>
<loc>http://www.example.com/</loc>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
</url>
</urlset>
Replace www.example.com with the URL of your website.
The <changefreq> tag tells search engines how often the page is updated. The value can be set to always, hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, yearly, or never.
You can add as many <url> tags as you like, one for each page on your website.
Once you have created your sitemap, you need to submit it to search engines. This can be done using the webmaster tools provided by Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
Internal Links
Internal links are hyperlinks that point to other pages on the same website.
They are important for SEO because they help search engines understand the structure of a website and the relationships between its pages.
They can also help to increase the PageRank of a website by passing link equity from one page to another.
To optimize your internal link structure, you should ensure that your links use descriptive anchor text and point to pages that are relevant to the context in which they appear.
You should also avoid using too many links on a single page, as this can dilute the link equity that is passed.
A good rule of thumb is to have at least five internal links pointing to every single one of your pages with relevant, clear anchor texts.
Broken Links
A broken link is a link on a website that no longer works.
This can happen for a number of reasons, such as the page that the link points to has been deleted, the website has changed its URL, or the link has simply been typed incorrectly.
Broken links can hurt your website’s SEO in a number of ways.
First, they can prevent search engines from being able to crawl and index your website properly. This can lead to lower search engine rankings and less traffic.
Second, broken links can create a poor user experience, which can lead to higher bounce rates and less time spent on your website.
Finally, broken links can also damage your website’s reputation, as they make it appear less reliable and trustworthy.

Of course, you should always be on the lookout for broken links on your site and fix them as soon as you find them.
One great free tool for this is the Google Search Console.
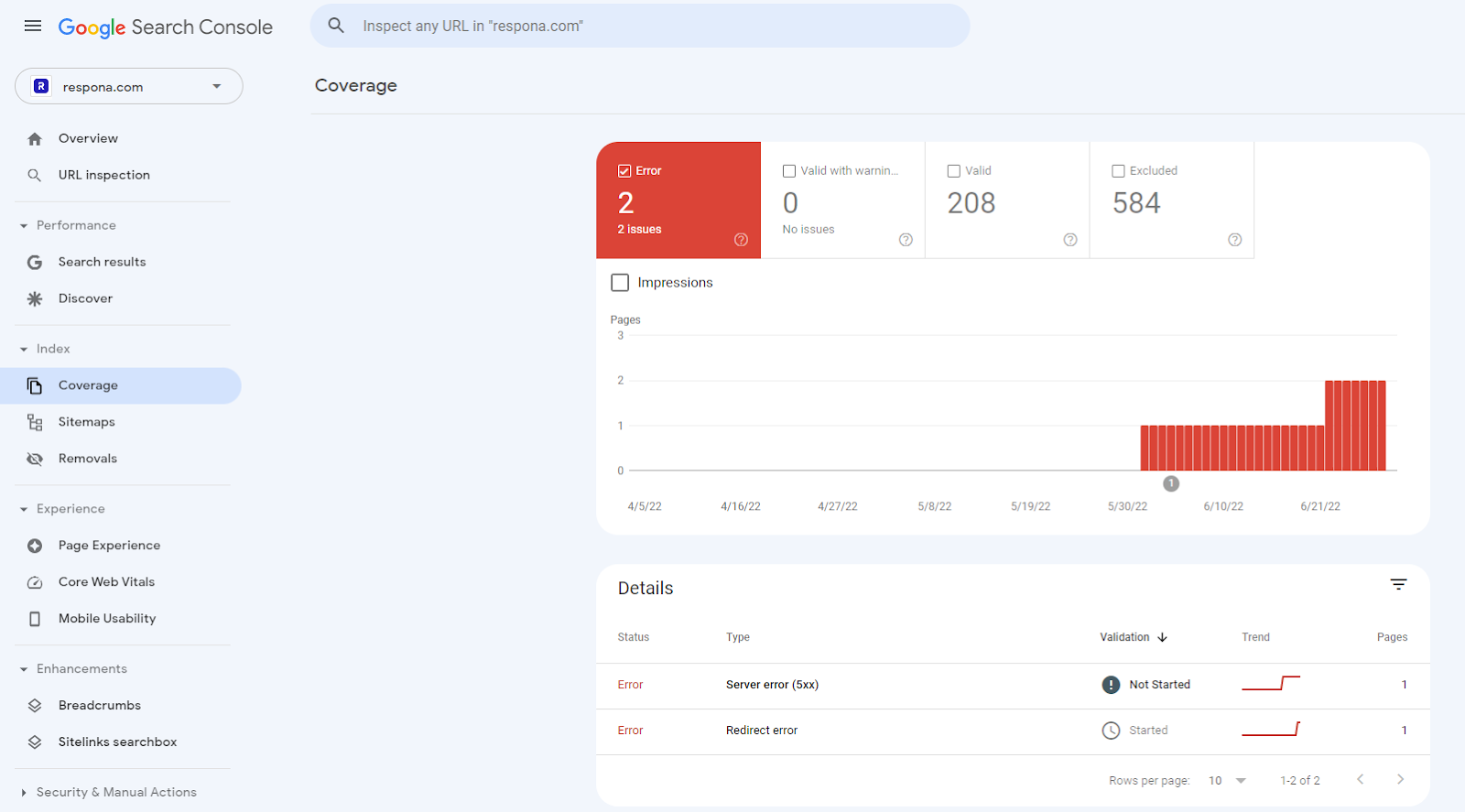
If you navigate to Index > Coverage, you will find a report with all crawled pages: valid, excluded, valid with warnings, and, of course, pages with errors.
GSC also sends you emails with performance and error reports, which is very convenient – you don’t even have to actively scan your site to spot broken links.
Of course, there are many other broken link checkers – and even Ahrefs features this functionality.
301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect from one URL to another. 301 redirects are important for SEO because they preserve your search engine rankings when you change the URL of a page on your site.
Setting up redirects on your own website is easy. You can use a free WordPress plugin like Redirection to set up redirects.
You can also set up manual redirects.
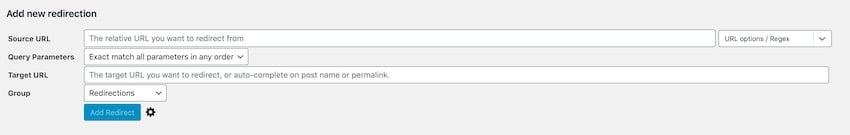
To set up a manual redirect in WordPress, you need to navigate to Tools > Redirection.
There, click “Add New Redirection” and configure your redirect.
Regularly Conduct SEO Audits
SEO never really ends.
You always have to keep producing new blog content to stay relevant.
With that comes the need to build more and more backlinks, and optimize your new pages’ technical aspects.
In addition, Google’s algorithm constantly evolves, so old SEO strategies can lose their former value in favor of something completely different.
Regular SEO audits should be a part of your SEO strategy.
There are five main steps to conducting an SEO audit:
- Conduct a site audit using a tool like Screaming Frog. This will help you to identify any technical issues with your site that could be negatively impacting your SEO.
- Analyze your site’s current keyword rankings. Use a tool like SEMrush to research the keywords your site is currently ranking for and identify any opportunities for improvement.
- Review your site’s on-page SEO. Make sure your titles and meta descriptions are optimized and that your content is relevant to your target keywords.
- Conduct a competitor analysis. Research your competitors to see what they’re doing well and identify any areas where you could improve your own SEO.
- Put together an action plan. Based on your audit findings, create a plan of action to address any issues and improve your site’s SEO.
Vital SEO Tools
Of course, it’s impossible to optimize your website for search engines without the proper tools.
In this section, we will discuss (in our opinion), the most important software for any SEO’s toolkit.
Google Search Console
The number one tool in this list is, of course, the GSC.
It allows you to manually submit pages for indexing, monitor your traffic, and spot technical issues before they cost you revenue.
You can also submit your sitemap through the Google Search Console, remove content from search results, monitor your page experience, site speed, and mobile optimization.
And the best thing about it is that it’s free.
Google PageSpeed Insights
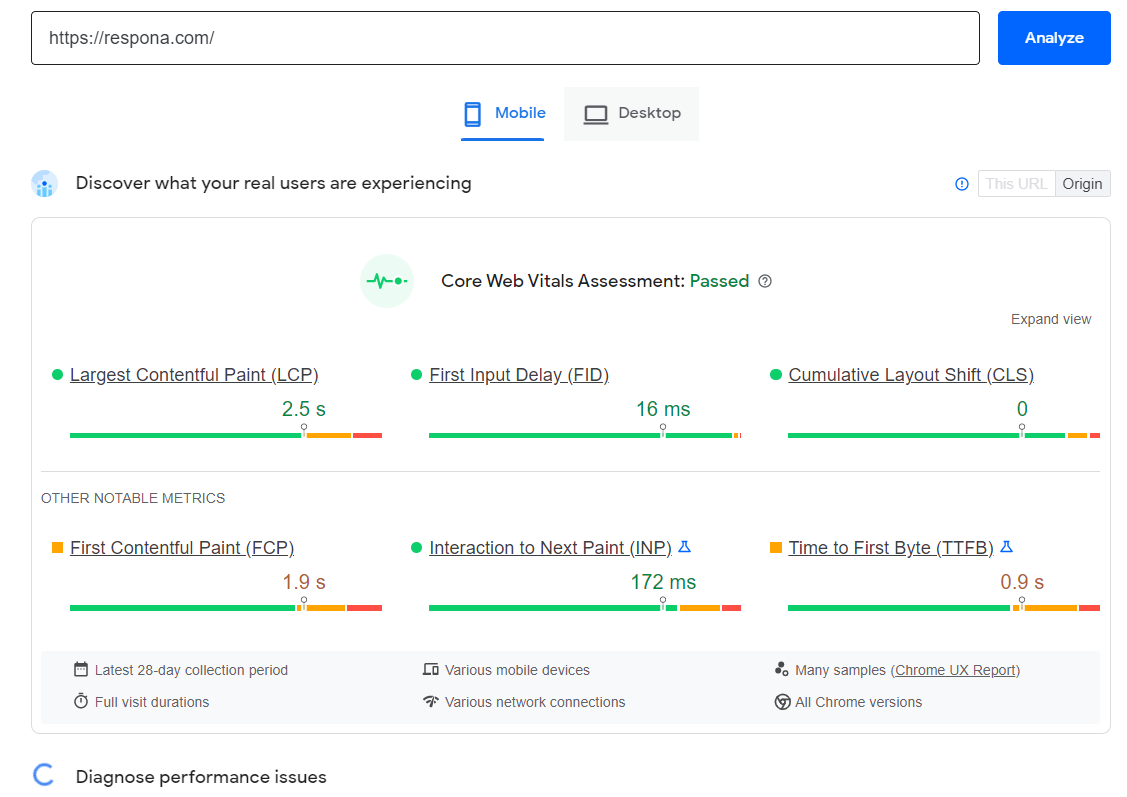
As the name suggests, PageSpeed Insights provides you with data regarding how fast your website loads, and aids with identifying the slowest elements.
This includes your Core Web Vitals such as:
- Largest Contentful Paint
- First Input Delay
- Cumulative Layout Shift
- First Contentful Paint
- Interaction to Next Paint
- Time to First Byte
It also provides suggestions as to which elements could be optimized to shorten your loading times.
Much like the GSC, Google PageSpeed Insights are free to use.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a freemium platform that provides detailed insights about your website’s performance and your user’s behavior.
It shows exactly which pages are getting how many clicks, which channels these clicks are coming from, how long to people stay on your pages, how many of them i click over to the next page or bounce, and really every other metric you can even think of.
Google Analytics also offers a comprehensive audience overview, including:
- Active users
- Lifetime value
- Cohort analytics
- Demographics
- Geographic location
- Technology
- Benchmarking
- And more
All of these reports are provided in real-time, and you can even see exactly how many people are on your website at any given moment.
Google Analytics is an indispensable tool for any SEO that is serious about their website.
Ahrefs
Ahrefs is a very comprehensive SEO tool that will be useful to you at any stage of your search engine optimization journey.
Its main features are:
- Backlink analysis
- Keyword research
- Website auditing
- Content exploring
- Rank tracking
Whether it’s content production, link building, or simply running an audit of your website, chances are that Ahrefs has a feature that will be useful to what you’re doing.
Price: Starting at $99/month.
Yoast SEO
Yoast SEO is one of the most popular plugins for WordPress and Shopify.
Its goal is to help you streamline your technical SEO, regardless of your skill level.
It also helps you create more SEO-friendly content by scanning your articles for:
- Internal and external links
- Number of images
- Title tag and meta description lengths
- Keyword density
- Text length
- And more
With Yoast, you will also be able to see both a mobile and desktop preview of your content in SERPs without ever having to leave your WordPress window.
Yoast’s redirect manager also automatically creates 301 redirects whenever you move or delete content, and even generates structured data.
These are just a few of Yoast’s main features – its functionality is extremely impressive for just a plugin.
Price: Starting at $99/year, but also offers a limited free version.
Search Engine Journal
Search Engine Journal is not a tool but rather a blog.
It is one of the biggest and most authoritative sources of information about anything related to SEO.
Whether it’s a new algorithm update that just released or something that’s been part of it for years, SEJ are always on top of delivering the most detailed and unbiased overview for it.
Search Engine Journal also has a newsletter that’s a goldmine of knowledge for both experiences SEOs and complete rookies.
Link building cheat sheet
Now Over To You
So, to build a strong SEO strategy in 2024, you need to:
- Research and produce high-quality content
- Optimize your website for on-page and technical SEO
- Build high-quality backlinks and earn mentions on other resources
Link building is one of the most time-consuming (but immensely important) process out of them all.
Building links on your own is a huge undertaking, which is why we have developed Respona.
It streamlines the whole process by aiding in identifying link building opportunities, finding the right contact information of your prospects, and even automating the personalization of your link building pitches.
If you need help with link building, don’t hesitate to start a free trial today!





![2455 Guest Posting Sites for 2024 [Updated List]](https://respona.com/wp-content/uploads/guest-posting-sites-1024x683.jpg)